学了之前的Android控件以及布局,我们就能够做一些UI的设计了,这里我结合之前的知识。以一个小的登录项目来解说下Activity之间跳转。
先看下效果图:
1.登录界面:

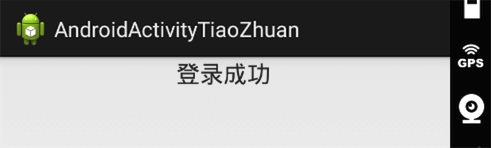
2.点击登录按钮跳转到另外一个Activity的界面,这个界面非常easy,就一个TextView:
首先我们须要建好两个Activity和两个xml布局文件,android程序启动会载入開始默认指定的MainActivity.java以及activity_main.xml。我们首先要做的是分别在两个Activity文件里设置好须要载入的xml布局以及须要处理的事情。
这里先直接给出两个xml布局文件的代码,用的是相对布局。须要自己熟悉这样的布局并进行对应的调整,能够參考我之前的博客:
activity_main.xml代码:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="username"
android:textSize="25sp"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv1"
android:layout_alignBottom ="@id/tv1"
android:hint="请输入username"
android:singleLine="true"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tv1"
android:layout_alignRight="@id/tv1"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/tv1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="password"
android:textSize="25sp"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/tv2"
android:layout_alignBottom ="@id/tv2"
android:hint="请输入password"
android:password="true"
android:singleLine="true"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tv2"
android:text="登录"/>
</RelativeLayout>activity_main.xml2代码:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/bv3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="登录成功" />
</RelativeLayout>然后对于2个Activity,先在 AndroidManifest.xml 中为 SecondActivity进行注冊:
这里给出AndroidManifest.xml中的代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.androidactivitytiaozhuan"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="16"
android:targetSdkVersion="22" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
//注冊SecondActivity,因为不是主活动,因此不须要配置intent-filter标签里的内容
<activity
android:name=".SecondActivity" >
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>接下来我们学习了解下Intent。
Intent是Android程序中各组件之间进行交互的一种重要方式,它不仅能够指明当前组件想要运行的动作,还能够在不同组件之间传递数据。Intent 一般可被用于启动活动、启动服务、以及发送广播等场景, 这里先仅仅讲下用Intent实现界面的跳转。
有非常多方法实现Activity之间的跳转,这里我仅仅给出一种使用显示的Intent(通过指定Intent组件名称来实现的,它一般用在知道目标组件名称的前提下,通常是在同样的应用程序内部实现的。
)方式,很多其它的能够參考浅谈显示Intent和隐式Intent。我们首先构建出了一个 Intent,传入MainActivity.this作为上下文,传入SecondActivity.class 作为目标活动,这样我们的“意图”就非常明显了,即在 MainActivity 这个活动的基础上打 开 SecondActivity 这个活动。
然后通过 startActivity()方法来运行这个 Intent。以下给出两个Activity中的代码。
MainActivity.java代码例如以下:
package com.example.androidactivitytiaozhuan;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button button;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt1);
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//显示方式声明Intent。直接启动SecondActivity
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}SecondActivity.java代码例如以下:
package com.example.androidactivitytiaozhuan;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class SecondActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2);
}
}