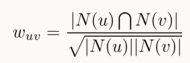只是简单谢了一个Demo,先贴上GitHub地址。
https://github.com/wang135139/recommend-system
基本概念就不过多介绍了,相信能看明白的都了解。如果想了解相关推荐先做好知识储备:
1.什么事推荐算法
2.什么是基于邻域的推荐算法
笔者选用的是GroupLens的MoviesLens数据
传送门GroupLens
数据集处理
此处截取数据 UserId + MovieId 作为隐反馈数据。个人的实现方式并不是很好,之后再考虑优化,如果有好的想法欢迎小纸条。
基本设置项目结构如下:
/project
/analyzer --推荐分析
-CollaborativeFileringanalyzer
/bean --数据元组
-BasicBean
-HabitsBean
/input --输入设置
-ReaderFormat
/recommender --推荐功能
-UserRecommender
首先思路是截取MovieLens数据,转化为格式化的书籍格式。MovieLens数据基本格式为
| user id | item id | rating | timestamp |
读取后的数据为表结构,实际可以用 Map 或者 二维数组 进行存储。
考虑到之后转化的问题,决定用二维数组。
设置BasicBean用于存储表结构中的行,主要设置List < String >用于存储一行数据中的单项数据
/**
* A row of data sets describes in witch the parameters are included.
*
* @author wqd
* 2016/01/18
*/
public class BasicBean {
private List<String> parameters;
// private int num;
private boolean tableHead;
///Default constructor,the row set n floders and is or not a table head
public BasicBean(boolean head) {
parameters = new ArrayList<String>();
this.tableHead = head;
}
//Default constructor,the row set table head and how much the row
//set is defined by the variable parameters,it isn't a table head
public BasicBean(String... strings) {
this(false, strings);
}
//Default constructor,the row set table head and how much the row
//set is defined by the variable parameters and is or not a table head
public BasicBean(boolean head, String... strings) {
parameters = new ArrayList<String>();
for(String string : strings) {
parameters.add(string);
}
// this.num = parameters.size();
this.tableHead = head;
}
public int add(String param) {
parameters.add(param);
return this.getSize();
}
//replace a parameter value pointed to a new value
//If success,return true.If not,return false.
public boolean set(int index, String param) {
if(index < this.getSize())
parameters.set(index, param);
else
return false;
return true;
}
//Get the head.If it has table head,return ture.
//If not,return flase;
public boolean isHead() {
return tableHead;
}
//Override toString()
public String toString() {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(" ");
int len = 1;
for (String string : parameters) {
str.append(" |" + string);
if(len++ % 20 == 0)
str.append("
");
}
return str.toString();
}
//Get number of parameters
public int getSize() {
return parameters.size();
}
//Get array
public List<String> getArray() {
return this.parameters;
}
//Get ID of a set
public int getId() {
return this.getInt(0);
}
public String getString(int index) {
return parameters.get(index);
}
public int getInt(int index) {
return Integer.valueOf(parameters.get(index));
}
public boolean getBoolean(int index) {
return Boolean.valueOf(parameters.get(index));
}
public float getFloat(int index) {
return Float.valueOf(parameters.get(index));
}
}在原数据读取之后,数据处理的话效率还是比较差,冗余字段比较多,因为一个用户会对多个电影反馈数据。因此,将
| user id | item id | rating | timestamp |
=>
| user id | item id 1 | item id 2 | item id 3 | item id 4 …
这边设置HabitsBean用于存储,单独将id进行抽取,直接存储在Bean中。实际在list中,存储user item ids,原因是在之后进行操作时,ID操作频繁。
public class HabitsBean extends BasicBean {
private int id ;
//get the ID
public int getId() {
return id;
}
//set the ID
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public HabitsBean() {
this(-1);
}
//default id is -1,it means the id hadn't been evaluated
public HabitsBean(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
//Override Object toString() method
public String toString() {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder("HabitBean " + this.id + " :");
str.append(super.toString());
return str.toString();
}
}
将元组数据读取之后,再将元组数据进行压缩重组,转化为方便与处理的数据格式。设置ReaderFormat进行处理,Demo如下:
/**
* This class for reading training and test files.It can
* be suitable for Grouplens and other data sets.
* @author wqd
*
*/
public class ReaderFormat {
List<BasicBean> lists;
List<HabitsBean> formLists;
public List<BasicBean> read (String filePath) throws IOException {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader(filePath));
String s;
BasicBean basicBean = null;
lists = new ArrayList<BasicBean>();
while((s = in.readLine()) != null) {
// System.out.println(s);
String[] params = s.split(" ");
// for (String string : params) {
// System.out.println(string);
// }
basicBean = new BasicBean(params);
lists.add(basicBean);
}
return lists;
}
//combine user log like | userID | habitID | ...
//to userID and | habitID1 | habitID2 | habitID3 | ...
//sort the userID
public List<HabitsBean> formateLogUser(String filePath) throws IOException {
lists = this.read(filePath);
formLists = new LinkedList<HabitsBean>();
HabitsBean row = null;
for (BasicBean basicBean : lists) {
if(basicBean.) {
row = new HabitsBean(1);
row.setId(basicBean.getInt(0));
row.add(basicBean.getString(1));
formLists.add(row);
} else {
this.addBinarySerch(formLists, basicBean);
}
}
return formLists;
}
//binary serch
private void addBinarySerch(List<HabitsBean> lists, BasicBean bean) {
int start = 0;
int end = lists.size()-1;
int pointer = (start + end + 1) / 2;
HabitsBean row = lists.get(pointer);
while(start <= end) {
if(row.getId() == bean.getId()) {
row.add(bean.getString(1));
lists.set(pointer, row);
return ;
} else if(start == end) {
break;
}else if(row.getId() > bean.getId()) {
end = pointer;
} else if(row.getId() < bean.getId()) {
start = pointer;
}
pointer = (start + end + 1) / 2;
row = lists.get(pointer);
}
HabitsBean newBean = new HabitsBean(bean.getId());
newBean.add(bean.getString(1));
lists.add(newBean);
return ;
}
// test
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReaderFormat readerFormat = new ReaderFormat();
try {
List<HabitsBean> lists = readerFormat.formateLogUser("E:/WorkSpace/Input/ml-100k/u1.base");
for (HabitsBean habitsBean : lists) {
System.out.println(habitsBean.toString());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
推荐算法
协同过滤算法的核心思想是根据用户间的相似度,来进行推荐。
N(u),N(v)表示u,v用户有过隐性反馈的集合,Jaccard公式
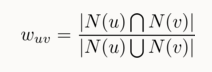
或者采用余弦相似度