▶ 使用逻辑地模型来进行分类,可以算出每个测试样本分属于每个类别的概率
● 二分类代码
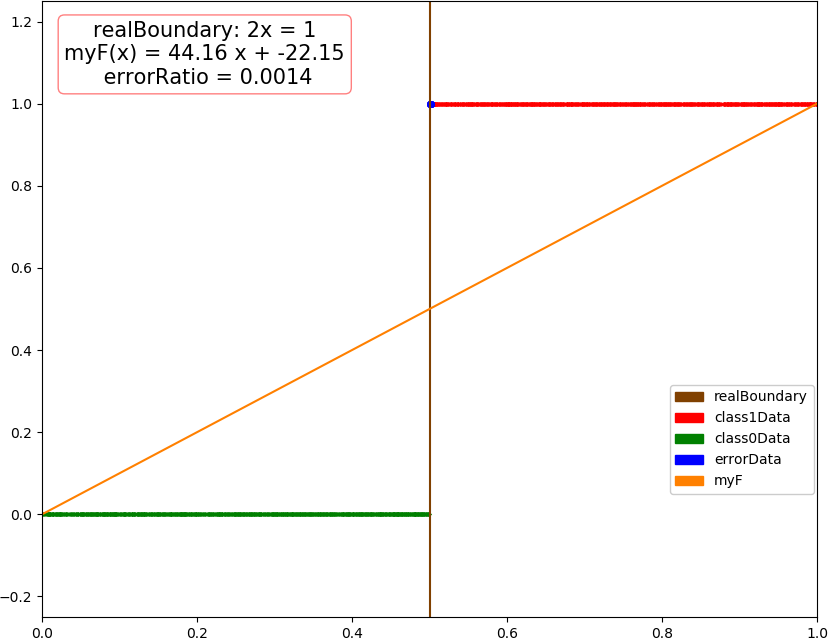
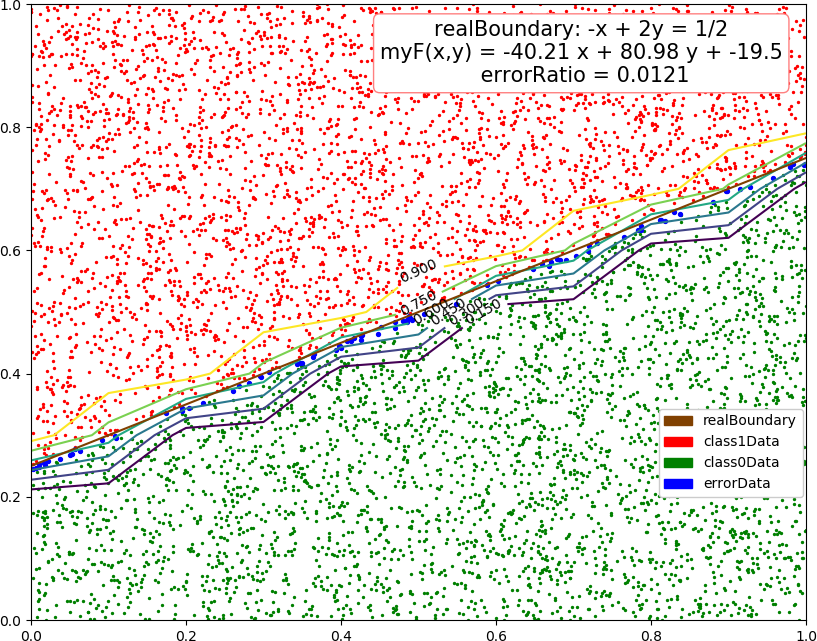
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D 4 from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection 5 from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle 6 7 dataSize = 10000 8 trainRatio = 0.3 9 ita = 0.03 # 学习效率 10 epsilon = 0.01 11 defaultTurn = 200 # 默认最大学习轮数 12 colors = [[0.5,0.25,0],[1,0,0],[0,0.5,0],[0,0,1],[1,0.5,0]] # 棕红绿蓝橙 13 trans = 0.5 14 15 def sigmoid(x): 16 return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-x)) 17 18 def function(x, para): # 回归函数 19 return sigmoid(np.sum(x * para[0]) + para[1]) 20 21 def judge(x, para): # 分类函数,用 0.5 做分界 22 return int(function(x, para) > 0.5) 23 24 def dataSplit(x, y, part): 25 return x[:part], y[:part],x[part:],y[part:] 26 27 def createData(dim, count = dataSize): # 创建数据集 28 np.random.seed(103) 29 X = np.random.rand(count, dim) 30 Y = ((3 - 2 * dim)*X[:,0] + 2 * np.sum(X[:,1:], 1) > 0.5).astype(int) # 只考虑 {0,1} 的二分类 31 class1Count = 0 32 for i in range(count): 33 class1Count += (Y[i] + 1)>>1 34 print("dim = %d, dataSize = %d, class 1 ratio -> %4f"%(dim, count, class1Count / count)) 35 return X, Y 36 37 def gradientDescent(dataX, dataY, turn = defaultTurn): # 梯度下降法 38 count, dim = np.shape(dataX) 39 xE = np.concatenate((dataX, np.ones(count)[:,np.newaxis]), axis = 1) # 补充最后一列的 1 作为零次项 40 w = np.ones(dim + 1) 41 42 for t in range(turn): 43 y = sigmoid(np.dot(xE, w).T) # 尺寸:xE:count*(dim+1),w:(dim+1)*1,y:1*count 44 error = dataY - y # 尺寸:error:1*count 45 w += ita * np.dot(error, xE) # 尺寸:w:1*(dim+1) 46 if np.sum(error * error) < count * epsilon: #if np.sum(error * error) / count < epsilon: 47 break 48 return (w[:-1], w[-1]) 49 50 def test(dim): 51 allX, allY = createData(dim) 52 trainX, trainY, testX, testY = dataSplit(allX, allY, int(dataSize * trainRatio)) 53 54 para = gradientDescent(testX, testY) # 训练 55 56 myResult = [ judge(x, para) for x in testX] 57 errorRatio = np.sum((np.array(myResult) - testY)**2) / (dataSize * (1 - trainRatio)) 58 print("dim = %d, errorRatio = %4f "%(dim, errorRatio)) 59 60 if dim >= 4: # 4维以上不画图,只输出测试错误率 61 return 62 errorPX = [] # 测试数据集分为错误类,1 类和 0 类 63 errorPY = [] 64 class1 = [] 65 class0 = [] 66 for i in range(len(testX)): 67 if myResult[i] != testY[i]: 68 errorPX.append(testX[i]) 69 errorPY.append(testY[i]) 70 elif myResult[i] == 1: 71 class1.append(testX[i]) 72 else: 73 class0.append(testX[i]) 74 errorPX = np.array(errorPX) 75 errorPY = np.array(errorPY) 76 class1 = np.array(class1) 77 class0 = np.array(class0) 78 79 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) 80 81 if dim == 1: 82 plt.xlim(0.0,1.0) 83 plt.ylim(-0.25,1.25) 84 plt.plot([0.5, 0.5], [-0.5, 1.25], color = colors[0],label = "realBoundary") 85 plt.plot([0, 1], [ function(i, para) for i in [0,1] ],color = colors[4], label = "myF") 86 plt.scatter(class1, np.ones(len(class1)), color = colors[1], s = 2,label = "class1Data") 87 plt.scatter(class0, np.zeros(len(class0)), color = colors[2], s = 2,label = "class0Data") 88 if len(errorPX) != 0: 89 plt.scatter(errorPX, errorPY,color = colors[3], s = 16,label = "errorData") 90 plt.text(0.21, 1.12, "realBoundary: 2x = 1 myF(x) = " + str(round(para[0][0],2)) + " x + " + str(round(para[1],2)) + " errorRatio = " + str(round(errorRatio,4)), 91 size=15, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1., 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1., 1., 1.))) 92 R = [Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = colors[k]) for k in range(5)] 93 plt.legend(R, ["realBoundary", "class1Data", "class0Data", "errorData", "myF"], loc=[0.81, 0.2], ncol=1, numpoints=1, framealpha = 1) 94 95 if dim == 2: 96 plt.xlim(0.0,1.0) 97 plt.ylim(0.0,1.0) 98 plt.plot([0,1], [0.25,0.75], color = colors[0],label = "realBoundary") 99 xx = np.arange(0, 1 + 0.1, 0.1) 100 X,Y = np.meshgrid(xx, xx) 101 contour = plt.contour(X, Y, [ [ function((X[i,j],Y[i,j]), para) for j in range(11)] for i in range(11) ]) 102 plt.clabel(contour, fontsize = 10,colors='k') 103 plt.scatter(class1[:,0], class1[:,1], color = colors[1], s = 2,label = "class1Data") 104 plt.scatter(class0[:,0], class0[:,1], color = colors[2], s = 2,label = "class0Data") 105 if len(errorPX) != 0: 106 plt.scatter(errorPX[:,0], errorPX[:,1], color = colors[3], s = 8,label = "errorData") 107 plt.text(0.71, 0.92, "realBoundary: -x + 2y = 1/2 myF(x,y) = " + str(round(para[0][0],2)) + " x + " + str(round(para[0][1],2)) + " y + " + str(round(para[1],2)) + " errorRatio = " + str(round(errorRatio,4)), 108 size = 15, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1., 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1., 1., 1.))) 109 R = [Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = colors[k]) for k in range(4)] 110 plt.legend(R, ["realBoundary", "class1Data", "class0Data", "errorData"], loc=[0.81, 0.2], ncol=1, numpoints=1, framealpha = 1) 111 112 if dim == 3: 113 ax = Axes3D(fig) 114 ax.set_xlim3d(0.0, 1.0) 115 ax.set_ylim3d(0.0, 1.0) 116 ax.set_zlim3d(0.0, 1.0) 117 ax.set_xlabel('X', fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'k'}) 118 ax.set_ylabel('Y', fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'k'}) 119 ax.set_zlabel('W', fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'k'}) 120 v = [(0, 0, 0.25), (0, 0.25, 0), (0.5, 1, 0), (1, 1, 0.75), (1, 0.75, 1), (0.5, 0, 1)] 121 f = [[0,1,2,3,4,5]] 122 poly3d = [[v[i] for i in j] for j in f] 123 ax.add_collection3d(Poly3DCollection(poly3d, edgecolor = 'k', facecolors = colors[0]+[trans], linewidths=1)) 124 ax.scatter(class1[:,0], class1[:,1],class1[:,2], color = colors[1], s = 2, label = "class1") 125 ax.scatter(class0[:,0], class0[:,1],class0[:,2], color = colors[2], s = 2, label = "class0") 126 if len(errorPX) != 0: 127 ax.scatter(errorPX[:,0], errorPX[:,1],errorPX[:,2], color = colors[3], s = 8, label = "errorData") 128 ax.text3D(0.74, 0.95, 1.15, "realBoundary: -3x + 2y +2z = 1/2 myF(x,y,z) = " + str(round(para[0][0],2)) + " x + " + 129 str(round(para[0][1],2)) + " y + " + str(round(para[0][2],2)) + " z + " + str(round(para[1],2)) + " errorRatio = " + str(round(errorRatio,4)), 130 size = 12, ha="center", va="center", bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", ec=(1, 0.5, 0.5), fc=(1, 1, 1))) 131 R = [Rectangle((0,0),0,0, color = colors[k]) for k in range(4)] 132 plt.legend(R, ["realBoundary", "class1Data", "class0Data", "errorData"], loc=[0.83, 0.1], ncol=1, numpoints=1, framealpha = 1) 133 134 fig.savefig("R:\dim" + str(dim) + ".png") 135 plt.close() 136 137 if __name__=='__main__': 138 test(1) 139 test(2) 140 test(3) 141 test(4) 142 test(5)
● 输出结果
dim = 1, dataSize = 10000, class 1 ratio -> 0.509000 dim = 1, errorRatio = 0.015000 dim = 2, dataSize = 10000, class 1 ratio -> 0.496000 dim = 2, errorRatio = 0.008429 dim = 3, dataSize = 10000, class 1 ratio -> 0.498200 dim = 3, errorRatio = 0.012429 dim = 4, dataSize = 10000, class 1 ratio -> 0.496900 dim = 4, errorRatio = 0.012857 dim = 5, dataSize = 10000, class 1 ratio -> 0.500000 dim = 5, errorRatio = 0.012143
● 画图

● 补充,从【https://www.cnblogs.com/zhizhan/p/4868555.html】了解到,低度下降方法的变种
1 # 梯度下降法 2 weight += alpha * dataX.T * ( dataY - sigmoid(dataXx * weight) ) 3 4 # Stochastic 梯度下降法,每次取一个样本 5 for i in range(numSamples): 6 weight += ita * dataX[i].T * ( dataY[i] - sigmoid(dataXx[i] * weight) ) 7 8 # 平滑 Stochastic 低度下降法,学习效率逐渐递减,并保证有下限 0.01 9 indexList = range(count) # count 为样本数 10 for i in range(count): 11 ita = 0.01 + 4.0 / (1.0 + t + i) # t 为 轮数 12 index = np.random.choice(indexList) 13 weight += ita * dataX[index].T * ( dataY[index] - sigmoid(train_x[index] * weight) ) 14 del(indexList[index]) # 单轮学习中样本只用一次