- 梯形积分法
基本思想是,将x轴上区间划分成n个等长的子区间。估计介于函数图像以及每个子区间内梯形区域的面积。
设子区间端点为xi和xi+1 ,长度h=xi+1 - xi, 同样的两条垂直线的长度为f(xi)和f(xi+1)
那么面积为:h/2[ f(xi) + f(xi+1) ]
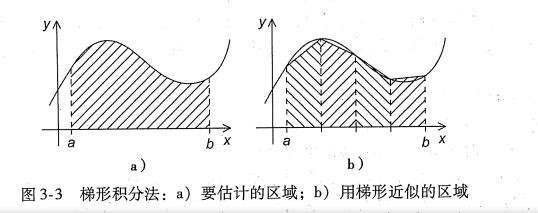
n个区间是等分的,如果两条垂直线包围区域的边界分别为a和b,那么
h = (b-a) / n

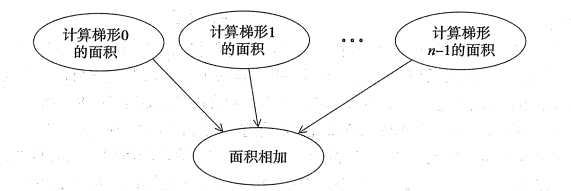
- 设计并行程序的四个步骤
- 将问题的解决方案划分成多个任务
- 在任务间识别出需要的通信信道(识别出联系,是否需要交流)
- 将任务聚合成复合任务 --->减少通信
- 在核上分配复合任务
- 串行代码
/* Input a ,b , n*/
h = (b-a)/n
approx = (f(a) + f(b))/2.0
for(i =1; i <= n-1; i++){
x_i = a + i * h;
approx = h * approx
}
approx = h*approx
- 并行程序
伪代码:
Get a,b,n;
h = (b-a)/n;
local_n = n/comm_sz;
local_a = a + my_rank * local_n * h;
local_b = local_a + local_n*h;
local_integral = Trap(local_a, local_b, local_n, h) /*Trap函数作用*/
if( my_rank != 0 )
Send local_integral to process 0;
else /*my_rank == 0*/
total_integral = local_integral;
for(proc = 1;proc < comm_sz; proc++){
Receive local_integral from proc;
total_integral += local_integral;
}
if(my_rank == 0)
print result;
- 第一个MPI代码----输出
int main(void){
int my_rank , comm_sz, n = 1024, local_n;
double a = 0.0, b=3.0, h, local_a,local_b;
double local_int,total_int;
int source;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &my_rank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &comm_sz);
h = (b-a)/n;
local_n = n/comm_sz;
local_a = a + my_rank * local_n * h;
local_b = local_a +local_n * h;
local_int = Trap(local_a , local_b , local_n, h )
if (my_rank != 0){
MPI_Send(&local_int , 1 , MPI_DOUBLE , 0, 0 , MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}else{
total_int = local_int;
for(source = 1 ; source < comm_sz ; source++){
MPI_Recv(&local_int, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, source, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE);
total_int += local_int;
}
}
if (my_rank == 0 ){
printf("With n = %d trapezoids, our estimate
",n);
printf("of the integral from %f to %f = %.15e
",a,b,total_int);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
其中Trap函数
double Trap(
double left_endpt .
double right_endpt,
int trap_count,
double base_len
){
double estimate , x;
int i;
estimate = (f(left_endpt) + f(right_endpt))/2.0
for(i = 1;i <= trap_count-1 ; i++){
x = left_endpt + i*base_len;
estimate += f(x);
}
estimate = estimate * base_len;
return estimate;
}
- 输入
void Get_input(
int my_rank,
int comm_sz,
double* a_p,
double* b_p,
int* n_p
){
int dest;
if(my_rank == 0){
printf("Enter a, b,and n
");
scanf("%lf %lf %d",a_p,b_p,n_p);
for(dest = 1; dest < comm_sz;dest++){
MPI_Send(a_p , 1 , MPI_DOUBLE, dest , 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Send(b_p , 1 , MPI_DOUBLE, dest , 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Send(n_p , 1 , MPI_INT, dest , 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
}else{
MPI_Recv(a_p , 1, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, 0,MPI_COMM_WORLD, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE);
MPI_Recv(b_p , 1, MPI_DOUBLE, 0, 0,MPI_COMM_WORLD, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE);
MPI_Recv(n_p , 1, MPI_INT, 0, 0,MPI_COMM_WORLD, MPI_STATUS_IGNORE);
}
}
- 树形通信