Given a binary tree, flatten it to a linked list in-place.
For example,
Given
Given
1The flattened tree should look like:
/ \
2 5
/ \ \
3 4 6
1» Solve this problem
\
2
\
3
\
4
\
5
\
6
[解题思路]
递归解法。对于任一节点,flatten左树,然后节点插入左树最左边,成为新的头节点。flatten右树,右树最左边接上新链表的最右节点。
[Code]
1: void flatten(TreeNode *root) {
2: // Start typing your C/C++ solution below
3: // DO NOT write int main() function
4: if(root == NULL)
5: return;
6: ConvertToLink(root);
7: }
8: TreeNode* ConvertToLink(TreeNode* node)
9: {
10: if(node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL)
11: return node;
12: TreeNode* rHead = NULL;
13: if(node->right != NULL)
14: rHead = ConvertToLink(node->right);
15: TreeNode* p = node;
16: if(node->left!=NULL)
17: {
18: TreeNode* lHead = ConvertToLink(node->left);
19: node->right = lHead;
20: lHead->left = NULL;
21: node->left = NULL;
22: while(p->right!=NULL)
23: p = p->right;
24: }
25: if(rHead != NULL)
26: {
27: p->right = rHead;
28: rHead->left = NULL;
29: }
30: return node;
31: }
[已犯错误]
1. Line 13~14
刚开始的时候,首先flatten左树,然后处理右树。但是这样会导致处理右树的时候,节点的值已经在处理树的时候被破坏了。比如树为{1,2,3},
1
/ \
2 3
如果先处理左树的话,当执行node->right = lhead的时候,右节点就已经被破坏了,node->right指向了2,而不是3。
1
\
2 (3)
当然,也可以用一个变量在处理左树前,保存右树地址。但是没必要,先处理右树就好了。
2. Line 22~23
该循环是用于将p指针遍历到左树链表的最右节点。第一版时,这个循环是放在if语句以外,这就导致了,不必要的迭代了。比如当输入为{1,#,2}时,这个while循环会导致p指针遍历到右子树的最右节点,这显然是错的。
3. Line 20, 28
不要忘了清空每一个指针,在新的链表中,左指针没必要保留。
Update 08/25/2014 being asked this question today. But the interviewer asked for an in-order flatten.
Review previous solution. Actually, I made it too complicate. If travel this tree in pre-order, from the hint, it is easy to construct the linked list.
1: void flatten(TreeNode *root) {
2: if(root == NULL) return;
3: TreeNode* right = root->right;
4: if(lastVisitedNode != NULL)
5: {
6: lastVisitedNode->left = NULL;
7: lastVisitedNode->right = root;
8: }
9: lastVisitedNode = root;
10: flatten(root->left);
11: flatten(right);
12: }
pre-order is simple because the root always is the head of flatten list. But if flatten the tree with in-order sequence, need extra parameter to track the head and tail of each flattened sun-tree.
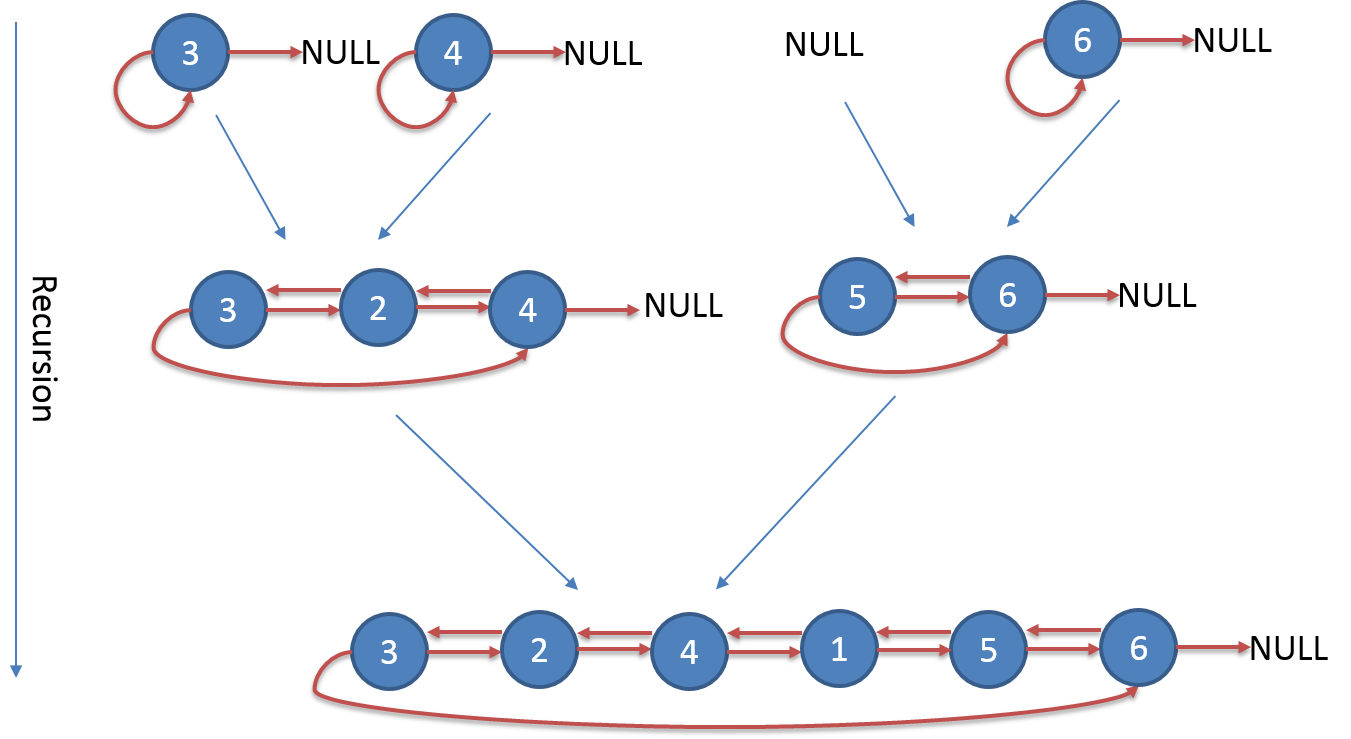
For example, below binary tree.
If we flatten it with in-order, the process should like below. And here I use the left pointer of head node to track the tail node.
1: TreeNode* flatten(TreeNode *root) {
2: if (root == NULL) return NULL;
3: TreeNode* rightTree = root->right;
4: TreeNode* newHead = root;
5: TreeNode* leftList = flatten(root->left);
6: if (leftList != NULL)
7: {
8: newHead = leftList;
9: TreeNode* tail = leftList->left;
10: tail->right = root;
11: root->left = tail;
12: leftList->left = root;
13: }
14: TreeNode* rightList = flatten(rightTree);
15: if (rightList != NULL)
16: {
17: root->right = rightList;
18: newHead->left = rightList->left;
19: rightList->left = root;
20: }
21: return newHead;
22: }