0 什么是继承
继承就是获得存在对象已有的属性和方法的一种方式。
【2019.4.26 更新】今日又重新学习了一下JS的继承,在这里整理一下以前的笔记并补充一些新的感悟。
1 JS中继承的几种实现方法
-
属性拷贝
-
原型式继承
-
原型链继承
-
call/apply方法继承(借用构造函数)
-
组合式继承:借用构造函数 + 原型式继承
-
圣杯模式
-
深拷贝(递归)
2 继承的具体实现
2-0 属性拷贝
【实现方法】
遍历对象中的key进行赋值
【问题】
继承过来的引用类型在父子对象中是共享的,即对其修改会同时影响父子对象中的值。
【示例代码】
1 // 继承方式1:属性拷贝(遍历对象中的key进行赋值) 2 // 创建父对象 3 var superObj = { 4 name : 'Xianxian', 5 age : 20, 6 friends : ['Shuoshuo', 'Srue' , 'YanShuo' ], 7 showName : function(){ 8 console.log(this.name); 9 } 10 } 11 // 创建子对象 12 var subObj = {}; 13 14 for(var i in superObj){ 15 subObj[i] = superObj[i]; 16 } 17 18 subObj.friends.push('MyLove'); 19 console.log(superObj); 20 console.log(subObj,subObj.friends);
2-1 原型式继承
【实现方法】
-
借用构造函数的原型对象继承 即子类.prototype = 父类.prototype
-
子类构造函数的原型被覆盖,其构造函数指向父类,需要修正其值指向子构造函数:
【存在问题】
- 继承过来的引用类型在父子对象中是共享的,即对其修改会同时影响父子对象中的值。
- 只能继承父构造函数原型对象上的成员,不能继承父构造函数实例对象上的成员。
【样例代码】
1 // 继承方式2:原型式继承 2 // 创建父类构造函数 3 function SuperClass(name){ 4 this.name = name; 5 this.sayName = function(){ 6 console.log(this.name); 7 } 8 } 9 10 // 设置父类构造原型对象 11 SuperClass.prototype.age = 20; 12 SuperClass.prototype.friends = ['Shuoshuo','Yanshuo']; 13 SuperClass.prototype.showAge = function(){ 14 console.log(this.age); 15 } 16 17 18 // 创建空的子类构造函数 19 function SubClass(){ 20 21 } 22 23 // 借用构造函数的原型对象继承 即子类.prototype = 父类.prototype 24 SubClass.prototype = SuperClass.prototype; 25 // 此时,子类构造函数的原型被覆盖,其构造函数指向父类,需要修正其值指向子构造函数,验证如下: 26 console.log(SubClass.prototype.constructor == SuperClass); // true 27 console.log(SuperClass.prototype.constructor == SuperClass); // true 28 // 修改如下,之后即完成继承 29 SubClass.prototype.constructor = SubClass; 30 var child = new SubClass(); 31 console.log(child.friends); 32 child.friends.push('Mylove'); 33 child.age = 10; 34 var father = new SuperClass("ChrisChen"); 35 // child中继承的只有显示表示出的prototype部分的属性值,父构造函数中的属性不会被继承 36 // 即只能继承父构造函数原型对象上的成员,不能继承父构造函数实例对象上的成员 37 console.log(child); //没有name,sayName()这些属性 38 father.showAge(); 39 // 同样,该继承方式存在引用属性的成员共享问题 40 console.log(father.friends); // 会多出'MyLove'
2-2 原型链继承
【实现方式】
-
子构造函数.prototype = new 父构造函数();
-
同原型式继承,也要对子构造函数构造器进行修改(由于子构造器原型被覆盖),从而实现继承:
SubClass1.prototype.constructor = SubClass;
【存在问题】
继承过来的引用类型在父子对象中是共享的,即对其修改会同时影响父子对象中的值。
【总结】
-
会将父构造函数实例对象中的属性继承,过多的继承了没用的属性,继承冗余
-
不支持多继承,只能继承自通过一个父类
-
创建子类实例时,不能向父类构造函数传参
【样例代码】
1 // 继承方式3:原型链继承 2 // 创建父构造函数 3 function SuperClass1(){ 4 this.name = 'ChenQixian'; 5 this.age = 20; 6 this.sayName = function(){ 7 console.log(this.name); 8 } 9 } 10 11 // 设置父构造函数的原型 12 SuperClass1.prototype.friends = ['YanShuo' , 'Sure!']; 13 SuperClass1.prototype.showAge = function(){ 14 console.log(this.age); 15 } 16 17 // 创建子构造函数 18 function SubClass1(){ 19 20 } 21 22 // 原型链继承方式:子构造函数.prototype = new 父构造函数() 23 SubClass1.prototype = new SuperClass1(); 24 // 同原型式继承,也要对子构造函数构造器进行修改(由于子构造器原型被覆盖),从而实现继承 25 SubClass1.prototype.constructor = SubClass; 26 // 不同于原型式继承,这里会将父构造函数实例对象中的属性也继承 27 var child = new SubClass1(); 28 console.log(child.name); // ChenQixian 29 console.log(child.friends); // ["YanShuo", "Sure!"] 30 child.sayName(); // ChenQixian 31 child.showAge(); // 20 32 // 同样存在父子对象中引用属性的共享问题 33 var father = new SuperClass1(); 34 console.log(father.friends); // ["YanShuo", "Sure!"] 35 child.friends.push('myLove'); 36 console.log(father.friends); // ["YanShuo", "Sure!", "myLove"] 37 console.log(child.friends); // ["YanShuo", "Sure!", "myLove"]
2-3 借用构造函数
【实现方式】
在子构造函数中,使用call,apply函数:区别在于apply传参数数组,call传参数列表,作用为改变this指向
/*apply()方法*/
function.apply(thisObj[, argArray])
/*call()方法*/
function.call(thisObj[, arg1[, arg2[, [,...argN]]]]);
【存在问题】
-
不能借用原型
-
每次构造多调一个函数,增加了函数调用
- 子类的功能需求必须完全涵盖父类提供的属性和方法
【总结】
【样例代码】
// 继承方式4:call(),apply()借用构造函数 // 创建父构造函数 function Person(name){ this.name = name; this.friends = ['ShuoShuo','Sure']; this.sayName = function(){ console.log(this.name); } } // 创建子构造函数 function Student(name){ console.log(this); // 调用call借用Person构造函数改变this指向 Person.call(this , name); } // 可以给父构造函数传参(这里传递了name),同时引用成员不存在共享问题 var stu = new Student('ChenQixian'); stu.sayName(); // ChenQixian var pcs = new Person('Person'); console.log(pcs.friends); // ["ShuoShuo", "Sure"] stu.friends.push('My_Love'); console.log(pcs.friends); // ["ShuoShuo", "Sure"] console.log(stu.friends); // ["ShuoShuo", "Sure", "My_Love"]
2-4 组合继承
【实现方式】
结合借用式继承和原型式继承的方式
在子构造函数里调用call
在设置原型继承,并调整构造器:
SubClass.prototype = SuperClass.prototype;
【存在问题】
仍存在引用成员共享问题。
【总结】
-
继承了父构造函数原型对象上的成员以及父构造函数上的属性
-
实现了向父构造对象的参数传递
【样例代码】
1 // 继承方式5:借用构造函数 + 原型式继承 2 // 创建父构造函数 3 function Person1(name , age){ 4 this.name = name; 5 this.age = age; 6 this.sayName = function(){ 7 console.log(this.name); 8 } 9 } 10 // 设置父构造函数的原型对象 11 Person1.prototype.showAge = function(){ 12 console.log(this.age); 13 } 14 Person1.prototype.friends = ['ShuoYan','SureYan']; 15 // 创建子构造函数 16 function Student1(name , age){ 17 Person1.call(this , name , age); 18 } 19 // 设置原型式继承 20 Student1.prototype = Person1.prototype; 21 Student1.prototype.constructor = Student1; 22 // 验证如下 23 var stu1 = new Student1('ChenQixian' , 19); 24 stu1.sayName(); // ChenQixian 25 stu1.showAge(); // 19 26 var pcs = new Person1('Person' , 21); 27 console.log(pcs.friends); // ["ShuoYan", "SureYan"] 28 stu.friends.push('My_Love'); 29 console.log(pcs.age); 30 console.log(pcs.friends); // ["ShuoYan", "SureYan", "My_Love"] 31 console.log(stu.friends); // ["ShuoYan", "SureYan", "My_Love"]
2-5 圣杯模式(特别重要)
【特别重要】
圣杯模式可被称作是JS继承的“标准答案”。
【总结】
圣杯模式是在原型式继承的基础上进行改进的。
主要解决的问题,是子类与父类共享原型链,导致在子类原型链上的修改也会导致父类原型链上相应属性值的改变。
解决问题的方式为:引入一个中间层构造函数function F(){},使用F与父类共享原型,子类是由构造函数F构造的一个全新的对象。从而在拷贝了父类的同时,又彻底剥离了与父类的关系。
作为补充,应该设置子类的构造函数指向子类来代替默认值以避免混乱,此外使用uber存储超类(即该子类继承自谁)。
【基本代码】
1 function inherit(origin , target){ 2 function F(){}; 3 F.prototype = origin.prototype; 4 target.prototype = new F(); 5 target.prototype.constructor = target; 6 target.prototype.uber = origin.prototype; 7 }
【测试代码】
1 inherit(Father,Son); 2 function Father(){} 3 function Son(){} 4 Father.prototype.lastName = "Chen"; 5 var father = new Father(); 6 var son = new Son(); 7 Son.prototype.firstName = "Xianxian"; 8 console.log(son); 9 console.log(father);
【测试结果】

测试结果表明,在子类中成功添加了firstName属性,而不影响父类的原型。
【改进代码】
在雅虎时代,雅虎封装了YUI3库实现圣杯模式。现今,已经有jQuery代替YUI3。但我们仍需致敬经典,来了解一下,YUI3库中封装好的继承方法(形成闭包实现F的变量私有化)。
这种继承方式必须熟练!
1 var inherit = (function(){ 2 function F(){} 3 return function(origin,target){ 4 F.prototype = origin.prototype; 5 target.prototype = new F(); 6 target.prototype.constructor = target; 7 target.prototype.uber = origin.prototype; 8 } 9 })();
3 深拷贝(深度克隆)
【实现思路】
-
先把所有的值都遍历一遍(看是引用值和原始值)用 for ( var prop in obj )。
-
注意这里for_in的用法:对象和数组的遍历都可以使用该方法。prop取得的是在对象中的key值,结果为string类型。
- 判断是否为该对象的私有属性,不拷贝系统自带的对象属性。使用origin.hasOwnProperty(prop)方法
-
判断是原始值,还是引用值?
- 先判断是否为null
- 用 typeof 判断是不是 object
- 如果是原始值就直接拷贝
- 如果是引用值,判断是数组还是对象
- 判断是数组还是对象
- 使用Object.prototype.toString.call()来判断
- 结果为"[object Array]"则是数组否则为对
- 数组则建立一个空数组[],否则建立空对象{}
-
递归深拷贝
【实现代码】
1 function deepClone(origin,target){ 2 var target = target || {},// 容错,防止忘记传入target 3 toStr = Object.prototype.toString, 4 arrStr = '[object Array]';// 用于判断object是否为一个数组 5 for(var prop in origin){ 6 if(origin.hasOwnProperty(prop)){// 首先判断是否为origin的私有属性,不是的话不克隆 7 if(origin[prop] !== "null" && typeof(origin[prop]) == 'object'){ 8 // 先判断是否为null,再判断该位置应该是数组还是对象 9 target[prop] = (toStr.call(origin[prop]) == arrStr) ? [] : {}; 10 // 递归调用深拷贝 11 deepClone(origin[prop],target[prop]); 12 } 13 else{ 14 // 递归调用出口 15 target[prop] = origin[prop]; 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 return target; 20 }
【测试代码】
var obj = { name : "ChenQX", age : 18, card : ['visa','unionpay','master'], son :{ name : "LiuCJ", age : 18, card : ['unionpay'], grade :{ math : 59, english :58, history : 57 } } }; var obj1 = {}; deepClone(obj,obj1); obj1['card'].push('ICBC'); console.log(obj); console.log(obj1);
【测试结果】
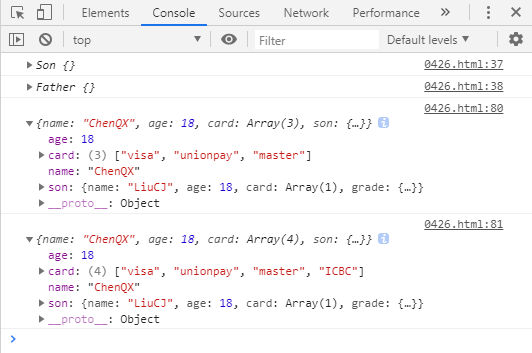
从测试结果中看出,深拷贝后的对象obj1与原对象obj一致,且对obj1中的引用属性进行修改不会对obj产生影响。
4 后记
继承是面向对象编程OOP里的一个重要概念,JavaScript是一种面向对象语言,因此有必要对JS里的继承机制有一个深度的了解。
深拷贝是一种重要的对象拷贝机制,可以拷贝原始值和引用值,同时引用值又不与源对象关联。
继承里的圣杯模式是JS发展到现在为止最重要的一种继承机制,可以被称为是所有JS继承问题的“标准答案”。