知识点1:PKMS启动流程
SystemServer.java::ServerThread::run--->PKMS::main--->PKMS::构造函数
如下,在PKMS的main函数中将PKMS服务添加到到ServiceManager中。
public static final IPackageManager main(Context context, boolean factoryTest, boolean onlyCore) { PackageManagerService m = new PackageManagerService(context, factoryTest, onlyCore); ServiceManager.addService("package", m); return m; }
接下来对构造函数进行分析,这个是重点,将其分为3个大部分讨论。
知识点2:PKMS之构造函数分析
PKMS构造函数的主要功能是:扫描Android系统中几个目标文件夹中的APK,从而建立合适的数据结构以管理诸如package信息、四大组件信息、权限信息等。
第1大部分:构造函数分析之前期准备
将前期准备分为2个小部分,Settings类分析和xml文件扫描。先来看Settings类分析。
第1大部分之第1小部分:Settings类分析
 PackageManagerService.java::构造函数
PackageManagerService.java::构造函数
public PackageManagerService(Context context, boolean factoryTest, boolean onlyCore) { EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_START, SystemClock.uptimeMillis()); //mSdkVersion的值取自系统属性ro.build.version.sdk,即编译的SDK版本。如果没有定义,则APK就不知道自己运行在Android哪个版本上。 if (mSdkVersion <= 0) { Slog.w(TAG, "**** ro.build.version.sdk not set!"); } mContext = context; mFactoryTest = factoryTest; mOnlyCore = onlyCore; //如果系统是eng版,则扫描package后,不对package做dex优化 mNoDexOpt = "eng".equals(SystemProperties.get("ro.build.type")); //mMetrics用于存储与显示屏相关的一些属性,比如屏幕宽/高/分辨率等信息 mMetrics = new DisplayMetrics(); //1.Settings是一个非常重要的类,该类用于存储系统运行过程中的一些设置 mSettings = new Settings(); mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.system", Process.SYSTEM_UID, ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM); mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.phone", MULTIPLE_APPLICATION_UIDS ? RADIO_UID : FIRST_APPLICATION_UID, ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM); mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.log", MULTIPLE_APPLICATION_UIDS ? LOG_UID : FIRST_APPLICATION_UID, ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM); mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.nfc", MULTIPLE_APPLICATION_UIDS ? NFC_UID : FIRST_APPLICATION_UID, ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM); mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.fm_radio", MULTIPLE_APPLICATION_UIDS ? FM_RADIO_UID : FIRST_APPLICATION_UID, ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM); //-----------------第1大部分之第1小部分代码结束-----------------------
第1大部分之第1小部分的代码主要是了解Settings类及其addSharedUserLPw函数。
1.初识Settings
先来看PKMS的构造函数中,使用Settings类的地方:
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.system", //字符串
Process.SYSTEM_UID, //系统进程使用的用户id,值为1000
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM); //标识系统package
接下来分析上述语句,两个知识点:(1)UID/GID的介绍;(2) addSharedUserLPw函数
(1) UID/GID的介绍
UID/GID和进程权限有关,系统定义的UID/GID在Process.java中。
 Process.java::UID/GID
Process.java::UID/GID
/** * Defines the UID/GID under which system code runs. */ public static final int SYSTEM_UID = 1000; /** * Defines the UID/GID under which the telephony code runs. */ public static final int PHONE_UID = 1001; /** * Defines the UID/GID under which the bluetooth code runs. * {@hide} */ public static final int BLUETOOTH_UID = 1002; /** * Defines the UID/GID for the user shell. * @hide */ public static final int SHELL_UID = 2000; /** * Defines the UID/GID for the log group. * @hide */ public static final int LOG_UID = 1007; /** * Defines the UID/GID for the WIFI supplicant process. * @hide */ public static final int WIFI_UID = 1010; /** * Defines the UID/GID for the mediaserver process. * @hide */ public static final int MEDIA_UID = 1013; /** * Defines the GID for the group that allows write access to the SD card. * @hide */ public static final int SDCARD_RW_GID = 1015; /** * Defines the UID/GID for the FM process. * @hide */ public static final int FM_RADIO_UID = 1028; /** * Defines the UID/GID for the NFC service process. * @hide */ public static final int NFC_UID = 1027; /** * Defines the GID for the group that allows write access to the internal media storage. * @hide */ public static final int MEDIA_RW_GID = 1023; /** * Defines the start of a range of UIDs (and GIDs), going from this * number to {@link #LAST_APPLICATION_UID} that are reserved for assigning * to applications. */ public static final int FIRST_APPLICATION_UID = 10000; /** * Last of application-specific UIDs starting at * {@link #FIRST_APPLICATION_UID}. */ public static final int LAST_APPLICATION_UID = 99999; /** * Defines a secondary group id for access to the bluetooth hardware. */ public static final int BLUETOOTH_GID = 2000;
(2) addSharedUserLPw函数的分析
 addSharedUserLPw
addSharedUserLPw
SharedUserSetting addSharedUserLPw(String name, int uid, int pkgFlags) { //(2.1)mSharedUsers是一个HashMap,key为字符串,值为SharedUserSetting对象 SharedUserSetting s = mSharedUsers.get(name); if (s != null) { if (s.userId == uid) { return s; } PackageManagerService.reportSettingsProblem(Log.ERROR, "Adding duplicate shared user, keeping first: " + name); return null; } //创建一个新的SharedUserSetting对象,并设置userId为uid s = new SharedUserSetting(name, pkgFlags); s.userId = uid; //(2.2)分析addUserIdLPw if (addUserIdLPw(uid, s, name)) { mSharedUsers.put(name, s); //将name与s键值对添加到mSharedUsers中 return s; } return null; }
addSharedUserLPw函数中也有两个知识点:(2.1) SharedUserSetting类的分析;(2.2) addUserIdLPw函数的分析
(2.1) SharedUserSetting类的分析
该类包含了3个数据成员,
final String name; int userId; final HashSet<PackageSetting> packages = new HashSet<PackageSetting>();
这里,通过一个例子来分析SharedUserSetting的数据成员的作用。该例子来源于SystemUI的AndroidManifest.xml,如下所示:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.android.systemui" android:sharedUserId="android.uid.system" android:process="system" >
在xml文件中声明了一个android:sharedUserId属性,值为"android.uid.system"。该属性有两个作用:
* 两个或多个声明了同一种sharedUserId的APK可以共享彼此的数据,并可运行在同一进程中。
* 声明特定的sharedUserId之后,该APK所在进程将被赋予指定的UID(即用户权限)。
ps:要想实现”赋予指定的UID”,还需要在其Android.mk文件中声明额外的LOCAL_CERTIFICATE:=platform。
通过以上分析,可以获得以下3个关键点,即三个数据成员的作用:
* name(String):xml中sharedUserId属性指定了一个字符串,它是UID的字符串描述,故对应数据结构中也应该有一个字符串,这样就把代码和xml中的属性联系起来了。
* userId(int): linux系统中uid是一个整数,所以该数据结构中必然有一个整型变量。
* packages(HashSet<PackageSetting>):多个Package可声明同一个sharedUserId,故该数据结构必然会保存那些声明了相同sharedUserId的package的某些信息。
了解了3个关键点后,再看看Android系统如何设计相应数据结构的,SharedUserSetting类的关系图如下:
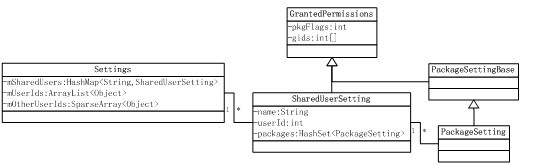
分析关系图中的各个类之间的关系:
* Settings类定义了一个mSharedUsers成员变量,它是一个HashMap,以字符串 (android.uid.system)为key,对应的value是一个SharedUserSetting对象。
* SharedUserSetting继承自GrantedPermission,定义了一个packages成员变量,类型为HashSet,用于保存声明了相同SharedUserId的Package的权限设置信息。
* 每个Package都有自己的权限设置。权限的概念由PackageSetting类表达。
* Settings中还有两个成员变量。mUserIds和mOtherUserIds变量,类型分别为ArrayList和SparseArray。目的是以UID为索引,得到对应的SharedUserSetting对象。
* 一般情况下,”以索引获取数组元素的速度”比”以key获取HashMap中的元素的速度”快得多。由此可知,这是以空间换取时间的做法。
(2.2) addUserIdLPw函数的分析
该函数的功能是将SharedUserSetting对象保存到对应的数组中。代码如下:
 addUserIdLPw
addUserIdLPw
private boolean addUserIdLPw(int uid, Object obj, Object name) { //Android中,应用apk所在进程的uid从10000开始,系统apk所在进程的uid小于1000 if (uid >= PackageManagerService.FIRST_APPLICATION_UID + PackageManagerService.MAX_APPLICATION_UIDS) { return false; } if (uid >= PackageManagerService.FIRST_APPLICATION_UID) { int N = mUserIds.size(); //计算索引,其值是uid和FIRST_APPLICATION_UID的差 final int index = uid - PackageManagerService.FIRST_APPLICATION_UID; while (index >= N) { mUserIds.add(null); N++; } //判断该索引的值是否为空 if (mUserIds.get(index) != null) { PackageManagerService.reportSettingsProblem(Log.ERROR, "Adding duplicate user id: " + uid + " name=" + name); return false; } mUserIds.set(index, obj); // mUserIds保存应用Package的uid } else { if (mOtherUserIds.get(uid) != null) { PackageManagerService.reportSettingsProblem(Log.ERROR, "Adding duplicate shared id: " + uid + " name=" + name); return false; } mOtherUserIds.put(uid, obj); // mOtherUserIds保存系统Package的uid } return true; }
Setting的作用是管理Android系统运行过程中的一些设置信息。分析完毕。
第1大部分之第2小部分:xml文件扫描
1. xml文件扫描
继续分析PKMS的构造函数:
 PKMS::构造函数
PKMS::构造函数
String separateProcesses = SystemProperties.get("debug.separate_processes");
if (separateProcesses != null && separateProcesses.length() > 0) {
if ("*".equals(separateProcesses)) {
mDefParseFlags = PackageParser.PARSE_IGNORE_PROCESSES;
mSeparateProcesses = null;
Slog.w(TAG, "Running with debug.separate_processes: * (ALL)");
} else {
mDefParseFlags = 0;
mSeparateProcesses = separateProcesses.split(",");
Slog.w(TAG, "Running with debug.separate_processes: "
+ separateProcesses);
}
} else {
mDefParseFlags = 0;
mSeparateProcesses = null;
}
//创建一个Installer对象,该对象和Native进程installd交互
mInstaller = new Installer();
//得到一个WindowManager对象
WindowManager wm = (WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
Display d = wm.getDefaultDisplay();
d.getMetrics(mMetrics); //获取当前设备的显示屏信息
synchronized (mInstallLock) {
// writer
synchronized (mPackages) {
//该线程的工作是:程序的安装和卸载等
mHandlerThread.start();
mHandler = new PackageHandler(mHandlerThread.getLooper());
File dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory();
// mAppDataDir指向/data/data目录
mAppDataDir = new File(dataDir, "data");
// mUserAppDataDir指向/data/user目录
mUserAppDataDir = new File(dataDir, "user");
// mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir指向/data/app-private目录
mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app-private");
//创建一个UserManager对象
mUserManager = new UserManager(mInstaller, mUserAppDataDir);
//(a)从文件中读权限
readPermissions();
//(b) readLPw分析
mRestoredSettings = mSettings.readLPw();
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//---------------------第1大部分之第2小部分代码结束---------------
…...…...
}
接下来对代码中的(a)(b)进行分析。
(a) readPermissions函数分析
代码如下:
 readPermissions()
readPermissions()
void readPermissions() { //从"etc/permissions"读取权限,该目录中存储了和设备相关的一些权限信息。 File libraryDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "etc/permissions"); if (!libraryDir.exists() || !libraryDir.isDirectory()) { Slog.w(TAG, "No directory " + libraryDir + ", skipping"); return; } if (!libraryDir.canRead()) { Slog.w(TAG, "Directory " + libraryDir + " cannot be read"); return; } // Iterate over the files in the directory and scan .xml files for (File f : libraryDir.listFiles()) { // We'll read platform.xml last //先处理非platform.xml文件 if (f.getPath().endsWith("etc/permissions/platform.xml")) { continue; } if (!f.getPath().endsWith(".xml")) { Slog.i(TAG, "Non-xml file " + f + " in " + libraryDir + " directory, ignoring"); continue; } if (!f.canRead()) { Slog.w(TAG, "Permissions library file " + f + " cannot be read"); continue; } //调用readPermissionsFromXml函数解析此xml文件 readPermissionsFromXml(f); } // Read permissions from .../etc/permissions/platform.xml last so it will take precedence final File permFile = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "etc/permissions/platform.xml"); //解析platform.xml文件,该文件优先级最高 readPermissionsFromXml(permFile); }
可见,readPermissions函数就是调用readPermissionXml函数解析/system/etc/permissions目录下的文件。两个知识点:/system/etc/permissions下的xml文件和readPermissionXml函数。
(a.1)先来分析手机上/system/etc/permissions目录下的platform.xml文件:
 platform.xml
platform.xml
<permissions>
<!—建立权限名和gid的映射关系-->
<permission name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" >
<group gid="net_bt_admin" />
</permission>
<permission name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" >
<group gid="net_bt" />
</permission>
<permission name="android.permission.INTERNET" >
<group gid="inet" />
</permission>
<permission name="android.permission.CAMERA" >
<group gid="camera" />
</permission>
<permission name="android.permission.READ_LOGS" >
<group gid="log" />
</permission>
<permission name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" >
<group gid="sdcard_rw" />
</permission>
<!-- The group that /cache belongs to, linked to the permission
set on the applications that can access /cache -->
<permission name="android.permission.ACCESS_CACHE_FILESYSTEM" >
<group gid="cache" />
</permission>
<!-- RW permissions to any system resources owned by group 'diag'.
This is for carrier and manufacture diagnostics tools that must be
installable from the framework. Be careful. -->
<permission name="android.permission.DIAGNOSTIC" >
<group gid="input" />
<group gid="diag" />
</permission>
<!-- ================================= -->
<!—赋予uid(shell所在线程)对应的权限-->
<assign-permission name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.SEND_SMS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.CALL_PHONE" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.WRITE_CONTACTS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.READ_CALENDAR" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.WRITE_CALENDAR" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.READ_USER_DICTIONARY" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.WRITE_USER_DICTIONARY" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.ACCESS_LOCATION_EXTRA_COMMANDS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" uid="shell" />
<!-- System tool permissions granted to the shell. -->
<assign-permission name="android.permission.GET_TASKS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.CHANGE_CONFIGURATION" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.REORDER_TASKS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.SET_ANIMATION_SCALE" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.SET_PREFERRED_APPLICATIONS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.WRITE_SECURE_SETTINGS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.BROADCAST_STICKY" uid="shell" />
<!-- Development tool permissions granted to the shell. -->
<assign-permission name="android.permission.SET_DEBUG_APP" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.SET_PROCESS_LIMIT" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.SET_ALWAYS_FINISH" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.DUMP" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.SIGNAL_PERSISTENT_PROCESSES" uid="shell" />
<!-- Internal permissions granted to the shell. -->
<assign-permission name="android.permission.FORCE_BACK" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.BATTERY_STATS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.INTERNAL_SYSTEM_WINDOW" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.INJECT_EVENTS" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.SET_ACTIVITY_WATCHER" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.READ_INPUT_STATE" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.SET_ORIENTATION" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.INSTALL_PACKAGES" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.CLEAR_APP_USER_DATA" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.DELETE_CACHE_FILES" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.DELETE_PACKAGES" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.ACCESS_SURFACE_FLINGER" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.READ_FRAME_BUFFER" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.DEVICE_POWER" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.INSTALL_LOCATION_PROVIDER" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.BACKUP" uid="shell" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.MODIFY_AUDIO_SETTINGS" uid="media" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.ACCESS_DRM" uid="media" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.ACCESS_SURFACE_FLINGER" uid="media" />
<assign-permission name="android.permission.ACCESS_SURFACE_FLINGER" uid="graphics" />
<!—系统提供的Java库,应用程序运行时必须要链接这些库,该工作由系统自动完成-->
<library name="android.test.runner"
file="/system/framework/android.test.runner.jar" />
<library name="javax.obex"
file="/system/framework/javax.obex.jar"/>
</permissions>
platform.xml文件中主要由4个标签:
*permission和group:用于建立Linux层和Android层permission之间的映射关系。
*assign-permission:用于向指定的uid赋予相应的权限。
*library:用于指定系统库。
另外/system/etc/permissions目录下还有其他xml文件,包含feature标签。该标签的作用是用来描述一个手持终端应该支持的硬件特性。比如支持camera、支持蓝牙等。
真实设备上/system/etc/permissions目录中的文件来源:在编译时阶段由不同硬件平台根据自己的配置信息复制相关文件(路径是/frameworks/base/data/etc/)到/system/etc/permissions目录中。编译完成后,将生成system镜像,最终烧到手机里,这就是来源。
(a.2) readPermissionsFromXml分析
作用:将xml文件中的标签以及它们之间的关系转换成代码中的相应的数据结构。
 readPermissionsFromXml
readPermissionsFromXml
private void readPermissionsFromXml(File permFile) { FileReader permReader = null; try { permReader = new FileReader(permFile); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Couldn't find or open permissions file " + permFile); return; } try { XmlPullParser parser = Xml.newPullParser(); parser.setInput(permReader); XmlUtils.beginDocument(parser, "permissions"); while (true) { XmlUtils.nextElement(parser); if (parser.getEventType() == XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { break; } String name = parser.getName(); //解析group标签 if ("group".equals(name)) { String gidStr = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "gid"); if (gidStr != null) { //转换xml中的gid字符串为整型,并保存到mGlobalGids中 int gid = Integer.parseInt(gidStr); mGlobalGids = appendInt(mGlobalGids, gid); } else { Slog.w(TAG, "<group> without gid at " + parser.getPositionDescription()); } XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } else if ("permission".equals(name)) { String perm = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "name"); if (perm == null) { Slog.w(TAG, "<permission> without name at " + parser.getPositionDescription()); XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } perm = perm.intern(); //调用readPermission处理 readPermission(parser, perm); //解析assign-permission标签 } else if ("assign-permission".equals(name)) { String perm = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "name"); if (perm == null) { Slog.w(TAG, "<assign-permission> without name at " + parser.getPositionDescription()); XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } String uidStr = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "uid"); if (uidStr == null) { Slog.w(TAG, "<assign-permission> without uid at " + parser.getPositionDescription()); XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } //根据字符串uidstr,然后获得uid值 int uid = Process.getUidForName(uidStr); if (uid < 0) { Slog.w(TAG, "<assign-permission> with unknown uid \"" + uidStr + "\" at " + parser.getPositionDescription()); XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } perm = perm.intern(); //和assign相关的信息保存在mSystemPermissions中 HashSet<String> perms = mSystemPermissions.get(uid); if (perms == null) { perms = new HashSet<String>(); mSystemPermissions.put(uid, perms); } perms.add(perm); XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); } else if ("library".equals(name)) { //解析library String lname = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "name"); String lfile = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "file"); if (lname == null) { Slog.w(TAG, "<library> without name at " + parser.getPositionDescription()); } else if (lfile == null) { Slog.w(TAG, "<library> without file at " + parser.getPositionDescription()); } else { //Log.i(TAG, "Got library " + lname + " in " + lfile); mSharedLibraries.put(lname, lfile); //将xml中的name和library保存到mSharedLibraries中 } XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } else if ("feature".equals(name)) { //解析feature标签 String fname = parser.getAttributeValue(null, "name"); if (fname == null) { Slog.w(TAG, "<feature> without name at " + parser.getPositionDescription()); } else { //Log.i(TAG, "Got feature " + fname); //在xml中定义的feature由FeatureInfo表达 FeatureInfo fi = new FeatureInfo(); fi.name = fname; mAvailableFeatures.put(fname, fi); //保存到mAvailableFeatures中 } XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } else { XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } } permReader.close(); } catch (XmlPullParserException e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Got execption parsing permissions.", e); } catch (IOException e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Got execption parsing permissions.", e); } }
总结:主要还是了解各标签的作用;对于数据结构,知道就好~~
(b) readLPw函数分析
readLPw函数的功能也是解析文件,不过这些文件的内容却是在PKMS正常启动后生成的。
这里介绍几个文件,具体位置在Settings构造函数中指明。代码如下:
 Settings::构造函数
Settings::构造函数
Settings() { File dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory(); File systemDir = new File(dataDir, "system"); systemDir.mkdirs(); FileUtils.setPermissions(systemDir.toString(), FileUtils.S_IRWXU|FileUtils.S_IRWXG |FileUtils.S_IROTH|FileUtils.S_IXOTH, -1, -1); /* packages.xml和packages-backup.xml为一组,用于描述系统中安装的Package的信息,其中backup为临时文件。 packages-stopped.xml和packages-stopped-backup.xml为一组,用于描述系统中强制停止运行的Package的信息。 package.list列出当前系统中应用级(uid>10000)Package的信息 */ mSettingsFilename = new File(systemDir, "packages.xml"); mBackupSettingsFilename = new File(systemDir, "packages-backup.xml"); mPackageListFilename = new File(systemDir, "packages.list"); mStoppedPackagesFilename = new File(systemDir, "packages-stopped.xml"); mBackupStoppedPackagesFilename = new File(systemDir, "packages-stopped-backup.xml"); }
文件的来历:
*package.xml:PKMS扫描完目标文件后会创建该文件。当系统进行安装、卸载和更新等操作时,均会更新该文件。下次开机会直接从里面读取相关信息添加到内存相关列表中。
*package-stopped.xml:该文件保存系统中被用户强制停止的Package的信息。
*package.list:描述系统中存在的非系统自带的APK的信息。
readLPw函数的功能就是解析这些xml文件的内容,然后建立并更新对应的数据结构。
总结:”第1大部分:构造函数分析之前期准备”这一阶段的工作就到此为止了。在这个阶段的工作就是扫描并解析xml文件,将其中的信息保存到特定的数据结构中。
这个阶段扫描的xml文件与权限以及上一次扫描得到的Package信息有关,它为PKMS下一阶段的工作提供了重要的参考信息。
第2大部分:构造函数分析之扫描Package
PKMS构造函数第二阶段的工作就是扫描系统中的APK了。由于需要逐个扫描文件,因此手机上装的APK越多,PKMS工作量就越大,系统启动速度就越慢。
将扫描Package分为3个小部分,系统库的dex优化、扫描系统package、扫描非系统package。
第2大部分之第1小部分:系统库的dex优化
dex优化的主要工作是:检查 BOOTCLASSPATH,mSharedLibraries 及 /system/framework 下的jar是否需要dexopt,需要的话,则通过 dexopt 进行优化。
接上一阶段的PKMS的构造函数,代码如下:
 PKMS::构造函数
PKMS::构造函数
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); //记录扫描开始的时间 EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_SYSTEM_SCAN_START, startTime); // Set flag to monitor and not change apk file paths when // scanning install directories. int scanMode = SCAN_MONITOR | SCAN_NO_PATHS | SCAN_DEFER_DEX; //定义扫描参数 if (mNoDexOpt) { Slog.w(TAG, "Running ENG build: no pre-dexopt!"); scanMode |= SCAN_NO_DEX; //在控制扫描过程中是否对APK文件进行dex优化 } final HashSet<String> libFiles = new HashSet<String>(); // mFrameworkDir指向/system/framework目录 mFrameworkDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "framework"); // mDalvikCacheDir指向/data/dalvik-cache目录 mDalvikCacheDir = new File(dataDir, "dalvik-cache"); boolean didDexOpt = false; /* Out of paranoia, ensure that everything in the boot class path has been dexed. 获取Java启动类库的路径,在init.rc文件中通过BOOTCLASSPATH环境变量输出,该变量指明了framwork所有核心库及文件位置。该值如下(init.rc中可找到): /system/framework/core.jar:/system/framework/core-junit.jar:/system/framework/bouncycastle.jar:/system/framework/ext.jar:/system/framework/framework.jar:/system/framework/android.policy.jar:/system/framework/services.jar:/system/framework/apache-xml.jar:/system/framework/filterfw.jar:/system/framework/com.qrd.plugin.feature_query.jar:/system/framework/com.qrdinside.impl.jar */ String bootClassPath = System.getProperty("java.boot.class.path"); if (bootClassPath != null) { String[] paths = splitString(bootClassPath, ':'); for (int i=0; i<paths.length; i++) { try { //判断该Jar包是否需要重新做dex优化 if (dalvik.system.DexFile.isDexOptNeeded(paths[i])) { //将该Jar包文件路径保存到libFiles中,然后通过mInstall对象发送命令给installd,让其对该Jar包进行dex优化 libFiles.add(paths[i]); mInstaller.dexopt(paths[i], Process.SYSTEM_UID, true); didDexOpt = true; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Boot class path not found: " + paths[i]); } catch (IOException e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Cannot dexopt " + paths[i] + "; is it an APK or JAR? " + e.getMessage()); } } } else { Slog.w(TAG, "No BOOTCLASSPATH found!"); } //判断系统库是否需要做dex优化。处理方式同上 if (mSharedLibraries.size() > 0) { Iterator<String> libs = mSharedLibraries.values().iterator(); while (libs.hasNext()) { String lib = libs.next(); try { if (dalvik.system.DexFile.isDexOptNeeded(lib)) { libFiles.add(lib); mInstaller.dexopt(lib, Process.SYSTEM_UID, true); didDexOpt = true; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Library not found: " + lib); } catch (IOException e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Cannot dexopt " + lib + "; is it an APK or JAR? " + e.getMessage()); } } } // Gross hack for now: we know this file doesn't contain any // code, so don't dexopt it to avoid the resulting log spew. // framework-res.apk定义了系统常用的资源,还有几个重要的Activity,如长按power键后弹出的选择框 libFiles.add(mFrameworkDir.getPath() + "/framework-res.apk"); /** * And there are a number of commands implemented in Java, which * we currently need to do the dexopt on so that they can be * run from a non-root shell. */ //列举/system/framework目录中的文件 String[] frameworkFiles = mFrameworkDir.list(); if (frameworkFiles != null) { //判断该目录下的APK或Jar文件是否需要做dex优化。处理方式同上 for (int i=0; i<frameworkFiles.length; i++) { File libPath = new File(mFrameworkDir, frameworkFiles[i]); String path = libPath.getPath(); // Skip the file if we alrady did it. if (libFiles.contains(path)) { continue; } // Skip the file if it is not a type we want to dexopt. if (!path.endsWith(".apk") && !path.endsWith(".jar")) { continue; } try { if (dalvik.system.DexFile.isDexOptNeeded(path)) { mInstaller.dexopt(path, Process.SYSTEM_UID, true); didDexOpt = true; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Jar not found: " + path); } catch (IOException e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Exception reading jar: " + path, e); } } } /* 上面代码对系统库(包括BOOTCLASSPATH指定的、platform.xml定义的、/system/framework目录下的Jar包与APK文件)进行一次仔细检查,对该优化的进行优化。如果优化期间,对任何一个文件都进行了优化,则设置didDexOpt为true */ if (didDexOpt) { // If we had to do a dexopt of one of the previous // things, then something on the system has changed. // Consider this significant, and wipe away all other // existing dexopt files to ensure we don't leave any // dangling around. String[] files = mDalvikCacheDir.list(); if (files != null) { /*如果前面对任意一个系统库重新做过dex优化,就需要删除cache文件。从删除cache的操作来看,这些cache文件应该是使用了dex优化后的系统库,当系统库重新做dex优化后,这些cache就失效了,需要删除。 */ for (int i=0; i<files.length; i++) { String fn = files[i]; if (fn.startsWith("data@app@") || fn.startsWith("data@app-private@")) { Slog.i(TAG, "Pruning dalvik file: " + fn); (new File(mDalvikCacheDir, fn)).delete(); } } } } ............ //-------------------系统库的dex优化到此为止----------------------
第2大部分之第2小部分:扫描系统Package
清空cache文件后,PKMS进入了这个阶段的核心内容,即扫描Package,代码如下:
 PKMS::构造函数
PKMS::构造函数
// Find base frameworks (resource packages without code). //创建文件夹监控对象,监视/system/frameworks目录。利用了Linux平台的tify机制 mFrameworkInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver( mFrameworkDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, true); mFrameworkInstallObserver.startWatching(); //调用scanDirLI函数扫描/system/framework目录 scanDirLI(mFrameworkDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM | PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanMode | SCAN_NO_DEX, 0); // Collect all system packages. //创建文件夹监控对象,监视/system/app目录 mSystemAppDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "app"); mSystemInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver( mSystemAppDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, true); mSystemInstallObserver.startWatching(); //扫描/system/app目录 scanDirLI(mSystemAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM | PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanMode, 0); // Collect all vendor packages. //监视并扫描/vendor/app目录 mVendorAppDir = new File("/vendor/app"); mVendorInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver( mVendorAppDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, true); mVendorInstallObserver.startWatching(); scanDirLI(mVendorAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM | PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanMode, 0); if (DEBUG_UPGRADE) Log.v(TAG, "Running installd update commands"); //和installd交互 mInstaller.moveFiles();
由以上代码可知,PKMS将扫描以下几个目录:
* /system/framework:该目录中的文件都是系统库,例如framework.jar、services.jar、framework-res.apk。不过scanDirLI只扫描APK文件,所以framework-res.apk是该目录中唯一”受宠”的文件。 * /system/app:该目录下全是默认的系统应用,如Browser.apk、Settings.apk等。 * /vendor/app:该目录中的文件由厂商提供。
PKMS调用scanDirLI函数进行扫描,接下来分析该函数。
1.scanDirLI函数分析
代码如下:
 scanDirLI
scanDirLI
private void scanDirLI(File dir, int flags, int scanMode, long currentTime) { String[] files = dir.list(); //列举该目录下的文件 if (files == null) { Log.d(TAG, "No files in app dir " + dir); return; } if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) { Log.d(TAG, "Scanning app dir " + dir); } int i; for (i=0; i<files.length; i++) { File file = new File(dir, files[i]); if (!isPackageFilename(files[i])) { // Ignore entries which are not apk's,即这里只扫描APK文件 continue; } /* 调用scanPackageLI函数扫描一个特定的文件,返回值是PackageParser的内部类Package,该类的实例代表一个APK文件,所以它就是APK文件对应的数据结构 */ PackageParser.Package pkg = scanPackageLI(file, flags|PackageParser.PARSE_MUST_BE_APK, scanMode, currentTime); // Don't mess around with apps in system partition. if (pkg == null && (flags & PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) == 0 && mLastScanError == PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK) { //注意flag的作用,只有非系统Package扫描失败,才会删除该文件 // Delete the apk Slog.w(TAG, "Cleaning up failed install of " + file); file.delete(); } } }
接着分析scanPackageLI函数。PKMS中有两个同名的scanPackageLI函数。先看初遇的scanPackageLI函数。
2.初会scanPackageLI函数[-->PKMS:: scanPackageLI]
 PackageParser.Package::scanPackageLI
PackageParser.Package::scanPackageLI
private PackageParser.Package scanPackageLI(File scanFile, int parseFlags, int scanMode, long currentTime) { mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED; String scanPath = scanFile.getPath(); parseFlags |= mDefParseFlags; //默认的扫描标志,正常情况下为0 //创建一个PackageParser对象 PackageParser pp = new PackageParser(scanPath); pp.setSeparateProcesses(mSeparateProcesses); // mSeparateProcesses为空 pp.setOnlyCoreApps(mOnlyCore); //mOnlyCore为false //调用parsePackage函数解析APK文件。注意,这里把mMetric对象也作为参数传递进去了 final PackageParser.Package pkg = pp.parsePackage(scanFile, scanPath, mMetrics, parseFlags); if (pkg == null) { mLastScanError = pp.getParseError(); return null; } PackageSetting ps = null; PackageSetting updatedPkg; //--------BEGIN: 接下来主要是关于Package升级方面的工作----------- synchronized (mPackages) { // Look to see if we already know about this package. String oldName = mSettings.mRenamedPackages.get(pkg.packageName); if (pkg.mOriginalPackages != null && pkg.mOriginalPackages.contains(oldName)) { // This package has been renamed to its original name. Let's use that. ps = mSettings.peekPackageLPr(oldName); } // If there was no original package, see one for the real package name. if (ps == null) { ps = mSettings.peekPackageLPr(pkg.packageName); } // Check to see if this package could be hiding/updating a system // package. Must look for it either under the original or real // package name depending on our state. updatedPkg = mSettings.mDisabledSysPackages.get( ps != null ? ps.name : pkg.packageName); } // First check if this is a system package that may involve an update if (updatedPkg != null && (parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) != 0) { if (ps != null && !ps.codePath.equals(scanFile)) { // The path has changed from what was last scanned... check the // version of the new path against what we have stored to determine // what to do. if (pkg.mVersionCode < ps.versionCode) { // The system package has been updated and the code path does not match // Ignore entry. Skip it. Log.i(TAG, "Package " + ps.name + " at " + scanFile + " ignored: updated version " + ps.versionCode + " better than this " + pkg.mVersionCode); mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_DUPLICATE_PACKAGE; return null; } else { // The current app on the system partion is better than // what we have updated to on the data partition; switch // back to the system partition version. // At this point, its safely assumed that package installation for // apps in system partition will go through. If not there won't be a working // version of the app // writer synchronized (mPackages) { // Just remove the loaded entries from package lists. mPackages.remove(ps.name); } Slog.w(TAG, "Package " + ps.name + " at " + scanFile + "reverting from " + ps.codePathString + ": new version " + pkg.mVersionCode + " better than installed " + ps.versionCode); InstallArgs args = new FileInstallArgs(ps.codePathString, ps.resourcePathString, ps.nativeLibraryPathString); args.cleanUpResourcesLI(); mSettings.enableSystemPackageLPw(ps.name); } } } if (updatedPkg != null) { // An updated system app will not have the PARSE_IS_SYSTEM flag set initially parseFlags |= PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM; } //--------END: 关于Package升级方面的工作结束----------- // Verify certificates against what was last scanned if (!collectCertificatesLI(pp, ps, pkg, scanFile, parseFlags)) { Slog.w(TAG, "Failed verifying certificates for package:" + pkg.packageName); return null; } // The apk is forward locked (not public) if its code and resources are kept in different files.目前只有/vendor/app目录下的扫描会使用该PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK标志。 // TODO grab this value from PackageSettings if (ps != null && !ps.codePath.equals(ps.resourcePath)) { parseFlags |= PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK; } String codePath = null; String resPath = null; if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK) != 0) { if (ps != null && ps.resourcePathString != null) { resPath = ps.resourcePathString; } else { // Should not happen at all. Just log an error. Slog.e(TAG, "Resource path not set for pkg : " + pkg.packageName); } } else { resPath = pkg.mScanPath; } codePath = pkg.mScanPath; //mScanPath指向该APK文件所在的位置 // Set application objects path explicitly.其中codePath和resPath都指向APK文件所在位置 setApplicationInfoPaths(pkg, codePath, resPath); // Note that we invoke the following method only if we are about to unpack an application //调用第二个scanPackageLI函数 return scanPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanMode | SCAN_UPDATE_SIGNATURE, currentTime); }
scanPackageLI函数首先调用PackageParser类的相关函数(parsePackage函数)对APK文件进行解析。PackageParser类完成了从物理文件到对应数据结构的转换。下面来分析它。
3.PackageParser分析
PackageParser主要负责APK文件的解析,即解析APK文件中的AndroidManifest.xml文件。代码如下:[-->PackageParser.java::parsePackage]
 parsePackage
parsePackage
public Package parsePackage(File sourceFile, String destCodePath, DisplayMetrics metrics, int flags) { mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED; mArchiveSourcePath = sourceFile.getPath(); if (!sourceFile.isFile()) { Slog.w(TAG, "Skipping dir: " + mArchiveSourcePath); mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NOT_APK; return null; } if (!isPackageFilename(sourceFile.getName()) && (flags&PARSE_MUST_BE_APK) != 0) { if ((flags&PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) == 0) { // We expect to have non-.apk files in the system dir, // so don't warn about them. Slog.w(TAG, "Skipping non-package file: " + mArchiveSourcePath); } mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NOT_APK; return null; } if (DEBUG_JAR) Slog.d(TAG, "Scanning package: " + mArchiveSourcePath); //检查是否为APK文件 XmlResourceParser parser = null; AssetManager assmgr = null; Resources res = null; boolean assetError = true; try { assmgr = new AssetManager(); int cookie = assmgr.addAssetPath(mArchiveSourcePath); if (cookie != 0) { res = new Resources(assmgr, metrics, null); assmgr.setConfiguration(0, 0, null, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, Build.VERSION.RESOURCES_SDK_INT); //获得一个xml资源解析对象,该对象解析的是APK中的AndroidManifest.xml parser = assmgr.openXmlResourceParser(cookie, ANDROID_MANIFEST_FILENAME); assetError = false; } else { Slog.w(TAG, "Failed adding asset path:"+mArchiveSourcePath); } } catch (Exception e) { Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to read AndroidManifest.xml of " + mArchiveSourcePath, e); } if (assetError) { if (assmgr != null) assmgr.close(); mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_MANIFEST; return null; } //出错处理 String[] errorText = new String[1]; Package pkg = null; Exception errorException = null; try { // 调用另外一个parsePackage函数 pkg = parsePackage(res, parser, flags, errorText); } catch (Exception e) { errorException = e; mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_UNEXPECTED_EXCEPTION; } if (pkg == null) { // If we are only parsing core apps, then a null with INSTALL_SUCCEEDED // just means to skip this app so don't make a fuss about it. if (!mOnlyCoreApps || mParseError != PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) { if (errorException != null) { Slog.w(TAG, mArchiveSourcePath, errorException); } else { Slog.w(TAG, mArchiveSourcePath + " (at " + parser.getPositionDescription() + "): " + errorText[0]); } if (mParseError == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) { mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED; } } parser.close(); assmgr.close(); return null; } parser.close(); assmgr.close(); // 设置代码和资源路径,都指向APK文件所在的位置 pkg.mPath = destCodePath; pkg.mScanPath = mArchiveSourcePath; pkg.mSignatures = null; return pkg; }
该函数中调用了另一个同名的parsePackage函数。这个同名函数的作用单一,就是解析AndroidManifest.xml中的各种标签。分析其中的关键代码:
 parsePackage
parsePackage
private Package parsePackage( Resources res, XmlResourceParser parser, int flags, String[] outError) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException { AttributeSet attrs = parser; mParseInstrumentationArgs = null; mParseActivityArgs = null; mParseServiceArgs = null; mParseProviderArgs = null; //得到Package的名字,其实就是得到AndroidManifest.xml中的Package属性的值,每个APK都必须定义该属性 .......... int type; .......... //以pkgName名字为参数,创建一个Package对象,后面的工作就是解析xml并填充该Package信息 final Package pkg = new Package(pkgName); boolean foundApp = false; TypedArray sa = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifest); pkg.mVersionCode = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifest_versionCode, 0); pkg.mVersionName = sa.getNonConfigurationString( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifest_versionName, 0); if (pkg.mVersionName != null) { pkg.mVersionName = pkg.mVersionName.intern(); } String str = sa.getNonConfigurationString( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifest_sharedUserId, 0); if (str != null && str.length() > 0) { String nameError = validateName(str, true); if (nameError != null && !"android".equals(pkgName)) { outError[0] = "<manifest> specifies bad sharedUserId name \"" + str + "\": " + nameError; mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_SHARED_USER_ID; return null; } pkg.mSharedUserId = str.intern(); pkg.mSharedUserLabel = sa.getResourceId( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifest_sharedUserLabel, 0); } sa.recycle(); pkg.installLocation = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifest_installLocation, PARSE_DEFAULT_INSTALL_LOCATION); pkg.applicationInfo.installLocation = pkg.installLocation; // Resource boolean are -1, so 1 means we don't know the value. int supportsSmallScreens = 1; int supportsNormalScreens = 1; int supportsLargeScreens = 1; int supportsXLargeScreens = 1; int resizeable = 1; int anyDensity = 1; int outerDepth = parser.getDepth(); while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT && (type != XmlPullParser.END_TAG || parser.getDepth() > outerDepth)) { if (type == XmlPullParser.END_TAG || type == XmlPullParser.TEXT) { continue; } String tagName = parser.getName(); //得到标签名 if (tagName.equals("application")) { if (foundApp) { if (RIGID_PARSER) { outError[0] = "<manifest> has more than one <application>"; mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED; return null; } else { Slog.w(TAG, "<manifest> has more than one <application>"); XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } } foundApp = true; //解析application标签 if (!parseApplication(pkg, res, parser, attrs, flags, outError)) { return null; } } else if (tagName.equals("permission-group")) { //解析permission-group标签 if (parsePermissionGroup(pkg, res, parser, attrs, outError) == null) { return null; } } else if (tagName.equals("permission")) { //解析permission标签 if (parsePermission(pkg, res, parser, attrs, outError) == null) { return null; } } else if (tagName.equals("permission-tree")) { if (parsePermissionTree(pkg, res, parser, attrs, outError) == null) { return null; } } else if (tagName.equals("uses-permission")) { //从xml文件中获取uses-permission标签的属性 sa = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesPermission); // Note: don't allow this value to be a reference to a resource // that may change. //取出属性值,也就是对应的权限使用声明 String name = sa.getNonResourceString( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesPermission_name); sa.recycle(); if (name != null && !pkg.requestedPermissions.contains(name)) { //添加到Package的requestedPermissions数组 pkg.requestedPermissions.add(name.intern()); } XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); } else if (tagName.equals("uses-configuration")) { ConfigurationInfo cPref = new ConfigurationInfo(); sa = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesConfiguration); cPref.reqTouchScreen = sa.getInt( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesConfiguration_reqTouchScreen, Configuration.TOUCHSCREEN_UNDEFINED); cPref.reqKeyboardType = sa.getInt( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesConfiguration_reqKeyboardType, Configuration.KEYBOARD_UNDEFINED); if (sa.getBoolean( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesConfiguration_reqHardKeyboard, false)) { cPref.reqInputFeatures |= ConfigurationInfo.INPUT_FEATURE_HARD_KEYBOARD; } cPref.reqNavigation = sa.getInt( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesConfiguration_reqNavigation, Configuration.NAVIGATION_UNDEFINED); if (sa.getBoolean( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesConfiguration_reqFiveWayNav, false)) { cPref.reqInputFeatures |= ConfigurationInfo.INPUT_FEATURE_FIVE_WAY_NAV; } sa.recycle(); pkg.configPreferences.add(cPref);//保存到configPreference数组 XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); } else if (tagName.equals("uses-feature")) { FeatureInfo fi = new FeatureInfo(); sa = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesFeature); // Note: don't allow this value to be a reference to a resource // that may change. fi.name = sa.getNonResourceString( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesFeature_name); if (fi.name == null) { fi.reqGlEsVersion = sa.getInt( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesFeature_glEsVersion, FeatureInfo.GL_ES_VERSION_UNDEFINED); } if (sa.getBoolean( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesFeature_required, true)) { fi.flags |= FeatureInfo.FLAG_REQUIRED; } sa.recycle(); if (pkg.reqFeatures == null) { pkg.reqFeatures = new ArrayList<FeatureInfo>(); } pkg.reqFeatures.add(fi); if (fi.name == null) { ConfigurationInfo cPref = new ConfigurationInfo(); cPref.reqGlEsVersion = fi.reqGlEsVersion; pkg.configPreferences.add(cPref); } XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); } else if (tagName.equals("uses-sdk")) { if (SDK_VERSION > 0) { sa = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesSdk); int minVers = 0; String minCode = null; int targetVers = 0; String targetCode = null; TypedValue val = sa.peekValue( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesSdk_minSdkVersion); if (val != null) { if (val.type == TypedValue.TYPE_STRING && val.string != null) { targetCode = minCode = val.string.toString(); } else { // If it's not a string, it's an integer. targetVers = minVers = val.data; } } val = sa.peekValue( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestUsesSdk_targetSdkVersion); if (val != null) { if (val.type == TypedValue.TYPE_STRING && val.string != null) { targetCode = minCode = val.string.toString(); } else { // If it's not a string, it's an integer. targetVers = val.data; } } sa.recycle(); if (minCode != null) { if (!minCode.equals(SDK_CODENAME)) { if (SDK_CODENAME != null) { outError[0] = "Requires development platform " + minCode + " (current platform is " + SDK_CODENAME + ")"; } else { outError[0] = "Requires development platform " + minCode + " but this is a release platform."; } mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_OLDER_SDK; return null; } } else if (minVers > SDK_VERSION) { outError[0] = "Requires newer sdk version #" + minVers + " (current version is #" + SDK_VERSION + ")"; mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_OLDER_SDK; return null; } if (targetCode != null) { if (!targetCode.equals(SDK_CODENAME)) { if (SDK_CODENAME != null) { outError[0] = "Requires development platform " + targetCode + " (current platform is " + SDK_CODENAME + ")"; } else { outError[0] = "Requires development platform " + targetCode + " but this is a release platform."; } mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_OLDER_SDK; return null; } // If the code matches, it definitely targets this SDK. pkg.applicationInfo.targetSdkVersion = android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.CUR_DEVELOPMENT; } else { pkg.applicationInfo.targetSdkVersion = targetVers; } } XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); } else if (tagName.equals("supports-screens")) { sa = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestSupportsScreens); pkg.applicationInfo.requiresSmallestWidthDp = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestSupportsScreens_requiresSmallestWidthDp, 0); pkg.applicationInfo.compatibleWidthLimitDp = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestSupportsScreens_compatibleWidthLimitDp, 0); pkg.applicationInfo.largestWidthLimitDp = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestSupportsScreens_largestWidthLimitDp, 0); // This is a trick to get a boolean and still able to detect // if a value was actually set. supportsSmallScreens = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestSupportsScreens_smallScreens, supportsSmallScreens); supportsNormalScreens = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestSupportsScreens_normalScreens, supportsNormalScreens); supportsLargeScreens = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestSupportsScreens_largeScreens, supportsLargeScreens); supportsXLargeScreens = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestSupportsScreens_xlargeScreens, supportsXLargeScreens); resizeable = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestSupportsScreens_resizeable, resizeable); anyDensity = sa.getInteger( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestSupportsScreens_anyDensity, anyDensity); sa.recycle(); XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); } else if (tagName.equals("protected-broadcast")) { sa = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestProtectedBroadcast); // Note: don't allow this value to be a reference to a resource // that may change. String name = sa.getNonResourceString( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestProtectedBroadcast_name); sa.recycle(); if (name != null && (flags&PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) != 0) { if (pkg.protectedBroadcasts == null) { pkg.protectedBroadcasts = new ArrayList<String>(); } if (!pkg.protectedBroadcasts.contains(name)) { pkg.protectedBroadcasts.add(name.intern()); } } XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); } else if (tagName.equals("instrumentation")) { if (parseInstrumentation(pkg, res, parser, attrs, outError) == null) { return null; } } else if (tagName.equals("original-package")) { sa = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestOriginalPackage); String orig =sa.getNonConfigurationString( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestOriginalPackage_name, 0); if (!pkg.packageName.equals(orig)) { if (pkg.mOriginalPackages == null) { pkg.mOriginalPackages = new ArrayList<String>(); pkg.mRealPackage = pkg.packageName; } pkg.mOriginalPackages.add(orig); } sa.recycle(); XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); } else if (tagName.equals("adopt-permissions")) { sa = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestOriginalPackage); String name = sa.getNonConfigurationString( com.android.internal.R.styleable.AndroidManifestOriginalPackage_name, 0); sa.recycle(); if (name != null) { if (pkg.mAdoptPermissions == null) { pkg.mAdoptPermissions = new ArrayList<String>(); } pkg.mAdoptPermissions.add(name); } XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); } else if (tagName.equals("uses-gl-texture")) { // Just skip this tag XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } else if (tagName.equals("compatible-screens")) { // Just skip this tag XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } else if (tagName.equals("eat-comment")) { // Just skip this tag XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } else if (RIGID_PARSER) { outError[0] = "Bad element under <manifest>: " + parser.getName(); mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED; return null; } else { Slog.w(TAG, "Unknown element under <manifest>: " + parser.getName() + " at " + mArchiveSourcePath + " " + parser.getPositionDescription()); XmlUtils.skipCurrentTag(parser); continue; } } if (!foundApp && pkg.instrumentation.size() == 0) { outError[0] = "<manifest> does not contain an <application> or <instrumentation>"; mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_EMPTY; } final int NP = PackageParser.NEW_PERMISSIONS.length; StringBuilder implicitPerms = null; for (int ip=0; ip<NP; ip++) { final PackageParser.NewPermissionInfo npi = PackageParser.NEW_PERMISSIONS[ip]; if (pkg.applicationInfo.targetSdkVersion >= npi.sdkVersion) { break; } if (!pkg.requestedPermissions.contains(npi.name)) { if (implicitPerms == null) { implicitPerms = new StringBuilder(128); implicitPerms.append(pkg.packageName); implicitPerms.append(": compat added "); } else { implicitPerms.append(' '); } implicitPerms.append(npi.name); pkg.requestedPermissions.add(npi.name); } } if (implicitPerms != null) { Slog.i(TAG, implicitPerms.toString()); } if (supportsSmallScreens < 0 || (supportsSmallScreens > 0 && pkg.applicationInfo.targetSdkVersion >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.DONUT)) { pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SUPPORTS_SMALL_SCREENS; } if (supportsNormalScreens != 0) { pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SUPPORTS_NORMAL_SCREENS; } if (supportsLargeScreens < 0 || (supportsLargeScreens > 0 && pkg.applicationInfo.targetSdkVersion >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.DONUT)) { pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SUPPORTS_LARGE_SCREENS; } if (supportsXLargeScreens < 0 || (supportsXLargeScreens > 0 && pkg.applicationInfo.targetSdkVersion >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.GINGERBREAD)) { pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SUPPORTS_XLARGE_SCREENS; } if (resizeable < 0 || (resizeable > 0 && pkg.applicationInfo.targetSdkVersion >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.DONUT)) { pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_RESIZEABLE_FOR_SCREENS; } if (anyDensity < 0 || (anyDensity > 0 && pkg.applicationInfo.targetSdkVersion >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.DONUT)) { pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SUPPORTS_SCREEN_DENSITIES; } return pkg; }
上面介绍了PackageParser类对APK的解析流程,即对AndroidManifest.xml文件的解析流程。
现在来看一下PackageParser类内部的重要信息:

* 这些内部类主要是用来保存对应的信息。解析AndroidManifest.xml文件得到的信息由Package类保存。四大组件的信息也由对应的类保存。因为一个APK可声明多个组件,所以activities和services等都可以声明为ArrayList。
* 各种组件类还需要创造出XXIntentInfo类(最终继承自IntentFilter类)而不是直接使用XXInfo类,主要原因是为了支持Intent匹配查询。该类会判断自己是否满足某Intent中的Action等的要求,若满足,则返回对应的ActivityInfo。
* PackageLite仅用来存储Package的一些简单信息。在安装Package时,会用到该类。
4.再会scanPackageLI(函数重载,不是之前遇到的那个函数)
当PackageParse扫描完一个APK后,此时系统已经根据该APK中的AndroidManifest.xml创建了一个完整的Package对象,下一步就是将该Package对象加入到系统中。此时调用的函数就是另一个scanPackageLI,代码如下:
 PackageParser.Package::scanPackageLI
PackageParser.Package::scanPackageLI
private PackageParser.Package scanPackageLI(PackageParser.Package pkg, int parseFlags, int scanMode, long currentTime) { File scanFile = new File(pkg.mScanPath); ...... mScanningPath = scanFile; //设置Package对象中的applicationInfo的flags标签,用于标示该Package为系统Package。 if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) != 0) { pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM; } //单独判断包名是否为”android”,很重要!!! if (pkg.packageName.equals("android")) { synchronized (mPackages) { if (mAndroidApplication != null) { Slog.w(TAG, ...... // mPlatformPackage成员用于保存包名为”android”的Package信息。 mPlatformPackage = pkg; pkg.mVersionCode = mSdkVersion; // mAndroidApplication保存此Package中的ApplicationInfo。 mAndroidApplication = pkg.applicationInfo; // mResolveActivity指向表示ChooseActivity信息的ActivityInfo。 mResolveActivity.applicationInfo = mAndroidApplication; mResolveActivity.name = ResolverActivity.class.getName(); mResolveActivity.packageName = mAndroidApplication.packageName; mResolveActivity.processName = mAndroidApplication.processName; mResolveActivity.launchMode = ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_MULTIPLE; mResolveActivity.flags = ActivityInfo.FLAG_EXCLUDE_FROM_RECENTS; mResolveActivity.theme = com.android.internal.R.style.Theme_Holo_Dialog_Alert; mResolveActivity.exported = true; mResolveActivity.enabled = true; // mResolveInfo的ActivityInfo成员指向mResolveActivity。它用于存储系统解析Intent(经IntentFilter过滤)后得到的结果信息。比如满足某个Intent的Activity信息 mResolveInfo.activityInfo = mResolveActivity; mResolveInfo.priority = 0; mResolveInfo.preferredOrder = 0; mResolveInfo.match = 0; mResolveComponentName = new ComponentName( mAndroidApplication.packageName, mResolveActivity.name); } }
这里先分析下上述if (pkg.packageName.equals("android")) 这个判断条件,即单独判断PackageName为”android”的Package。与该Package对应的是framework-res.apk。
实际上,framework-res.apk还包含几个常用的Activity。
*ChooserActivity:当多个Activity符合某个Intent时,系统会弹出该Activity,由用户选择。
*RingtonePickerActivity:铃声选择Activity。
*ShutdownActivity:关机前弹出的选择对话框。
此处保存这些信息,主要是为了提高运行过程中的效率。
ps:从PKMS中查询满足某个Intent的Activity时,返回的就是ResolveInfo,再根据ResolveInfo的信息得到具体的Activity。
继续分析scanPackageLI函数。
 scanPackageLI
scanPackageLI
//mPackage用于保存系统内的所有Package,以packageName为key if (mPackages.containsKey(pkg.packageName) || mSharedLibraries.containsKey(pkg.packageName)) { Slog.w(TAG, "Application package " + pkg.packageName + " already installed. Skipping duplicate."); mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_DUPLICATE_PACKAGE; return null; } // Initialize package source and resource directories File destCodeFile = new File(pkg.applicationInfo.sourceDir); File destResourceFile = new File(pkg.applicationInfo.publicSourceDir); SharedUserSetting suid = null; PackageSetting pkgSetting = null; if (!isSystemApp(pkg)) { // Only system apps can use these features. pkg.mOriginalPackages = null; pkg.mRealPackage = null; pkg.mAdoptPermissions = null; } // writer synchronized (mPackages) { /*此处代码很长,概括其工作内容如下: 1.如果该Package声明了useslibraries,那么系统要判断library是否在mShareLibraries中 2.如果package声明了SharedUser,则需要处理SharedUserSettings相关内容,由Settings的getSharedUserLPw函数处理 3.处理pkgSetting,通过调用Settings的getPackageLPw函数完成 4.调用verifySignaturesLP函数,检查该Package的signature */ if (pkg.usesLibraries != null || pkg.usesOptionalLibraries != null) { if (mTmpSharedLibraries == null || mTmpSharedLibraries.length < mSharedLibraries.size()) { mTmpSharedLibraries = new String[mSharedLibraries.size()]; } int num = 0; int N = pkg.usesLibraries != null ? pkg.usesLibraries.size() : 0; for (int i=0; i<N; i++) { final String file = mSharedLibraries.get(pkg.usesLibraries.get(i)); if (file == null) { Slog.e(TAG, "Package " + pkg.packageName + " requires unavailable shared library " + pkg.usesLibraries.get(i) + "; failing!"); mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_MISSING_SHARED_LIBRARY; return null; } mTmpSharedLibraries[num] = file; num++; } N = pkg.usesOptionalLibraries != null ? pkg.usesOptionalLibraries.size() : 0; for (int i=0; i<N; i++) { final String file = mSharedLibraries.get(pkg.usesOptionalLibraries.get(i)); if (file == null) { Slog.w(TAG, "Package " + pkg.packageName + " desires unavailable shared library " + pkg.usesOptionalLibraries.get(i) + "; ignoring!"); } else { mTmpSharedLibraries[num] = file; num++; } } if (num > 0) { pkg.usesLibraryFiles = new String[num]; System.arraycopy(mTmpSharedLibraries, 0, pkg.usesLibraryFiles, 0, num); } } if (pkg.mSharedUserId != null) { suid = mSettings.getSharedUserLPw(pkg.mSharedUserId, pkg.applicationInfo.flags, true); if (suid == null) { Slog.w(TAG, "Creating application package " + pkg.packageName + " for shared user failed"); mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE; return null; } if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) { if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) Log.d(TAG, "Shared UserID " + pkg.mSharedUserId + " (uid=" + suid.userId + "): packages=" + suid.packages); } } // Check if we are renaming from an original package name. PackageSetting origPackage = null; String realName = null; if (pkg.mOriginalPackages != null) { // This package may need to be renamed to a previously // installed name. Let's check on that... final String renamed = mSettings.mRenamedPackages.get(pkg.mRealPackage); if (pkg.mOriginalPackages.contains(renamed)) { // This package had originally been installed as the // original name, and we have already taken care of // transitioning to the new one. Just update the new // one to continue using the old name. realName = pkg.mRealPackage; if (!pkg.packageName.equals(renamed)) { // Callers into this function may have already taken // care of renaming the package; only do it here if // it is not already done. pkg.setPackageName(renamed); } } else { for (int i=pkg.mOriginalPackages.size()-1; i>=0; i--) { if ((origPackage = mSettings.peekPackageLPr( pkg.mOriginalPackages.get(i))) != null) { // We do have the package already installed under its // original name... should we use it? if (!verifyPackageUpdateLPr(origPackage, pkg)) { // New package is not compatible with original. origPackage = null; continue; } else if (origPackage.sharedUser != null) { // Make sure uid is compatible between packages. if (!origPackage.sharedUser.name.equals(pkg.mSharedUserId)) { Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to migrate data from " + origPackage.name + " to " + pkg.packageName + ": old uid " + origPackage.sharedUser.name + " differs from " + pkg.mSharedUserId); origPackage = null; continue; } } else { if (DEBUG_UPGRADE) Log.v(TAG, "Renaming new package " + pkg.packageName + " to old name " + origPackage.name); } break; } } } } if (mTransferedPackages.contains(pkg.packageName)) { Slog.w(TAG, "Package " + pkg.packageName + " was transferred to another, but its .apk remains"); } // Just create the setting, don't add it yet. For already existing packages // the PkgSetting exists already and doesn't have to be created. pkgSetting = mSettings.getPackageLPw(pkg, origPackage, realName, suid, destCodeFile, destResourceFile, pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir, pkg.applicationInfo.flags, true, false); if (pkgSetting == null) { Slog.w(TAG, "Creating application package " + pkg.packageName + " failed"); mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE; return null; } if (pkgSetting.origPackage != null) { // If we are first transitioning from an original package, // fix up the new package's name now. We need to do this after // looking up the package under its new name, so getPackageLP // can take care of fiddling things correctly. pkg.setPackageName(origPackage.name); // File a report about this. String msg = "New package " + pkgSetting.realName + " renamed to replace old package " + pkgSetting.name; reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg); // Make a note of it. mTransferedPackages.add(origPackage.name); // No longer need to retain this. pkgSetting.origPackage = null; } if (realName != null) { // Make a note of it. mTransferedPackages.add(pkg.packageName); } if (mSettings.mDisabledSysPackages.get(pkg.packageName) != null) { pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_UPDATED_SYSTEM_APP; } pkg.applicationInfo.uid = pkgSetting.userId; pkg.mExtras = pkgSetting; if (!verifySignaturesLP(pkgSetting, pkg)) { if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) == 0) { return null; } // The signature has changed, but this package is in the system // image... let's recover! pkgSetting.signatures.mSignatures = pkg.mSignatures; // However... if this package is part of a shared user, but it // doesn't match the signature of the shared user, let's fail. // What this means is that you can't change the signatures // associated with an overall shared user, which doesn't seem all // that unreasonable. if (pkgSetting.sharedUser != null) { if (compareSignatures(pkgSetting.sharedUser.signatures.mSignatures, pkg.mSignatures) != PackageManager.SIGNATURE_MATCH) { Log.w(TAG, "Signature mismatch for shared user : " + pkgSetting.sharedUser); mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_INCONSISTENT_CERTIFICATES; return null; } } // File a report about this. String msg = "System package " + pkg.packageName + " signature changed; retaining data."; reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg); } // Verify that this new package doesn't have any content providers // that conflict with existing packages. Only do this if the // package isn't already installed, since we don't want to break // things that are installed. if ((scanMode&SCAN_NEW_INSTALL) != 0) { final int N = pkg.providers.size(); int i; for (i=0; i<N; i++) { PackageParser.Provider p = pkg.providers.get(i); if (p.info.authority != null) { String names[] = p.info.authority.split(";"); for (int j = 0; j < names.length; j++) { if (mProviders.containsKey(names[j])) { PackageParser.Provider other = mProviders.get(names[j]); Slog.w(TAG, "Can't install because provider name " + names[j] + " (in package " + pkg.applicationInfo.packageName + ") is already used by " + ((other != null && other.getComponentName() != null) ? other.getComponentName().getPackageName() : "?")); mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_CONFLICTING_PROVIDER; return null; } } } } } if (pkg.mAdoptPermissions != null) { // This package wants to adopt ownership of permissions from // another package. for (int i = pkg.mAdoptPermissions.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { final String origName = pkg.mAdoptPermissions.get(i); final PackageSetting orig = mSettings.peekPackageLPr(origName); if (orig != null) { if (verifyPackageUpdateLPr(orig, pkg)) { Slog.i(TAG, "Adopting permissions from " + origName + " to " + pkg.packageName); mSettings.transferPermissionsLPw(origName, pkg.packageName); } } } } } final String pkgName = pkg.packageName; final long scanFileTime = scanFile.lastModified(); final boolean forceDex = (scanMode&SCAN_FORCE_DEX) != 0; //确定运行该package的进程的进程名,一般用packageName作为进程名 pkg.applicationInfo.processName = fixProcessName( pkg.applicationInfo.packageName, pkg.applicationInfo.processName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid); File dataPath; if (mPlatformPackage == pkg) { // The system package is special. dataPath = new File (Environment.getDataDirectory(), "system"); pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir = dataPath.getPath(); } else { // 返回该package的目录,一般是/data/data/packageName/ dataPath = getDataPathForPackage(pkg.packageName, 0); boolean uidError = false; if (dataPath.exists()) { //如果该目录已存在,则要处理uid的问题 mOutPermissions[1] = 0; FileUtils.getPermissions(dataPath.getPath(), mOutPermissions); // If we have mismatched owners for the data path, we have a problem. if (mOutPermissions[1] != pkg.applicationInfo.uid) { boolean recovered = false; if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) != 0) { // If this is a system app, we can at least delete its // current data so the application will still work. int ret = mInstaller.remove(pkgName, 0); if (ret >= 0) { // TODO: Kill the processes first // Remove the data directories for all users mUserManager.removePackageForAllUsers(pkgName); // Old data gone! String msg = "System package " + pkg.packageName + " has changed from uid: " + mOutPermissions[1] + " to " + pkg.applicationInfo.uid + "; old data erased"; reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg); recovered = true; // And now re-install the app. ret = mInstaller.install(pkgName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid, pkg.applicationInfo.uid); if (ret == -1) { // Ack should not happen! msg = "System package " + pkg.packageName + " could not have data directory re-created after delete."; reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg); mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE; return null; } // Create data directories for all users mUserManager.installPackageForAllUsers(pkgName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid); } if (!recovered) { mHasSystemUidErrors = true; } } if (!recovered) { pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir = "/mismatched_uid/settings_" + pkg.applicationInfo.uid + "/fs_" + mOutPermissions[1]; pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir = pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir; String msg = "Package " + pkg.packageName + " has mismatched uid: " + mOutPermissions[1] + " on disk, " + pkg.applicationInfo.uid + " in settings"; // writer synchronized (mPackages) { mSettings.mReadMessages.append(msg); mSettings.mReadMessages.append('\n'); uidError = true; if (!pkgSetting.uidError) { reportSettingsProblem(Log.ERROR, msg); } } } } pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir = dataPath.getPath(); } else { //向installd发送install命令,实际上就是在/data/data目录下建立packageName目录。 if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) { if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) Log.v(TAG, "Want this data dir: " + dataPath); } //invoke installer to do the actual installation int ret = mInstaller.install(pkgName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid, pkg.applicationInfo.uid); if (ret < 0) { // Error from installer mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE; return null; } // 为系统所有user安装此程序 mUserManager.installPackageForAllUsers(pkgName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid); if (dataPath.exists()) { pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir = dataPath.getPath(); } else { Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to create data directory: " + dataPath); pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir = null; } } /* * Set the data dir to the default "/data/data/<package name>/lib" * if we got here without anyone telling us different (e.g., apps * stored on SD card have their native libraries stored in the ASEC * container with the APK). * * This happens during an upgrade from a package settings file that * doesn't have a native library path attribute at all. */ if (pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir == null && pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir != null) { //为该Package确定native library所在目录,一般是/data/data/packageName/lib if (pkgSetting.nativeLibraryPathString == null) { final String nativeLibraryPath = new File(dataPath, LIB_DIR_NAME).getPath(); pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir = nativeLibraryPath; pkgSetting.nativeLibraryPathString = nativeLibraryPath; } else { pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir = pkgSetting.nativeLibraryPathString; } } pkgSetting.uidError = uidError; } String path = scanFile.getPath(); /* Note: We don't want to unpack the native binaries for * system applications, unless they have been updated * (the binaries are already under /system/lib). * Also, don't unpack libs for apps on the external card * since they should have their libraries in the ASEC * container already. * * In other words, we're going to unpack the binaries * only for non-system apps and system app upgrades. */ //如果该APK包含了native动态库,则需要将它们从APK文件中解压并复制到对应目录中 if (pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir != null) { try { final File nativeLibraryDir = new File(pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir); final String dataPathString = dataPath.getCanonicalPath(); //从Android 2.3开始,系统package的native库统一放在/system/lib下。所以系统不会提取系统Package目录下的APK包中的native库 if (isSystemApp(pkg) && !isUpdatedSystemApp(pkg)) { /* * Upgrading from a previous version of the OS sometimes * leaves native libraries in the /data/data/<app>/lib * directory for system apps even when they shouldn't be. * Recent changes in the JNI library search path * necessitates we remove those to match previous behavior. */ if (NativeLibraryHelper.removeNativeBinariesFromDirLI(nativeLibraryDir)) { Log.i(TAG, "removed obsolete native libraries for system package " + path); } } else if (nativeLibraryDir.getParentFile().getCanonicalPath() .equals(dataPathString)) { /* * Make sure the native library dir isn't a symlink to * something. If it is, ask installd to remove it and create * a directory so we can copy to it afterwards. */ boolean isSymLink; try { isSymLink = S_ISLNK(Libcore.os.lstat(nativeLibraryDir.getPath()).st_mode); } catch (ErrnoException e) { // This shouldn't happen, but we'll fail-safe. isSymLink = true; } //判断是否为链接,如果是,需要删除该链接 if (isSymLink) { mInstaller.unlinkNativeLibraryDirectory(dataPathString); } /* * If this is an internal application or our * nativeLibraryPath points to our data directory, unpack * the libraries if necessary. */ //在lib下建立和CPU类型对应的目录,例如AMR平台的是arm/,MIPS平台的是mips/ NativeLibraryHelper.copyNativeBinariesIfNeededLI(scanFile, nativeLibraryDir); } else { Slog.i(TAG, "Linking native library dir for " + path); mInstaller.linkNativeLibraryDirectory(dataPathString, pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir); } } catch (IOException ioe) { Log.e(TAG, "Unable to get canonical file " + ioe.toString()); } } pkg.mScanPath = path; if ((scanMode&SCAN_NO_DEX) == 0) { //对该APK做dex优化 if (performDexOptLI(pkg, forceDex, (scanMode&SCAN_DEFER_DEX) != 0) == DEX_OPT_FAILED) { mLastScanError = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_DEXOPT; return null; } } if (mFactoryTest && pkg.requestedPermissions.contains( android.Manifest.permission.FACTORY_TEST)) { pkg.applicationInfo.flags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_FACTORY_TEST; } // Request the ActivityManager to kill the process(only for existing packages) // so that we do not end up in a confused state while the user is still using the older // version of the application while the new one gets installed. //如果该APK已经存在,要先杀掉运行该APK的进程 if ((parseFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_REPLACE_EXISTING) != 0) { killApplication(pkg.applicationInfo.packageName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid); } //在此之前,四大组件的信息都属于Package的私有财产,现在需要把它们登记注册到PKMS内部的财产管理对象中。这样PKMS就可对外提供统一的组件信息,而不必拘泥于具体的Package synchronized (mPackages) { // We don't expect installation to fail beyond this point, if ((scanMode&SCAN_MONITOR) != 0) { mAppDirs.put(pkg.mPath, pkg); } // Add the new setting to mSettings mSettings.insertPackageSettingLPw(pkgSetting, pkg); // Add the new setting to mPackages mPackages.put(pkg.applicationInfo.packageName, pkg); // Make sure we don't accidentally delete its data. mSettings.mPackagesToBeCleaned.remove(pkgName); // Take care of first install / last update times. if (currentTime != 0) { if (pkgSetting.firstInstallTime == 0) { pkgSetting.firstInstallTime = pkgSetting.lastUpdateTime = currentTime; } else if ((scanMode&SCAN_UPDATE_TIME) != 0) { pkgSetting.lastUpdateTime = currentTime; } } else if (pkgSetting.firstInstallTime == 0) { // We need *something*. Take time time stamp of the file. pkgSetting.firstInstallTime = pkgSetting.lastUpdateTime = scanFileTime; } else if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) != 0) { if (scanFileTime != pkgSetting.timeStamp) { // A package on the system image has changed; consider this // to be an update. pkgSetting.lastUpdateTime = scanFileTime; } } //处理该Package中的provider信息 int N = pkg.providers.size(); StringBuilder r = null; int i; for (i=0; i<N; i++) { PackageParser.Provider p = pkg.providers.get(i); p.info.processName = fixProcessName(pkg.applicationInfo.processName, p.info.processName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid); // mProvidersByComponent提供基于ComponentName的Provider信息查询 mProvidersByComponent.put(new ComponentName(p.info.packageName, p.info.name), p); p.syncable = p.info.isSyncable; if (p.info.authority != null) { String names[] = p.info.authority.split(";"); p.info.authority = null; for (int j = 0; j < names.length; j++) { if (j == 1 && p.syncable) { // We only want the first authority for a provider to possibly be // syncable, so if we already added this provider using a different // authority clear the syncable flag. We copy the provider before // changing it because the mProviders object contains a reference // to a provider that we don't want to change. // Only do this for the second authority since the resulting provider // object can be the same for all future authorities for this provider. p = new PackageParser.Provider(p); p.syncable = false; } if (!mProviders.containsKey(names[j])) { mProviders.put(names[j], p); if (p.info.authority == null) { p.info.authority = names[j]; } else { p.info.authority = p.info.authority + ";" + names[j]; } if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) { if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) Log.d(TAG, "Registered content provider: " + names[j] + ", className = " + p.info.name + ", isSyncable = " + p.info.isSyncable); } } else { PackageParser.Provider other = mProviders.get(names[j]); Slog.w(TAG, "Skipping provider name " + names[j] + " (in package " + pkg.applicationInfo.packageName + "): name already used by " + ((other != null && other.getComponentName() != null) ? other.getComponentName().getPackageName() : "?")); } } } if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) { if (r == null) { r = new StringBuilder(256); } else { r.append(' '); } r.append(p.info.name); } } if (r != null) { if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) Log.d(TAG, " Providers: " + r); } //处理该Package中的service信息 N = pkg.services.size(); r = null; for (i=0; i<N; i++) { PackageParser.Service s = pkg.services.get(i); s.info.processName = fixProcessName(pkg.applicationInfo.processName, s.info.processName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid); mServices.addService(s); if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) { if (r == null) { r = new StringBuilder(256); } else { r.append(' '); } r.append(s.info.name); } } if (r != null) { if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) Log.d(TAG, " Services: " + r); } //处理该Package中的receiver信息 N = pkg.receivers.size(); r = null; for (i=0; i<N; i++) { PackageParser.Activity a = pkg.receivers.get(i); a.info.processName = fixProcessName(pkg.applicationInfo.processName, a.info.processName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid); mReceivers.addActivity(a, "receiver"); if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) { if (r == null) { r = new StringBuilder(256); } else { r.append(' '); } r.append(a.info.name); } } if (r != null) { if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) Log.d(TAG, " Receivers: " + r); } //处理该Package中的Activity信息 N = pkg.activities.size(); r = null; for (i=0; i<N; i++) { PackageParser.Activity a = pkg.activities.get(i); a.info.processName = fixProcessName(pkg.applicationInfo.processName, a.info.processName, pkg.applicationInfo.uid); mActivities.addActivity(a, "activity"); if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) { if (r == null) { r = new StringBuilder(256); } else { r.append(' '); } r.append(a.info.name); } } if (r != null) { if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) Log.d(TAG, " Activities: " + r); } N = pkg.permissionGroups.size(); r = null; for (i=0; i<N; i++) { PackageParser.PermissionGroup pg = pkg.permissionGroups.get(i); PackageParser.PermissionGroup cur = mPermissionGroups.get(pg.info.name); if (cur == null) { mPermissionGroups.put(pg.info.name, pg); if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) { if (r == null) { r = new StringBuilder(256); } else { r.append(' '); } r.append(pg.info.name); } } else { Slog.w(TAG, "Permission group " + pg.info.name + " from package " + pg.info.packageName + " ignored: original from " + cur.info.packageName); if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) { if (r == null) { r = new StringBuilder(256); } else { r.append(' '); } r.append("DUP:"); r.append(pg.info.name); } } } if (r != null) { if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) Log.d(TAG, " Permission Groups: " + r); } N = pkg.permissions.size(); r = null; for (i=0; i<N; i++) { PackageParser.Permission p = pkg.permissions.get(i); HashMap<String, BasePermission> permissionMap = p.tree ? mSettings.mPermissionTrees : mSettings.mPermissions; p.group = mPermissionGroups.get(p.info.group); if (p.info.group == null || p.group != null) { BasePermission bp = permissionMap.get(p.info.name); if (bp == null) { bp = new BasePermission(p.info.name, p.info.packageName, BasePermission.TYPE_NORMAL); permissionMap.put(p.info.name, bp); } if (bp.perm == null) { if (bp.sourcePackage == null || bp.sourcePackage.equals(p.info.packageName)) { BasePermission tree = findPermissionTreeLP(p.info.name); if (tree == null || tree.sourcePackage.equals(p.info.packageName)) { bp.packageSetting = pkgSetting; bp.perm = p; bp.uid = pkg.applicationInfo.uid; if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) { if (r == null) { r = new StringBuilder(256); } else { r.append(' '); } r.append(p.info.name); } } else { Slog.w(TAG, "Permission " + p.info.name + " from package " + p.info.packageName + " ignored: base tree " + tree.name + " is from package " + tree.sourcePackage); } } else { Slog.w(TAG, "Permission " + p.info.name + " from package " + p.info.packageName + " ignored: original from " + bp.sourcePackage); } } else if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) { if (r == null) { r = new StringBuilder(256); } else { r.append(' '); } r.append("DUP:"); r.append(p.info.name); } if (bp.perm == p) { bp.protectionLevel = p.info.protectionLevel; } } else { Slog.w(TAG, "Permission " + p.info.name + " from package " + p.info.packageName + " ignored: no group " + p.group); } } if (r != null) { if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) Log.d(TAG, " Permissions: " + r); } N = pkg.instrumentation.size(); r = null; for (i=0; i<N; i++) { PackageParser.Instrumentation a = pkg.instrumentation.get(i); a.info.packageName = pkg.applicationInfo.packageName; a.info.sourceDir = pkg.applicationInfo.sourceDir; a.info.publicSourceDir = pkg.applicationInfo.publicSourceDir; a.info.dataDir = pkg.applicationInfo.dataDir; a.info.nativeLibraryDir = pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryDir; mInstrumentation.put(a.getComponentName(), a); if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_CHATTY) != 0) { if (r == null) { r = new StringBuilder(256); } else { r.append(' '); } r.append(a.info.name); } } if (r != null) { if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) Log.d(TAG, " Instrumentation: " + r); } if (pkg.protectedBroadcasts != null) { N = pkg.protectedBroadcasts.size(); for (i=0; i<N; i++) { mProtectedBroadcasts.add(pkg.protectedBroadcasts.get(i)); } } pkgSetting.setTimeStamp(scanFileTime); } //到此,Package的私有财产完成了公有化改造。 return pkg;
这个函数的代码好长好长啊...............................................终于over了~~~
5.scanDirLI函数总结
scanDirLI函数用于对指定目录下的APK文件进行扫描,该函数的工作流程如下图:

扫描完APK文件后,Package的私有财产就充公了。PKMS提供了几个重要数据结构来保存这些财产。
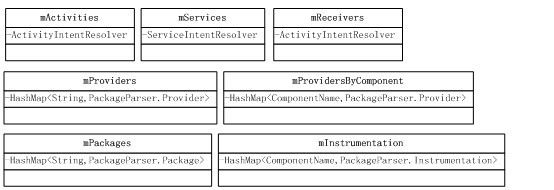
第2大部分之第3小部分:扫描非系统Package
非系统Package是指那些不存储在系统目录下的APK文件,在构造函数中的代码如下:
 PKMS::构造函数
PKMS::构造函数
// Prune any system packages that no longer exist. if (!mOnlyCore) { Iterator<PackageSetting> psit = mSettings.mPackages.values().iterator(); while (psit.hasNext()) { //删除系统package中那些不存在的APK PackageSetting ps = psit.next(); if ((ps.pkgFlags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) != 0 && !mPackages.containsKey(ps.name) && !mSettings.mDisabledSysPackages.containsKey(ps.name)) { psit.remove(); String msg = "System package " + ps.name + " no longer exists; wiping its data"; reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg); mInstaller.remove(ps.name, 0); mUserManager.removePackageForAllUsers(ps.name); } } } mAppInstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app"); //删除安装不成功的文件及临时文件 ArrayList<PackageSetting> deletePkgsList = mSettings.getListOfIncompleteInstallPackagesLPr(); //clean up list for(int i = 0; i < deletePkgsList.size(); i++) { //clean up here cleanupInstallFailedPackage(deletePkgsList.get(i)); } //delete tmp files deleteTempPackageFiles(); if (!mOnlyCore) { EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_DATA_SCAN_START, SystemClock.uptimeMillis()); //在普通模式下,还需要扫描/data/app以及/data/app_private目录 mAppInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver( mAppInstallDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, false); mAppInstallObserver.startWatching(); scanDirLI(mAppInstallDir, 0, scanMode, 0); mDrmAppInstallObserver = new AppDirObserver( mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir.getPath(), OBSERVER_EVENTS, false); mDrmAppInstallObserver.startWatching(); scanDirLI(mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir, PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK, scanMode, 0); } else { mAppInstallObserver = null; mDrmAppInstallObserver = null; }
系统中存放APK文件的目录:
*系统Package目录包括:/system/frameworks、/system/app和/vendor/app。
*非系统Package目录包括:/data/app、/data/app-private。
第2大部分的总结:PKMS在这个阶段的任务十分繁重,操作繁琐,而且还要创建比较多的对象,所以它是一个耗时耗内存的操作。作者认为没有较好的方案的原因可能是因为APK之间存在一些依赖关系,导致不好优化。其实我觉得,系统的APK不存在依赖非系统的APK的情况,所以完全可以将非系统的APK的信息保存在文件中,启动时直接读取文件,这样就可以节省一些时间。
第3大部分:构造函数分析之扫尾工作
扫尾工作是:将第2大部分收集的信息再集中整理一次,比如将这些信息保存到文件中。代码如下:
 PKMS::构造函数
PKMS::构造函数
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_SCAN_END, SystemClock.uptimeMillis()); Slog.i(TAG, "Time to scan packages: " + ((SystemClock.uptimeMillis()-startTime)/1000f) + " seconds"); // If the platform SDK has changed since the last time we booted, // we need to re-grant app permission to catch any new ones that // appear. This is really a hack, and means that apps can in some // cases get permissions that the user didn't initially explicitly // allow... it would be nice to have some better way to handle // this situation. final boolean regrantPermissions = mSettings.mInternalSdkPlatform != mSdkVersion; if (regrantPermissions) Slog.i(TAG, "Platform changed from " + mSettings.mInternalSdkPlatform + " to " + mSdkVersion + "; regranting permissions for internal storage"); mSettings.mInternalSdkPlatform = mSdkVersion; //汇总并更新和Permission相关的信息 updatePermissionsLPw(null, null, true, regrantPermissions, regrantPermissions); // 将信息写到package.xml、package.list及package-stopped.xml文件中 mSettings.writeLPr(); EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_READY, SystemClock.uptimeMillis()); // Now after opening every single application zip, make sure they // are all flushed. Not really needed, but keeps things nice and // tidy. Runtime.getRuntime().gc(); mRequiredVerifierPackage = getRequiredVerifierLPr(); } // synchronized (mPackages) } // synchronized (mInstallLock) }
对PKMS构造函数的分析就到底为止了~~~~终于结束了!!!
知识点3:APK Installation分析(分析APK的安装及相关处理流程)
1.adb install分析
adb install有多个参数,举个例子,这里分析adb install frameworktest.apk。adb是一个命令,install是它的参数。此处直接跳转到处理Install参数的代码:
[--->commandline.c::adb_commandline]
 adb_commandline
adb_commandline
int adb_commandline(int argc, char **argv) { ...... if(!strcmp(argv[0], "install")) { if (argc < 2) return usage(); //调用Install_app函数处理 return install_app(ttype, serial, argc, argv); } ...... }
[--->commandline.c::install_app]
 install_app
install_app
int install_app(transport_type transport, char* serial, int argc, char** argv) { //要安装的APK现在还在Host机器上,要先把APK复制到手机中。 //这里需要设置复制目标的目录,如果安装在内部存储中,则目标目录为/data/local/tmp; //如果安装在SD卡上,则目标目录为/sdcard/tmp。 static const char *const DATA_DEST = "/data/local/tmp/%s"; static const char *const SD_DEST = "/sdcard/tmp/%s"; const char* where = DATA_DEST; char apk_dest[PATH_MAX]; char verification_dest[PATH_MAX]; char* apk_file; char* verification_file = NULL; int file_arg = -1; int err; int i; for (i = 1; i < argc; i++) { if (*argv[i] != '-') { file_arg = i; break; } else if (!strcmp(argv[i], "-i")) { // Skip the installer package name. i++; } else if (!strcmp(argv[i], "-s")) { where = SD_DEST; //-s参数指明该APK安装到SD卡上 } } if (file_arg < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "can't find filename in arguments\n"); return 1; } else if (file_arg + 2 < argc) { fprintf(stderr, "too many files specified; only takes APK file and verifier file\n"); return 1; } apk_file = argv[file_arg]; if (file_arg != argc - 1) { verification_file = argv[file_arg + 1]; } if (check_file(apk_file) || check_file(verification_file)) { return 1; } snprintf(apk_dest, sizeof apk_dest, where, get_basename(apk_file)); if (verification_file != NULL) { snprintf(verification_dest, sizeof(verification_dest), where, get_basename(verification_file)); if (!strcmp(apk_dest, verification_dest)) { fprintf(stderr, "APK and verification file can't have the same name\n"); return 1; } } //获取目标文件的全路径,如果安装到内部存储中,则目标全路径为/data/local/tmp/安装包名,调用do_sync_push函数将此APK传送到手机的目标路径 err = do_sync_push(apk_file, apk_dest, 1 /* verify APK */); if (err) { return err; } else { argv[file_arg] = apk_dest; /* destination name, not source location */ } //(a) Android 4.0新增了一个安装过程中的Verification功能。稍后介绍。 if (verification_file != NULL) { err = do_sync_push(verification_file, verification_dest, 0 /* no verify APK */); if (err) { goto cleanup_apk; } else { argv[file_arg + 1] = verification_dest; /* destination name, not source location */ } } //(b) 执行pm命令。有意思! pm_command(transport, serial, argc, argv); if (verification_file != NULL) { delete_file(transport, serial, verification_dest); } cleanup_apk: //(c) 在手机中执行shell rm命令,删除刚才传送过去的目标APK文件。why? delete_file(transport, serial, apk_dest); return err; }
分析代码中的(a)(b)(c)三个关键点:
(a) 这个新增的Verification功能其实就是在安装时,把相关信息发送到指定的Verification程序(另外一个APK),由它对要安装的APK进行检查(Verify)。
(b) 调用pm_command进行安装,在下面分析。
(c) 为什么删除呢?因为PKMS在安装过程中会将该APK复制一份到/data/app目录下,所以/data/local/tmp目录下的对应文件就可以删除了。
2.pm分析
 pm_command
pm_command
static int pm_command(transport_type transport, char* serial, int argc, char** argv) { char buf[4096]; snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "shell:pm"); while(argc-- > 0) { char *quoted; quoted = dupAndQuote(*argv++); strncat(buf, " ", sizeof(buf)-1); strncat(buf, quoted, sizeof(buf)-1); free(quoted); } //发送”shell:pm install”参数给手机端的adbd send_shellcommand(transport, serial, buf); return 0; }
手机端的adbd在收到客户端发来的shell pm命令时会启动一个shell,然后在其中执行pm。那pm到底是什么?为什么可以在shell下执行?
实际上,pm是一个脚本。
[--->/frameworks/base/cmds/pm/pm]
 pm
pm
# Script to start "pm" on the device, which has a very rudimentary # shell. # base=/system export CLASSPATH=$base/framework/pm.jar exec app_process $base/bin com.android.commands.pm.Pm "$@"
在编译system.image时,Android.mk中会将该脚本复制到system/bin目录下。分析pm脚本克制,它就是通过app_process执行pm.jar包的main函数。
分析pm.java,app_process执行的就是它定义的main函数,它相当于java函数的入口函数。
 main() / run()
main() / run()
public static void main(String[] args) { new Pm().run(args); } //直接分析run函数 public void run(String[] args) { boolean validCommand = false; ...... mPm = IPackageManager.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager.getService("package")); ...... mArgs = args; String op = args[0]; mNextArg = 1; ...... if ("install".equals(op)) { runInstall(); return; } ...... }
接下来分析runInstall函数,代码如下:
 runInstall()
runInstall()
private void runInstall() { int installFlags = 0; String installerPackageName = null; String opt; while ((opt=nextOption()) != null) { if (opt.equals("-l")) { installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_FORWARD_LOCK; } else if (opt.equals("-r")) { installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_REPLACE_EXISTING; } else if (opt.equals("-i")) { installerPackageName = nextOptionData(); ...... } ...... final Uri apkURI; final Uri verificationURI; // Populate apkURI, must be present final String apkFilePath = nextArg(); System.err.println("\tpkg: " + apkFilePath); if (apkFilePath != null) { apkURI = Uri.fromFile(new File(apkFilePath)); } else { System.err.println("Error: no package specified"); showUsage(); return; } // Populate verificationURI, optionally present //获取Verification Package的文件位置 final String verificationFilePath = nextArg(); if (verificationFilePath != null) { System.err.println("\tver: " + verificationFilePath); verificationURI = Uri.fromFile(new File(verificationFilePath)); } else { verificationURI = null; } //创建PackageInstallObserver,用于接收PKMS的安装结果 PackageInstallObserver obs = new PackageInstallObserver(); try { //(a)调用PKMS的installPackageWithVerification完成安装 mPm.installPackageWithVerification(apkURI, obs, installFlags, installerPackageName, verificationURI, null); synchronized (obs) { while (!obs.finished) { try { obs.wait(); //等待安装结果 } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } if (obs.result == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) { System.out.println("Success"); } else { System.err.println("Failure [" + installFailureToString(obs.result) + "]");//输出安装失败的原因 } } } catch (RemoteException e) { System.err.println(e.toString()); System.err.println(PM_NOT_RUNNING_ERR); } }
pm解析参数后,最终通过PKMS的Binder客户端调用installPackageWithVerification以完成后续的安装工作。
以上写于2013-01-17 20:59
未完待续。。
先贴出来吧,有空看这块再补充,反思这半年.....
