中介者模式
概念介绍
中介者模式(Mediator):通过中介者对象封装一系列对象之间的交互,使对象之间不再相互引用降低他们之间的耦合,有时中介者对象也可以改变对象之间的交互。
创建一个中介
中介者模式,从生活的角度上来讲,和我们卖房子的中介很像,比如我有一套房想要出租,而你又想要租房子,那么我们就可以通过中介达成交易,我不考虑租给了岁,租房者也不用考虑租了谁的房子,因为有中介在所以显得很方便。
从代码的角度讲,如果有多个类或多个子系统相互交互,而且交互很繁琐,导致每个类都必须知道他需要交互的类,这样它们的耦合会显得异常厉害,如果这个时候我们需要处理某一个类,那很可能就要陷入无尽的调试中了。
那么这个时候我们就可以用到中介者模式,我们把对象全都交给中介者对象,然后通过中介者对象处理这些复杂的关系。
下面我们模拟一下房东找中介发布消息,租户找中介接收消息吧:
//中介者对象
var Mediator=function(){
//消息对象
var _msg={};
return{
//订阅方法
register:function(type,action){
//如果存在该消息
if(_msg[type]){
//存入回调函数
_msg[type].push(action);
}else{
//不存在我们建立消息容器
_msg[type]=[];
//存入新消息回调函数
_msg[type].push(action);
}
},
//发布方法
send:function(type){
//如果该消息被订阅
if(_msg[type]){
//遍历存储的消息回调函数
for (var i=0;i<_msg[type].length;i++) {
_msg[type][i]&&_msg[type][i]();
}
}
}
}
}();
我们的中介对象创建成功了下面我们来测试一下
Mediator.register('landlord',function(){
console.log('房东发布第一条消息');
});
Mediator.register('landlord',function(){
console.log('房东发布第二条消息');
})
Mediator.register('tenant',function(){
console.log('租户接收第一条消息');
});
Mediator.register('tenant',function(){
console.log('租户接收第二条消息');
})
Mediator.send('landlord');
Mediator.send('tenant');

现在我们的中介者模式成功了。
利用中介者模式实现商品购买
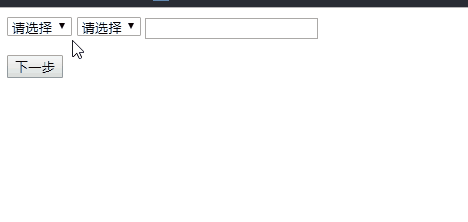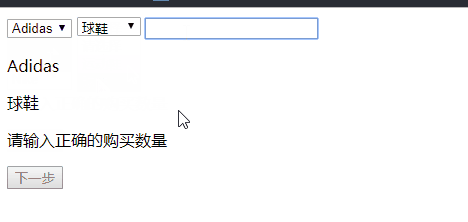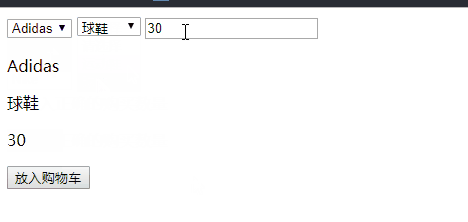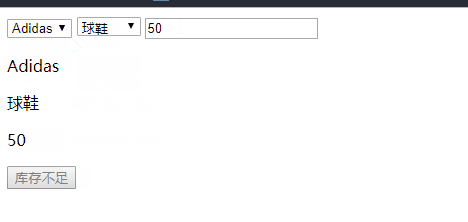
我们现在在编写一个商品购买的页面,在购买流程中,可以选择商品及样式输入购买的数量,同时页面中有两个展示区域,分别向用户展示刚刚选择的商品、种类与数量。还有一个按钮动态显示下一步的操作,我们查询商品对应的库存,如果库存数量少于这次的购买数量,按钮将被禁止且显示库存不足,反之按钮可以点击并且显示放入购买车
页面元素如下:
<select id="shoesBrands">
<option>请选择</option>
<option>Adidas</option>
<option>Nike</option>
</select>
<select id="shoesType">
<option>请选择</option>
<option>运动鞋</option>
<option>球鞋</option>
</select>
<input type="text" id="numberInput" />
<p id="shoesInfo"></p>
<p id="typeInfo"></p>
<p id="numberInfo"></p>
<button id="nextBtn">下一步</button>
接着我们开始写实现方法
//创建一个商品对象记录库存
var goods = {
"Adidas|运动鞋": 23,
"Adidas|球鞋": 35,
"Nike|运动鞋": 0,
"Nike|球鞋": 2
};
//创建中介者对象
var mediator = ( function(){
var shoesBrands = document.getElementById( "shoesBrands" ),
shoesType = document.getElementById( "shoesType" ),
numberInput = document.getElementById( "numberInput" ),
shoesInfo = document.getElementById( "shoesInfo" ),
typeInfo = document.getElementById( "typeInfo" ),
numberInfo = document.getElementById( "numberInfo" ),
nextBtn = document.getElementById( "nextBtn" );
return {
//当选项发生改变时触发下面方法
change: function( obj ){
var shoes = shoesBrands.value, //品牌
type = shoesType.value, //类型
number = numberInput.value, //数量
stock = goods[ shoes + "|" + type ]; //品牌类型下鞋子对应库存数量
if( obj === shoesBrands ){
shoesInfo.innerHTML = shoes;
}else if( obj === shoesType ){
typeInfo.innerHTML = type;
}else if( obj === numberInput ){
numberInfo.innerHTML = number;
}
if( !shoes ){
nextBtn.disabled = true;
shoesInfo.innerHTML = "请选择鞋的品牌";
return;
}
if( !type ){
nextBtn.disabled = true;
typeInfo.innerHTML = "请选择鞋的类型";
return;
}
if( !(Number.isInteger( number - 0 ) && number > 0) ){
//输入购买数量是否为正整数
nextBtn.disabled = true;
numberInfo.innerHTML = "请输入正确的购买数量";
return;
}
if(number>stock){
nextBtn.disabled = true;
nextBtn.innerHTML = "库存不足";
}else{
nextBtn.disabled = false;
nextBtn.innerHTML = "放入购物车";
}
}
}
} )();
我们调用看看
shoesBrands.onchange = function(){
mediator.change( this );
};
shoesType.onchange = function(){
mediator.change( this );
};
numberInput.onchange = function(){
mediator.change( this );
}
总结
同观察者模式一样,中介者模式的主要业务也是通过模块间或者对象间的复杂通信,来解决模块间或对象间的耦合,对于中介者对象的本质是封装多个对象的交互,并且这些交互一般都是在中介者内部实现的。
与外观模式的封装特性相比
中介者模式对多个对象交互地封装,且这些对象一般处于同一层面上,并且封装的交互在中介者内部,而外观模式的封装是为了提供更简单的医用的接口而不会添加其他功能
与观察者模式相比
虽然两种模式都是通过消息传递实现对象间或模块间的解耦。观察者模式中的订阅者是双向的,既可以是消息的发布者,也可以是消息的订阅者。而在中介者模式中,订阅者是单向的,只能是消息的订阅者, 而消息统一由中介者对象发布,所有的订阅者对象间接地被中介者管理
也谢谢大家看到这里:)如果你觉得我的分享还可以请点击推荐,分享给你的朋友让我们一起进步~
好了以上就是本次分享的全部内容,本次示例参考自JavaScript设计模式一书,让我们一点点积累一点点成长,希望对大家有所帮助。
欢迎转载,转载请注明作者,原文出处。