
依赖管理

基本套路

Dstream输入源 ---input DStream

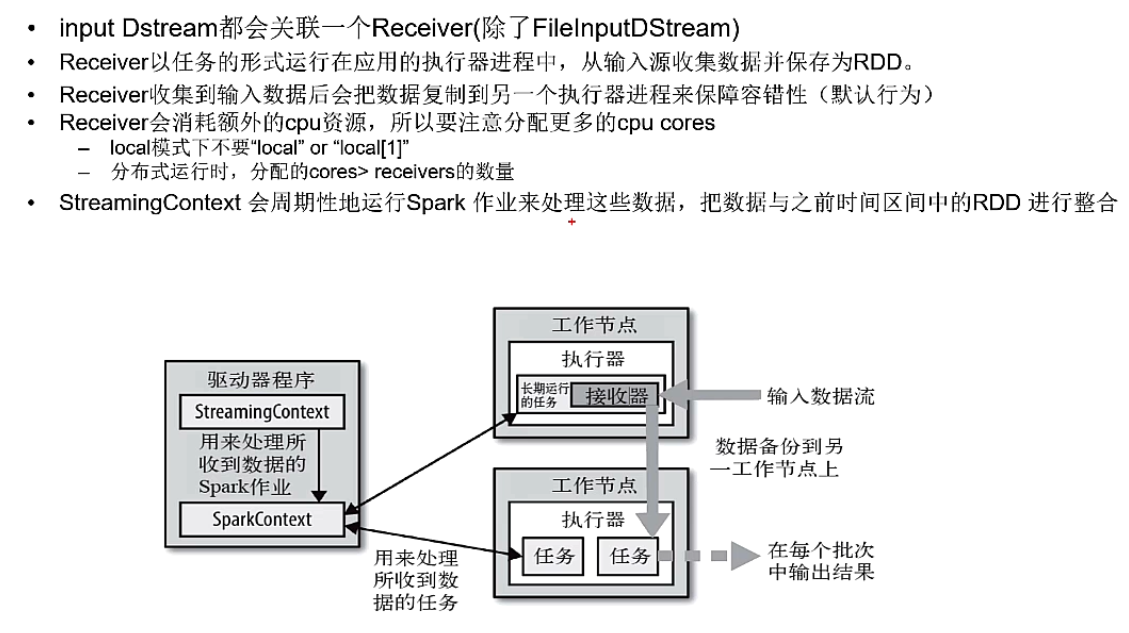
Dstream输入源--- Receiver
内置的input Dstream : Basic Source

内置的input Dstream :Advanced Sources

Dstream 输入源: multiple input DStream

Dstream 输入源: Custom Receiver

官方参考网站 http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.6.2/streaming-custom-receivers.html
scala 参考模版
class CustomReceiver(host: String, port: Int) extends Receiver[String](StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_2) with Logging { def onStart() { // Start the thread that receives data over a connection new Thread("Socket Receiver") { override def run() { receive() } }.start() } def onStop() { // There is nothing much to do as the thread calling receive() // is designed to stop by itself if isStopped() returns false } /** Create a socket connection and receive data until receiver is stopped */ private def receive() { var socket: Socket = null var userInput: String = null try { // Connect to host:port socket = new Socket(host, port) // Until stopped or connection broken continue reading val reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream(), "UTF-8")) userInput = reader.readLine() while(!isStopped && userInput != null) { store(userInput) userInput = reader.readLine() } reader.close() socket.close() // Restart in an attempt to connect again when server is active again restart("Trying to connect again") } catch { case e: java.net.ConnectException => // restart if could not connect to server restart("Error connecting to " + host + ":" + port, e) case t: Throwable => // restart if there is any other error restart("Error receiving data", t) } } }
java 参考模版
public class JavaCustomReceiver extends Receiver<String> { String host = null; int port = -1; public JavaCustomReceiver(String host_ , int port_) { super(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_2()); host = host_; port = port_; } public void onStart() { // Start the thread that receives data over a connection new Thread() { @Override public void run() { receive(); } }.start(); } public void onStop() { // There is nothing much to do as the thread calling receive() // is designed to stop by itself if isStopped() returns false } /** Create a socket connection and receive data until receiver is stopped */ private void receive() { Socket socket = null; String userInput = null; try { // connect to the server socket = new Socket(host, port); BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); // Until stopped or connection broken continue reading while (!isStopped() && (userInput = reader.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println("Received data '" + userInput + "'"); store(userInput); } reader.close(); socket.close(); // Restart in an attempt to connect again when server is active again restart("Trying to connect again"); } catch(ConnectException ce) { // restart if could not connect to server restart("Could not connect", ce); } catch(Throwable t) { // restart if there is any other error restart("Error receiving data", t); } } }
无状态的转换操作

有状态的转换操作1-updateStateByKey

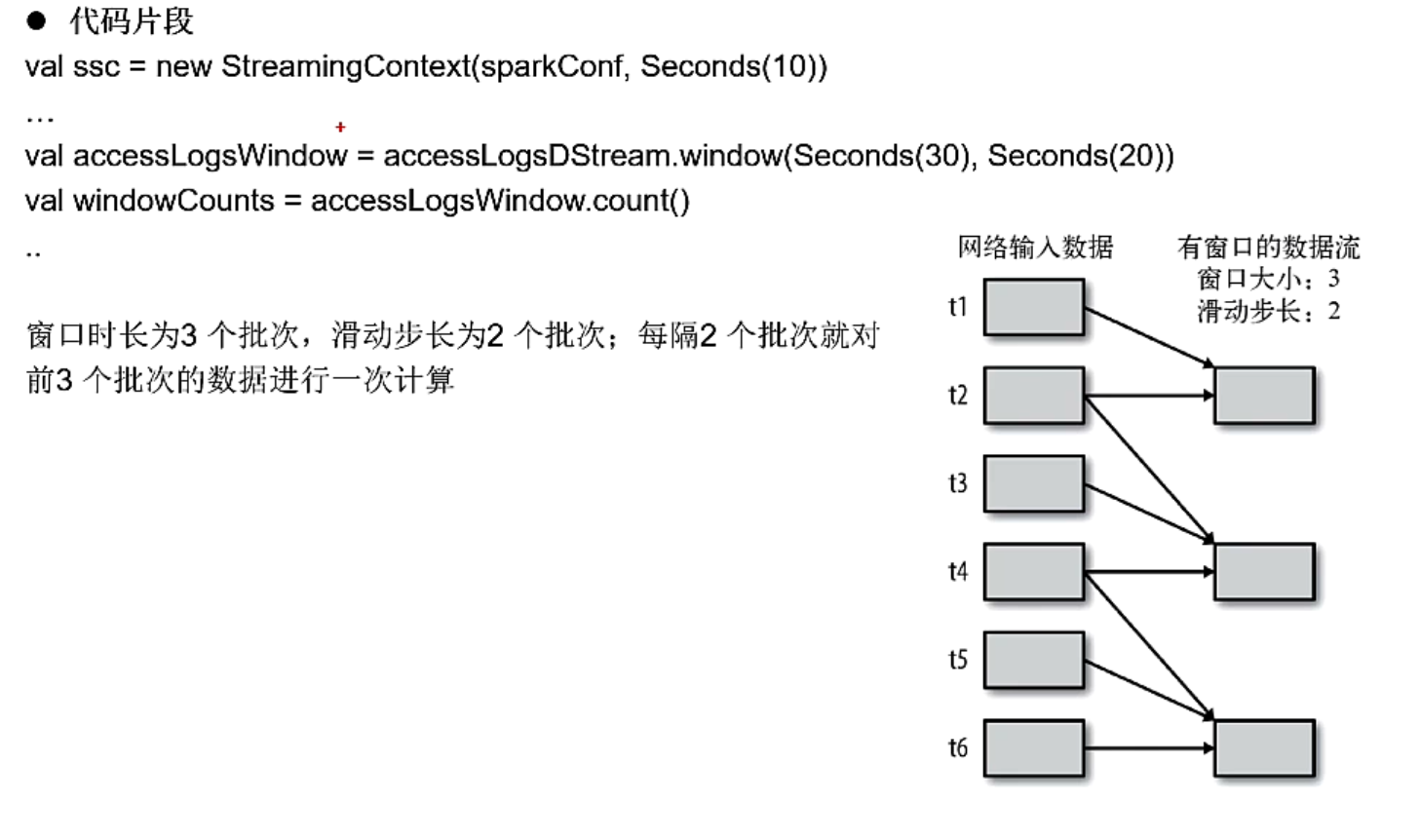
有状态的转换操作2-window

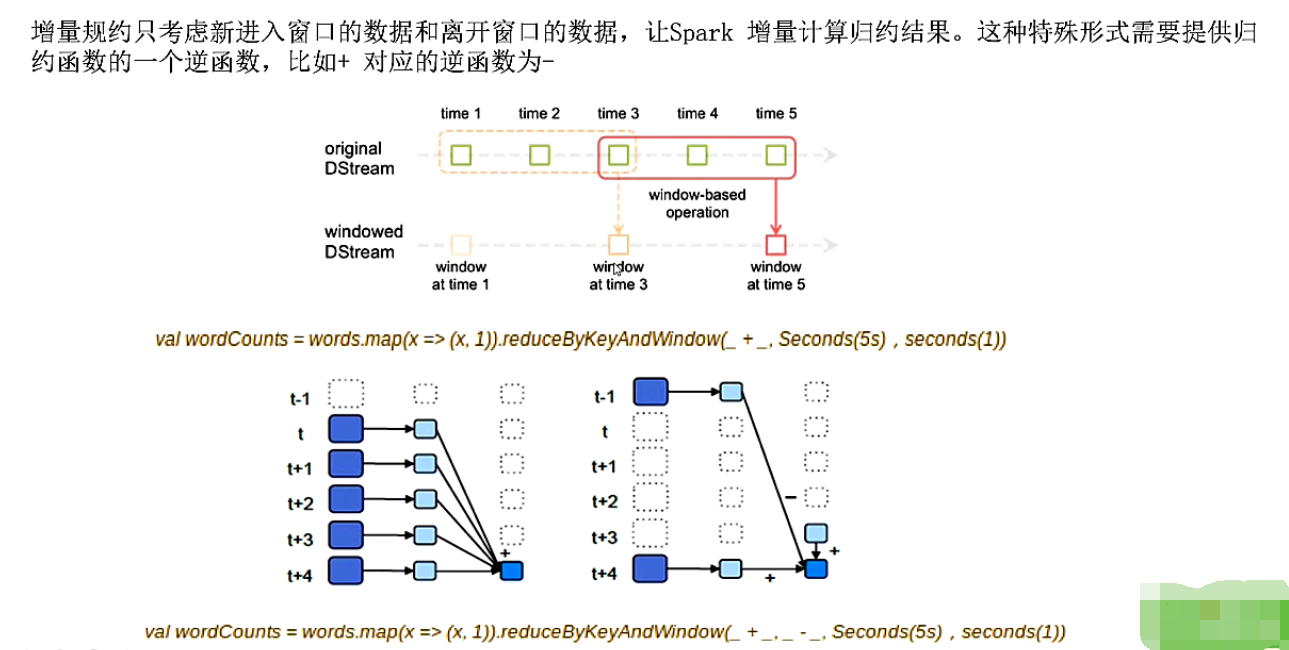
有状态的转换操作2-window普通规约与增量规约
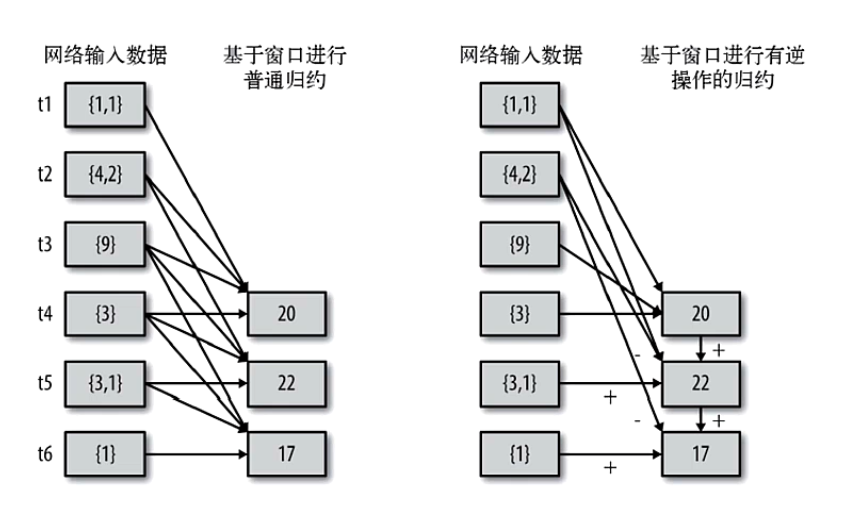
理解增量规约
输出操作
Dstream输出

持久化操作
