需求
- 一主两从,做读写分离。
- 多个从库之间实现负载均衡。
- 可手动强制部分读请求到主库上。(因为主从同步有延迟,对实时性要求高的系统,可以将部分读请求也走主库)
本次不讨论 MySQL如何配置主从同步相关问题
库表SQL
-- 主库
CREATE DATABASE `master`;
CREATE TABLE `t_order` (
`order_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`business_id` int(4) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `t_order` VALUES (1,1,112);
-- 从库1
CREATE DATABASE `slave1` ;
CREATE TABLE `t_order` (
`order_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`business_id` int(4) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ;
INSERT INTO `t_order` VALUES (2,2,112);
-- 从库2
CREATE DATABASE `slave2` ;
CREATE TABLE `t_order` (
`order_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`business_id` int(4) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `t_order` VALUES (3,3,112);
pom.xml
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.shardingjdbc/sharding-jdbc-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.shardingjdbc</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-core</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.M2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.shardingjdbc</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-namespace</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.M2</version>
</dependency>
spring配置文件
<bean id="master" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url.master}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username.master}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password.master}"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="100"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="10"/>
<property name="maxWait" value="60000"/>
<property name="minIdle" value="5"/>
</bean>
<bean id="slave1" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url.slave1}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username.slave1}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password.slave1}"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="100"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="10"/>
<property name="maxWait" value="60000"/>
<property name="minIdle" value="5"/>
</bean>
<bean id="slave2" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" init-method="init"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url.slave2}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username.slave2}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password.slave2}"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="100"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="10"/>
<property name="maxWait" value="60000"/>
<property name="minIdle" value="5"/>
</bean>
<bean id="randomStrategy" class="io.shardingjdbc.core.api.algorithm.masterslave.RandomMasterSlaveLoadBalanceAlgorithm" />
<master-slave:data-source id="shardingDataSource" master-data-source-name="master" slave-data-source-names="slave1,slave2" strategy-ref="randomStrategy" />
单测
写:
@Test
public void insert() throws Exception {
Order record = new Order();
record.setBusinessId(112);
record.setUserId(111);
record.setOrderId(12212121);
int result = orderMapper.insertSelective(record) ;
System.out.println( result > 0 ? "插入成功" : "插入失败");
}
运行结果:
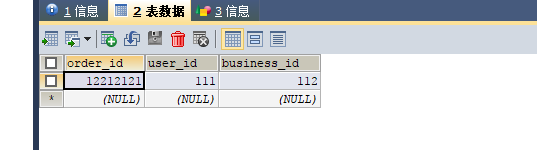
查:
slave1 只有1条数据,主键order_id = 2 ; slave2 也只有1条数据,主键order_id = 3 。所以,如果查询到的结果orderId等于1就说明读请求进入到slave1,同理,如果查询出来的orderId等于0 就说明读请求进入到slave2。
public void selectByExample3() throws Exception {
final int[] slave1 = {0};
final int[] slave2 = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
((Runnable) () -> {
OrderExample example = new OrderExample();
example.createCriteria().andBusinessIdEqualTo(112);
List<Order> orderList = orderMapper.selectByExample(example);
if (orderList.get(0).getOrderId() == 2) {
System.out.printf("读到slave1 读到的数据是{}", JSONObject.toJSONString(orderList.get(0)));
slave1[0]++;
} else if (orderList.get(0).getOrderId() == 3) {
System.out.printf("读到slave2 读到的数据是{}", JSONObject.toJSONString(orderList.get(0)));
slave2[0]++;
}
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(orderList));
}).run();
}
System.out.println("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
System.out.println("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
System.out.println("slave1读到的次数-->" + slave1[0]);
System.out.println("slave2读到的次数-->" + slave2[0]);
System.out.println("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
System.out.println("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++");
}
运行截图:

强制路由
通常做读写分离,都会遇到的一个问题就是主从同步延迟。有时,为了简单解决主从同步问题,我们会想强制部分读请求到主库上,而非从库上。
HintManager 分片键值管理器
官方文档的解释:
基于暗示(Hint)的分片键值管理器
但是对于读写分离这种形式的强制路由 , 其实官方文档说的几个方法都不适用. 我们可使用hintManager.setMasterRouteOnly() .
单测
@Test
public void HintManagerTest() {
HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance() ;
hintManager.setMasterRouteOnly();
OrderExample example = new OrderExample();
example.createCriteria().andBusinessIdEqualTo(112);
List<Order> orderList = orderMapper.selectByExample(example);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(orderList));
hintManager.close();
}