前两天被问到一个随机洗牌的问题,当时脑子里想这不很简单么,生成随机数列嘛。回来之后自己动手实现了出来,然后也测试了一番,也上网搜索了一下关于随机洗牌的算法,发现现实好像不是那么简单,有一个地方容易形成误区,所以把这些记录下来。
这个误区已经有人很专业地分析过了,如下方:http://www.matrix67.com/blog/archives/879
记得当年搞NOIp时,我犯过一个相当严重的错误:错误地把Floyd算法的i, j, k三层循环的位置顺序搞颠倒了。直到准备省选时我才突然意识到,Floyd算法应该最先枚举用于松驰操作的那个“中间变量”k,表示只经过从1到k的顶点的最短路;而我却一直习惯性地以为i, j, k应该顺次枚举。令人惊讶的是,这个错误跟了我那么久我居然从来都没有注意到过。后来,我发现有我这种经历的人不止一个。惯性思维很可能会让你接受一些明显错误的算法,并且让你用得坦坦荡荡,一辈子也发觉不了。
假使你需要把一个数组随机打乱顺序进行重排。你需要保证重排后的结果是概率均等、完全随机的。下面两种算法哪一种是正确的?其中,random(a,b)函数用于返回一个从a到b(包括a和b)的随机整数。1. for i:=1 to n do swap(a[i], a[random(1,n)]);
2. for i:=1 to n do swap(a[i], a[random(i,n)]);
如果不仔细思考的话,绝大多数人会认为第一个算法才是真正随机的,因为它的操作“更对称”,保证了概率均等。但静下心来仔细思考,你会发现第二种算法才是真正满足随机性的。为了证明这一点,只需要注意到算法的本质是“随机确定a[1]的值,然后递归地对后n-1位进行操作”,用数学归纳法即可轻易说明算法的正确性。而事实上,这段程序一共将会产生n*(n-1)*(n-2)*...*1种等可能的情况,它们正好与1至n的n!种排列一一对应。
有人会问,那第一种算法为什么就错了呢?看它的样子多么对称美观啊……且慢,我还没说第一种算法是错的哦!虽然第一种算法将产生比第二种算法更多的可能性,会导致一些重复的数列,但完全有可能每种数列重复了相同的次数,概率仍然是均等的。事实上,更有可能发生的是,这两种算法都是正确的,不过相比之下呢第一种算法显得更加对称美观一些。为此,我们需要说明,第一种算法产生的所有情况均等地分成了n!个等价的结果。显然,这个算法将会产生n^n种情况,而我们的排列一共有n!个,因此n^n必须能够被n!整除才行(否则就不能均等地分布了)。但是,n!里含有所有不超过n的质数,而n^n里却只有n的那几个质因子。这表明要想n^n能被n!整除,n的质因子中必须含有所有不超过n的质数。这个结论看上去相当荒唐,反例遍地都是,并且直觉上告诉我们对于所有大于2的n这都是不成立的。为了证明这一点,只需要注意到2是质数,并且根据Bertrand-Chebyshev定理,在n/2和n之间一定还有一个质数。这两个质数的乘积已经大于n了。搞了半天,第一种看似对称而美观的算法居然是错的!
我先写了一个测试程序
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Threading.Tasks; 6 using System.Collections; 7 using System.IO; 8 9 namespace Learning.useful.tool 10 { 11 class testWashCard 12 { 13 private ArrayList appearTimes = new ArrayList(); 14 private int cardCount; 15 public int CardCount 16 { 17 get { return cardCount; } 18 set { cardCount = value; } 19 } 20 private washCards algorithm; // 洗牌算法接口 [9/9/2013 Administrator] 21 public Learning.useful.tool.washCards Algorithm 22 { 23 get { return algorithm; } 24 set { algorithm = value; } 25 } 26 private int testTimes; 27 public int TestTimes 28 { 29 get { return testTimes; } 30 set { testTimes = value; } 31 } 32 public testWashCard( int cardsCount = 10, int testTimes = 1000 ) 33 { 34 CardCount = cardsCount; 35 TestTimes = testTimes; 36 } 37 38 public void runTest() 39 { 40 if (algorithm == null) 41 { 42 throw new Exception("algorithm haven't been set yet!"); 43 } 44 appearTimes.Clear(); 45 for (int i = 0; i < CardCount * CardCount; ++i ) 46 { 47 appearTimes.Add(0); 48 } 49 FileStream fs = new FileStream("record.txt", FileMode.Create); 50 StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(fs); 51 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 52 for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; ++i ) 53 { 54 System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1); 55 long tick = DateTime.Now.Ticks; 56 Random ran = new Random((int)(tick & 0xffffffffL) | (int)(tick >> 32)); 57 ArrayList result = algorithm.washCards(CardCount, ran); //随机洗牌测试 58 for (int cardIndex = 0; cardIndex < CardCount; ++cardIndex ) 59 { 60 int listIndex = cardIndex * CardCount + (int)result[cardIndex]; 61 appearTimes[listIndex] = (int)appearTimes[listIndex] + 1; //统计每张牌的随机位置 62 } 63 sb.Clear(); 64 for (int index = 0; index < result.Count; ++index ) 65 { 66 sb.AppendFormat("{0} ", result[index]); 67 } 68 sw.WriteLine(sb.ToString()); //把过程记录到record.txt文件中 69 } 70 sw.Flush(); 71 sw.Close(); 72 fs.Close(); 73 showResult(); 74 } 75 private void showResult() 76 { 77 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 78 for (int i = 0; i < CardCount; ++i ) 79 { 80 sb.AppendFormat("{0} ", i+1); 81 } 82 Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString()); 83 sb.Clear(); 84 double average = 0; 85 FileStream fs = new FileStream("result.txt", FileMode.Create); 86 StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(fs); 87 for (int x = 0, y = 0; x * CardCount + y < appearTimes.Count; ++x) 88 { 89 sb.AppendFormat("{0} ", appearTimes[x * CardCount + y]); 90 average += (int)appearTimes[x * CardCount + y]; 91 if (x == CardCount - 1) 92 { 93 x = -1; 94 y++; 95 Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString()); 96 sw.WriteLine(sb.ToString()); //把测试结果记录到result.txt文件中去 97 sb.Clear(); 98 } 99 } 100 sw.Flush(); 101 sw.Close(); 102 fs.Close(); 103 average /= appearTimes.Count; 104 double s = 0; 105 double deviation = 0; 106 for (int i = 0; i < appearTimes.Count; ++i) 107 { 108 s += Math.Pow(average - (int)appearTimes[i], 2); 109 double tmp = ((int)appearTimes[i] - average); 110 deviation = tmp > deviation ? tmp : deviation; 111 } 112 s /= appearTimes.Count; 113 Console.WriteLine("方差是:{0}", s); 114 Console.WriteLine("最大误差是:{0}", deviation / average); 115 } 116 } 117 }
最开始是想通过计算方差来判断测试的结果,方差是衡量离散程度的,但是用于衡量这个测试结果不太适用。后来加上了最大误差的判断,就适合多了。
再贴上我自己的错误算法
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace Learning.useful.tool 9 { 10 class MyWashCardAlgorithm : washCards 11 { 12 13 private ArrayList randomValue = new ArrayList(); 14 private ArrayList result = new ArrayList(); 15 public ArrayList washCards(int cardCount, Random ran) 16 { 17 randomValue.Clear(); 18 result.Clear(); 19 20 for (int i = 0; i < cardCount; ++i ) 21 { 22 randomValue.Add(ran.Next(0, cardCount)); // 问题就出在这里,ran的范围 23 result.Add(i); 24 } 25 sortRandomValue(); 26 return result; 27 } 28 private void sortRandomValue() 29 { 30 /// <summary> 31 /// 快速排序 32 /// </summary> 33 /// 34 quickSort(0, result.Count-1); 35 } 36 37 private void quickSort(int head, int tail) 38 { 39 if (head >= tail) 40 { 41 return; 42 } 43 int mid = (int)randomValue[head]; 44 int midIndex = (int)result[head]; 45 int p = head; 46 int q = head + 1; 47 for (; q <= tail; q++) 48 { 49 if ((int)randomValue[q] < mid) 50 { 51 randomValue[p] = randomValue[q]; 52 result[p] = result[q]; 53 p++; 54 randomValue[q] = randomValue[p]; 55 result[q] = result[p]; 56 } 57 } 58 randomValue[p] = mid; 59 result[p] = midIndex; 60 quickSort(head, p - 1); 61 quickSort(p + 1, tail); 62 } 63 } 64 }
以及正确的算法:
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections; 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 using System.Linq; 5 using System.Text; 6 using System.Threading.Tasks; 7 8 namespace Learning.useful.tool 9 { 10 class coolShellWashCardAlgorithm : washCards 11 { 12 13 private ArrayList randomValue = new ArrayList(); 14 private ArrayList result = new ArrayList(); 15 16 public ArrayList washCards(int cardCount, Random ran) 17 { 18 randomValue.Clear(); 19 result.Clear(); 20 for (int i = 0; i < cardCount; ++i ) 21 { 22 result.Add(i); 23 } 24 ShuffleArray_Fisher_Yates(result, ran); 25 return result; 26 } 27 28 private void ShuffleArray_Fisher_Yates(ArrayList arr, Random ran) 29 { 30 int i = arr.Count, j; 31 int temp; 32 33 if (i == 0) return; 34 while (--i > 0) 35 { 36 j = ran.Next(i + 1); 37 temp = (int)arr[i]; 38 arr[i] = arr[j]; 39 arr[j] = temp; 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 }
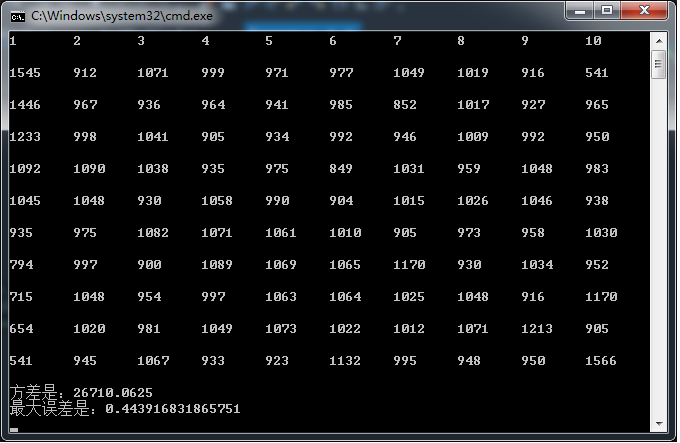

两个算法的运行结果如上图。