单例模式:
指的是在确定 "类中的属性与方法" 不变时,需要反复调用该类,产生不同的对象,会产生不同的内存地址,造成资源的浪费。
单例模式:多次实例化的结果指向同一个内存地址 ----> 无论产生多个对象,都会指向 单个 实例。
单例的优点:节省内存空间。
class Foo:
def __init__(self,x,y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
foo_obj1 =Foo(10,20)
print(foo_obj1.__dict__)
print(foo_obj1) #<__main__.Foo object at 0x00000261D305E708>
foo_obj2 =Foo(10,20)
print(foo_obj2.__dict__)
print(foo_obj2) #<__main__.Foo object at 0x00000261D30606C8>
foo_obj3 =Foo(10,20)
print(foo_obj3.__dict__)
print(foo_obj3) #<__main__.Foo object at 0x00000261D30639C8>
以上三个对象的内存地址都不一样。由此造成了内存资源的浪费
'''
单例模式:
1.通过classmethod
2.通过装饰器实现
3.通过__new__实现
4.通过导入模块时实现
5.通过元类实现。
'''
1.通过classmethod
class MySQL:
# 一个默认值,用于判断对象是否存在, 对象不存在证明值是None
# __instance是类的属性,可以由类来调用
__instance = None
#def __init__(self):
#pass
@classmethod
def singleton(cls): # 单例方法 ---》 类方法
# 判断__instance中若没有值,证明没有对象
if not cls.__instance:
# 产生一个对象并返回
obj = cls()
# None ---> obj
cls.__instance = obj
# 若__instance中有值,证明对象已经存在,则直接返回该对象
return cls.__instance
obj1 = MySQL.singleton()
obj2 = MySQL.singleton()
print(obj1)
print(obj2)
2.通过__new__:
class Singleton:
__instance = None
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if not cls.__instance:
# 造一个空对象
cls.__instance = object.__new__(cls)
return cls.__instance
obj1 = Singleton()
obj2 = Singleton()
print(obj1)
print(obj2)
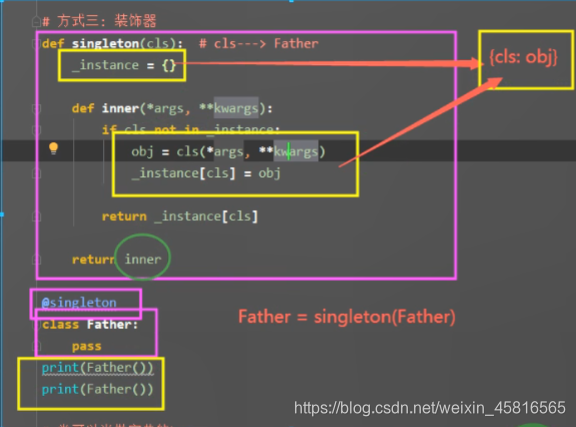
3.通过装饰器:
#无参
def singleton(cls): #cls --->Father
_instance = {} #_instance = {'cls':'obj'}
def inner(*args,**kwargs):
if cls not in _instance:
obj = cls(*args,**kwargs)
_instance[cls] = obj
return _instance[cls]
return inner
@singleton
class MySQL: #MySQL =singleton(MySQL) MYSQL=inner
pass
obj1 = MySQL() #inner()
obj2 = MySQL()
print(obj1)
print(obj2)
#有参
def singleton(cls): #func --->Father
_instance = {}
def inner(*args,**kwargs):
if cls not in _instance:
obj = cls(*args,**kwargs)
_instance[cls] = obj
return _instance[cls]
return inner
@singleton
class MySQL: #MySQL =singleton(MySQL) MYSQL=inner
def __init__(self,ip,port):
self.ip = ip
self.port = port
obj1 = MySQL('1224',3307) #inner()
obj2 = MySQL('1224',3307)
print(obj1)
print(obj2)
4.
通过导入模块:
Singleton.py
class Father:
pass
obj = Father()
单例模式.py
from Singleton import obj
print(obj)
from Singleton import obj
print(obj)
from Singleton import obj
print(obj)