1.目标在数据库的两张表中拿到以下数据,并完成状态、搜索和分页功能
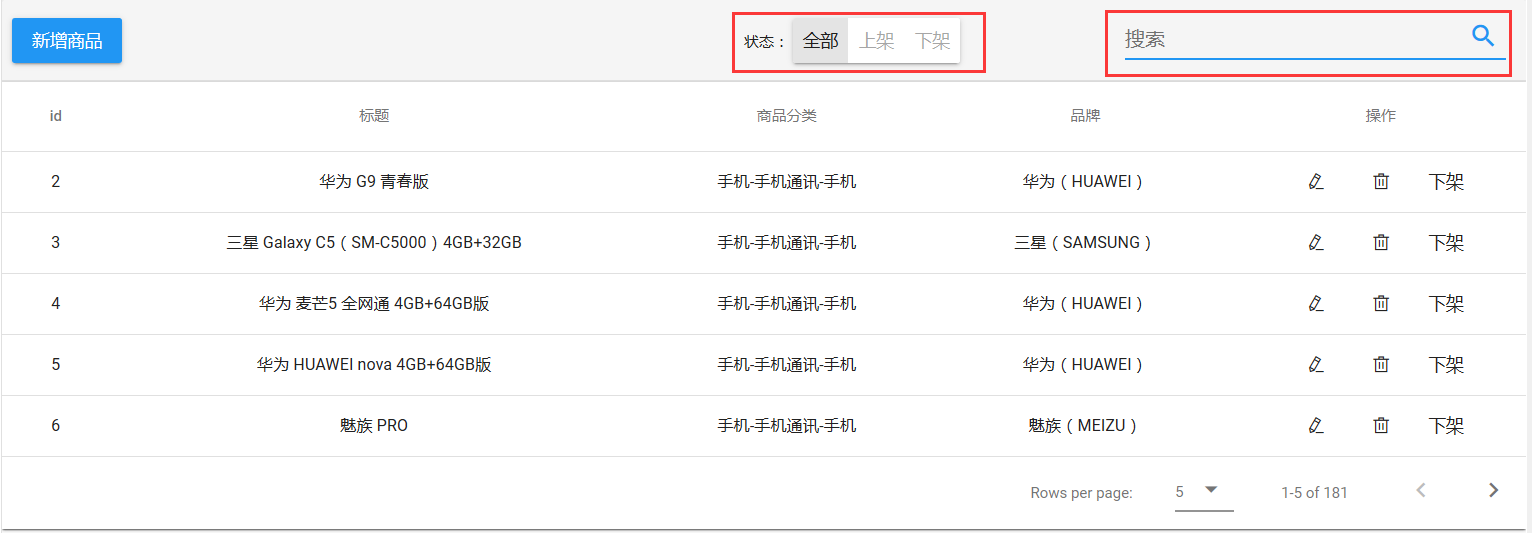
实体类Spu(页面需要的数据)
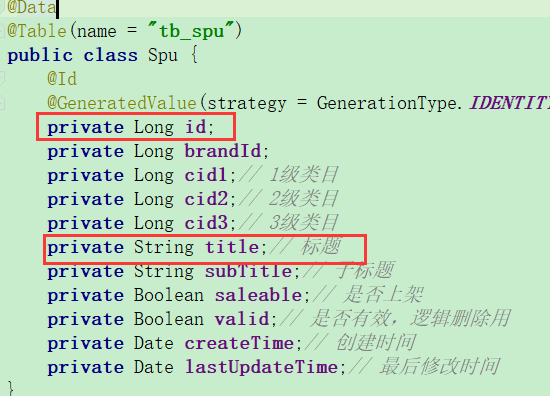
实体类Category(页面需要的数据) name:商品分类
2.分析:
返回的数据在两个实体类中,但我们不能修改实体类数据表,需要创建一个Bo实体类将需要的数据合并到一起
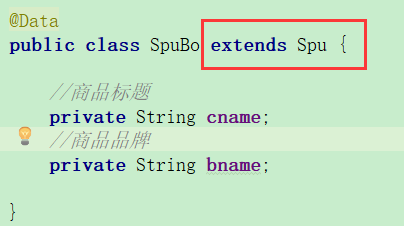
3.业务逻辑代码
@Service
public class GoodsService {
@Autowired
private SpuMapper supMapper;
@Autowired
private BrandMapper brandMapper;
@Autowired
private SpuDetailMapper spuDetailMapper;
@Autowired
private CategoryService categoryService;
/**
* 更具条件分页查询Spu
* 请求地址: http://api.leyou.com/api/item/spu/page?key=&saleable=true&page=1&rows=5
*
* @param key
* @param saleable
* @param page
* @param rows
* @return
*/
public PageResult<SpuBo> querySpuByPage(String key, Boolean saleable, Integer page, Integer rows) {
//添加查询条件
Example example = new Example(Spu.class);
Example.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(key)) {
criteria.andLike("title", "%" + key + "%");
}
//添加上下架的过滤条件
if (saleable != null) {
criteria.andEqualTo("saleable", saleable);
}
//添加分页
PageHelper.startPage(page, rows);
//执行查询,获得spu集合
List<Spu> spus = supMapper.selectByExample(example);
PageInfo<Spu> spuPageInfo = new PageInfo<>(spus);
//spu转化为SpuBo
List<SpuBo> spuBos = spus.stream().map(spu -> {
SpuBo spuBo = new SpuBo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(spu, spuBo);
Brand brand = brandMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(spu.getBrandId());
//查询品牌名称
spuBo.setBname(brand.getName());
//查询分类名称
List<String> names = categoryService.queryNameByIds(Arrays.asList(spu.getCid1(), spu.getCid2(), spu.getCid3()));
spuBo.setCname(StringUtils.join(names, "-"));
return spuBo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//返回pageResult<SpuBo>
return new PageResult<>(spuPageInfo.getTotal(),spuBos);
}
}
4.代码分析
1>通过example.createCriteria();拼接查询条件
2>spu代码分析:
BeanUtils.copyProperties(spu, spuBo);

将一个Object对象赋值给一个Object对象
//spu转化为SpuBo
List<SpuBo> spuBos = spus.stream().map(spu -> {
SpuBo spuBo = new SpuBo();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(spu, spuBo);
Brand brand = brandMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(spu.getBrandId());
//查询品牌名称
spuBo.setBname(brand.getName());
//查询分类名称
List<String> names = categoryService.queryNameByIds(Arrays.asList(spu.getCid1(), spu.getCid2(), spu.getCid3()));
spuBo.setCname(StringUtils.join(names, "-"));
return spuBo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
jdk8的特性stream().map() 将对象转换成另一个对象
List<SpuBo> spuBos = spus.stream().map(spu -> {}).collect(Collectors.toList());
循环List<Spu> spus 集合,将每一项赋值给spu,可以在{}中进行数据处理,最后分装到spuBos集合中去
3>spuBo.setCname(StringUtils.join(names, "-"));
将一个集合中的元素全部用字符串拼接,以"-"为分隔符,并且最后没有"-"号。效果a-b-c
4>selectByIdList(ids)的用法:遍历ids多次执行查询语句
需要继承:public interface CategoryMapper extends Mapper<Category>,SelectByIdListMapper<Category,Long> {
}
selectByIdList(ids):方法的作用
通俗的讲就是:遍历ids中的所有的元素,并执行select查询,返回多个结果封装到集合中
List<Category> categories = categoryMapper.selectByIdList(ids);
5>Arrays.List(value1,value2,value3...)将value封装到集合中去
List<String> names = categoryService.queryNameByIds(Arrays.asList(spu.getCid1(), spu.getCid2(), spu.getCid3()));