Partition table 三种基本类型:
ranage、hash、list partition table,另外composite partition就是对以上三种类型的组合类型.
Composite Partitioning
- Ideal for both historical data and data placement
- Provides high availability and manageability,like range partitioning
- Improves performance for parallel DML and supports partition-wise joins
- Allows more granular partition elimination
- Supports composite local indexes
- Does not support composite global indexes
Partitioned Indexes

Local Partitioned Indexes

Global NonPartitioned Indexes

Global Partitioned Indexes

oracle recommend:OLAP系统使用local partition index,OLTP系统使用Global partition index
local partition index易管理,一个表分区对应一个索引分区.
global partition index相对难管理一些,一个索引分区对应多个表分区.
 create partition table range2, range type
create partition table range2, range type
CREATE TABLE range2 ( a int, b int, data char(20) ) PARTITION BY RANGE(a) ( PARTITION p1 VALUES LESS THAN(2) tablespace TS1, PARTITION p2 VALUES LESS THAN(3) tablespace TS2 );
 create local index for range2
create local index for range2
CREATE INDEX local_idx1 ON RANGE2(a,b) LOCAL;
创建no-partition global index
 创建GLOBAL NON PARTITION INDEX
创建GLOBAL NON PARTITION INDEX
CREATE INDEX G_IDX1 ON RANGE2(data);
 --创建GLOBAL PARTATION INDEX
--创建GLOBAL PARTATION INDEX
CREATE INDEX GP_IDX ON RANGE2(b) GLOBAL PARTITION BY RANGE(b) ( PARTITION idx1 VALUES LESS THAN (1000), PARTITION idx2 VALUES LESS THAN (MAXVALUE) );


--往表中灌数据 INSERT INTO range2 SELECT mod(rownum -1,2)+1,rownum,'x' FROM all_objects; commit; --执行分析 BEGIN DBMS_STATS.GATHER_TABLE_STATS('U3','RANGE2',CASCADE=>TRUE); END;
Partition Pruning(核心思想,就是只查询相关的分区表,其他无关的分区表将会智能过滤掉.提高几个数量级的查询速度)
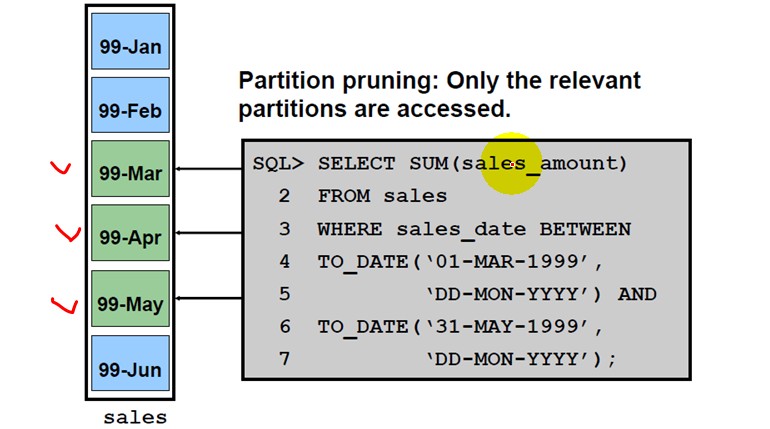
实验一
SQL> SELECT * FROM range2 WHERE a=1 and b=1; A B DATA ---------- ---------- -------------------- 1 1 x 1 1 x 1 1 x 1 1 x SQL> delete from plan_table; 0 rows deleted. SQL> explain plan for SELECT * FROM range2 WHERE a=1 and b=1; Explained.
SQL> set linesize 1000 SQL> select * from table(dbms_xplan.display); PLAN_TABLE_OUTPUT ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Plan hash value: 370859827 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | Pstart| Pstop | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 4 | 116 | 5 (0)| 00:00:01 | | | | 1 | PARTITION RANGE SINGLE | | 4 | 116 | 5 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 | | 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY LOCAL INDEX ROWID| RANGE2 | 4 | 116 | 5 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 | |* 3 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | LOCAL_IDX1 | 4 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | 1 | 1 | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 3 - access("A"=1 AND "B"=1) 15 rows selected.
解析:
SELECT * FROM range2 WHERE a=1 and b=1;执行查询语句之后,通过dbms_stats.gather_table_stats执行后发现,oracle智能的过滤掉不用的分区,只从Pstart=1,到Pstop=1分区内查询,其他分区都不会去过滤.大大提供性能.下面的实验也是如此道理.
SQL> select * from range2 where a=2 and b=2; A B DATA ---------- ---------- -------------------- 2 2 x 2 2 x 2 2 x 2 2 x SQL> delete from plan_table; 4 rows deleted. SQL> explain plan for select * from range2 where a=2 and b=2; Explained. SQL> select * from table(dbms_xplan.display); PLAN_TABLE_OUTPUT ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Plan hash value: 370859827 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | Pstart| Pstop | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 4 | 116 | 5 (0)| 00:00:01 | | | | 1 | PARTITION RANGE SINGLE | | 4 | 116 | 5 (0)| 00:00:01 | 2 | 2 | | 2 | TABLE ACCESS BY LOCAL INDEX ROWID| RANGE2 | 4 | 116 | 5 (0)| 00:00:01 | 2 | 2 | |* 3 | INDEX RANGE SCAN | LOCAL_IDX1 | 4 | | 1 (0)| 00:00:01 | 2 | 2 | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Predicate Information (identified by operation id): --------------------------------------------------- 3 - access("A"=2 AND "B"=2) 15 rows selected.
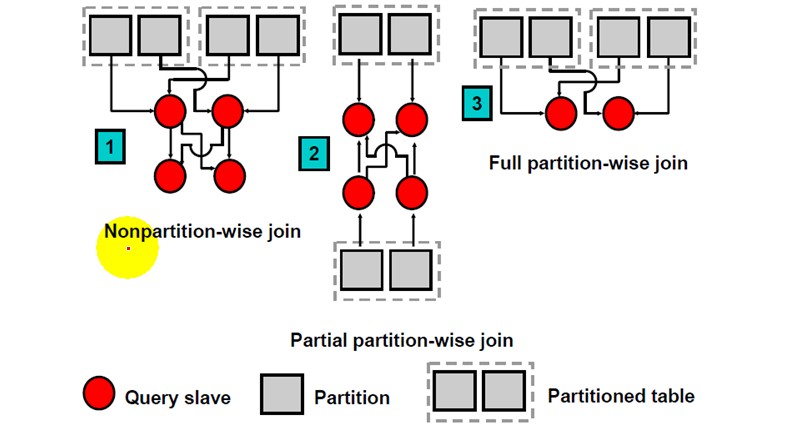
Partition-wise join(在进行Join的时候,能够智能的意识到哪些分区参与Join,哪些分区不参与)
Statistics Collection
- You can gather object-,partition-,or subpartition level statistics.
- There are GLOBAL or NON-GLOBAL statistics.
- The dbms_stats package can gahter global statistics at any level for tables only.
- It is not possible to gather:
- -Global histograms
- -Global statistics for indexes
Summary
In this lesson,you should have learned how to do the following:
- Compare and evaluate the different storage structures
- Examine different data access method
- Implement different partitioning mehtods
