Types of Variables

Guidelines for Declaring and Inititalizing PL/SQL Variables
- Follow naming conventions.
- Use meaningful identifiers for variables.
- Initialize variables designated as NOT NULL and CONSTANT.
- Initialize variables with the assignment operator (:=) or the DEFAULT keyword:
v_myName VARCHAR2(20) := 'John'; v_myName VARCHAR2(20) DEFAULT 'John';
- Declare one identifier per line for better readbility and code maintenance.
Guidelines for Declaring PL/SQL Variables
- Avoid using column names as identifiers.
PL/SQL里面,如果列名和变量名相同,优先PL/SQL引擎优先解析为列名.
DECLARE employee_id NUMBER(6); BEGIN SELECT employee_id--字段名称 INTO employee_id--变量名称
FROM employees WHERE last_name = 'Kochhar'; END; /
- Use the NOT NULL constrain when the variable must hold a value.
Scalar Data Types
- Hold a single value
- Have no iternal components

Base Scalar Data Types
- CHAR [(maximum_length)]
- VARCHAR2(maximum_length)
- NUMBER [(precision,scale)]
- BINARY_INTEGER
- PLS_INTEGER
- BOOLEAN
- BINARY_FLOAT
- BINARY_DOULBE
- DATE
- TIMESTAMP
- TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE
- TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE
- INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH
- INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND
Declaring Scalar Variables
Examples:
DECLARE v_emp_job VARCHAR2(9); v_count_job BINARY_INTEGER :=0; v_dept_total_sal NUMBER(9,2) :=0; v_orderdate DATE :=SYSDATE + 7; v_tax_rate CONSTANT NUMBER(3,2) :=8.25; v_valid BOOLEAN NOT NULL :=TRUE; ...
%TYPE Attribute
- Is used to decalre a variable according to:
- -A database column definition
- -Another declared variable
- Is prefixed with:
- -The database table and column
- -The name of the decared variable
Declaring Variables with the %TYPE Attribute
- Syntax
identifier table.column_name%TYPE;
- Examples
... employee_name employees.last_name%TYPE; ...
... balance NUMBER(7,2); min_balance balance%TYPE :=1000; ...
Declaring Boolean Variables
- Only the TRUE,FALSE,and NULL values can be assigned to a Boolean variable.
- Conditional expressions use the logical operators AND and OR and the unary operator NOT to check the variable values.
- The variables alwarys yield TRUE,FALSE,or NULL.
- Airthmetic,character,and date expressions can be used to return a Boolean value.
在PL/SQL中,Boolean型变量,不同于其他语言,其包含三种类型的值,分别是(TRUE,FALSE,NULL);
IF(TRUE) .... IF(FALSE | NULL) ...
Bind Variables
Bind variables are:
- Created in the enviroment
- Also called host variables.
- Created with the VARIABLE keyword.
- Used in SQL statements and PL/SQL blocks
- Accessed even after the PL/SQL block is executed
- Referenced with a preceding colon.
声明Bind Variables,使用关键字VARIABLE;绑定变量属于非PL/SQL变量.
PL/SQL声明变量,使用关键字DECLARE.
日常开发中,应当注意区别运用DECLARE 和 VARIABLE关键字,声明变量.通过绑定变量和PL/SQL,实现他们彼此之间的交互.
Pinting Bind Variables
Example:
 Demo
Demo
VARIABLE b_emp_salary NUMBER BEGIN SELECT salary INTO :b_emp_salary FROM employees WHERE employee_id = 178; END; / PRINT b_emp_salary; SELECT first_name,last_name FROM employees WHERE salary = :b_emp_salary; SQL> @bind.sql PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. B_EMP_SALARY ------------ 7000 FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME -------------------- ------------------------- Oliver Tuvault Sarath Sewall Kimberely Grant
 Demo 02 : With SET AUTOPRINT ON
Demo 02 : With SET AUTOPRINT ON
VARIABLE b_emp_salary SET AUTOPRINT ON DECLARE v_empno NUMBER(6) :=&empno; BEGIN SELECT salary INTO :b_emp_salary FROM employees WHERE employee_id = v_empno; END; / SQL> @bind2.sql variable b_emp_salary datatype NUMBER Enter value for empno: 100 old 2: v_empno NUMBER(6) :=&empno; new 2: v_empno NUMBER(6) :=100; PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. B_EMP_SALARY ------------ 24000
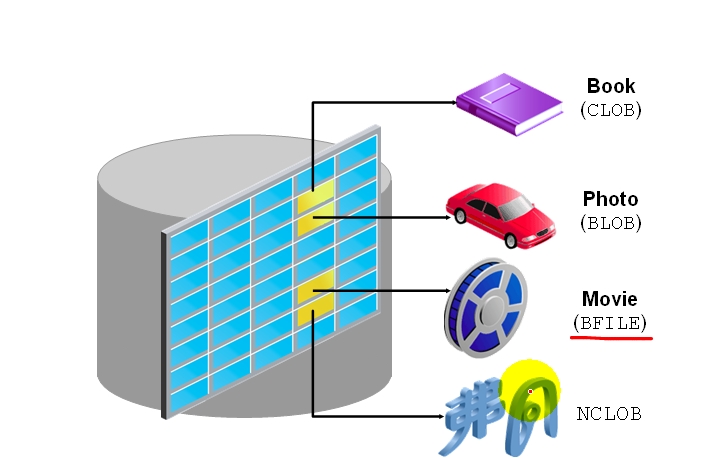
LOB Data Type Variables
Composite Data Types

Summary
In this lesson,you should have learned how to:
- Recognize valid and invalid identifiers.
- Declare variables in the declarative section of a PL/SQL block.
- Initialize variables and use them in the executable section.
- Differentiate between scalar and composite data types.
- Use the %TYPE attribute
- Use bind variables.
