文字描算
之前分析顺序查找和折半查找的算法性能都是在“等概率”的前提下进行的,但是如果有序表中各记录的查找概率不等呢?换句话说,概率不等的情况下,描述查找过程的判定树为何类二叉树,其查找性能最佳?
如果只考虑查找成功的情况,则使查找性能达最佳的判定树是其带权内路径长度之和PH值取最小的二叉树。
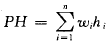
其中n为二叉树上结点的个数(即有序表的长度);hi为第i个结点在二叉树上的层次数;结点的权wi=cpi(i=1,2,…,n),其中pi为结点的查找概率,c为某个常量。称PH值取最小的二叉树为静态最优查找树。由于构造静态最优查找树代价较高,在此介绍一种构造近似最优查找树的有效算法。该算法的过程描述如下:
已知一个按关键字有序的记录序列 ,其中
,其中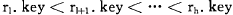 , 与每个记录相应的权值为
, 与每个记录相应的权值为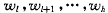

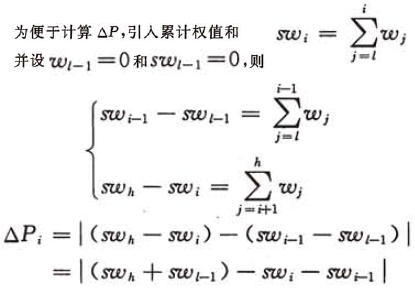
首先在记录序列中取第i(l<=i && i<=h)个记录构造根结点 ,使得
,使得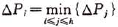 取最小值,然后分别对子序列
取最小值,然后分别对子序列 和
和 构造两棵次优查找树,并分别设为根结点
构造两棵次优查找树,并分别设为根结点 的左子树和右子树。
的左子树和右子树。
示意图

算法分析
从次优查找树的结构特定可知,其查找过程类似于折半查找。查找过程和二叉排序树算法类型,待二叉排序树会讲。由于查找过程是走了一条从根到待查记录所在节点(或叶子结点)的一条路径,进行过比较的关键字个数不超过树的深度,因此,次优查找树的平均查找长度和logn成正比。可见,在记录的查找概率不等时,可用次优查找树表示静态查找表,故又称为静态树表。
另外,大量实验表明,次优查找树和最优查找树的查找性能之差仅仅为1%-2%,很少查过3%,而且构造次优查找树的算法的时间复杂度为nlogn。
代码实现

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 5 #define DEBUG 6 #define EQ(a, b) ((a)==(b)) 7 #define LT(a, b) ((a)< (b)) 8 #define LQ(a, b) ((a)<=(b)) 9 #define MAX_SIZE 50 10 11 typedef char KeyType; 12 //数据元素类型 13 typedef struct{ 14 //关键字 15 KeyType key; 16 //权值 17 int weight; 18 }ElemType; 19 //静态查找表 20 typedef struct{ 21 //数据元素存储空间基址,0号单元留空 22 ElemType *elem; 23 //表长度 24 int length; 25 }SSTable; 26 //二叉链表, 次优查找树采用二叉链表的存储结构 27 typedef struct{ 28 ElemType data; 29 struct BiTNode *lchild; 30 struct BiTNode *rchild; 31 }BiTNode, *BiTree; 32 33 //由有序表R[low,...,high]及累计权值表sw(其中sw[0]==0)递归构造次优查找树T 34 BiTNode* SecondOptimal(ElemType R[], int sw[], int low, int high) 35 { 36 int i = low, j = 0; 37 int min = abs(sw[high]-sw[low]); 38 int dw = sw[high]+sw[low-1]; 39 //选择最小的<>Pi值 40 for(j=low+1; j<=high; ++j){ 41 if(abs(dw-sw[j]-sw[j-1])<min){ 42 i = j; 43 min = abs(dw-sw[j]-sw[j-1]); 44 } 45 } 46 #ifdef DEBUG 47 printf("i=%d, low=%d, high=%d ", i, low, high); 48 #endif 49 //生成结点 50 BiTNode* T = (BiTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode)); 51 T->data = R[i]; 52 T->lchild = T->rchild = NULL; 53 if(i==low){ 54 //左子树空 55 T->lchild = NULL; 56 }else{ 57 //构造左子树 58 T->lchild = SecondOptimal(R, sw, low, i-1); 59 } 60 if(i==high){ 61 //右子树空 62 T->rchild = NULL; 63 }else{ 64 //构造右子树 65 T->rchild = SecondOptimal(R, sw, i+1, high); 66 } 67 return T; 68 } 69 70 //按照由有序表ST中各数据元素的weight域求累计权值表sw 71 void FindSW(int sw[], SSTable ST) 72 { 73 int i = 1; 74 sw[0] = 0; 75 for(i=1; i<=ST.length; i++){ 76 sw[i] = sw[i-1]+ST.elem[i].weight; 77 } 78 #ifdef DEBUG 79 printf("SW : "); 80 for(i=1; i<=ST.length; i++){ 81 printf("[%d]=%-3d ", i, sw[i]); 82 } 83 printf(" "); 84 #endif 85 return ; 86 } 87 88 //由有序表ST构造一棵次优查找树. ST的数据元素含有权域weight 89 BiTree CreateSOSTree(SSTable ST) 90 { 91 if(ST.length == 0) 92 return NULL; 93 else{ 94 int sw[MAX_SIZE+1] = {0}; 95 //按照由有序表ST中各数据元素的weight域求累计权值表sw 96 FindSW(sw, ST); 97 //由有序表ST.elem[low,...,high]及累计权值表sw(其中sw[0]==0)递归构造次优查找树并返回 98 return (BiTree)SecondOptimal(ST.elem, sw, 1, ST.length); 99 } 100 } 101 102 //顺序打印有序表ST中的数据元素。 103 void print(SSTable SS){ 104 printf("data: "); 105 int i = 0; 106 for(i=1; i<=SS.length; i++){ 107 printf("[%d]=%c,%d ", i, SS.elem[i].key, SS.elem[i].weight); 108 } 109 printf(" "); 110 } 111 112 int PreOrderTraverse(BiTree T); //先序遍历 113 int InOrderTraverse(BiTree T); //中序遍历 114 int PostOrderTraverse(BiTree T);//后序遍历 115 116 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 117 { 118 119 KeyType key; 120 int weight; 121 int i = 1; 122 char tmp[10] = {0}; 123 #ifdef DEBUG 124 ElemType arr[MAX_SIZE+1] = {{'0',0},{'A',1}, {'B',1}, {'C',2}, {'D',5}, {'E',3},{'F',4},{'G',4},{'H',3},{'I',5},}; 125 i = 10; 126 #else 127 ElemType arr[MAX_SIZE+1]; 128 while(1){ 129 printf("输入 关键字,权值('0,0'是结束):"); 130 memset(tmp, 0, sizeof(tmp)); 131 scanf("%s", tmp); 132 sscanf(tmp, "%c,%d", &key, &weight); 133 if(key == '0' && weight ==0){ 134 break; 135 }else{ 136 arr[i].key = key; 137 arr[i].weight = weight; 138 i+=1; 139 } 140 } 141 #endif 142 SSTable SS; 143 SS.elem = arr; 144 SS.length = i-1; 145 #ifdef DEBUG 146 print(SS); 147 #endif 148 BiTree T = CreateSOSTree(SS); 149 printf("先序遍历:"); 150 PreOrderTraverse(T); 151 printf(" "); 152 153 printf("中序遍历:"); 154 InOrderTraverse(T); 155 printf(" "); 156 157 printf("后序遍历:"); 158 PostOrderTraverse(T); 159 printf(" "); 160 return 0; 161 } 162 163 int PreOrderTraverse(BiTree T){ 164 if(T){ 165 printf("%c,%d ", ((BiTNode*)T)->data.key, ((BiTNode*)T)->data.weight); 166 PreOrderTraverse((BiTree)T->lchild); 167 PreOrderTraverse((BiTree)T->rchild); 168 } 169 return 0; 170 } 171 172 int InOrderTraverse(BiTree T){ 173 if(T){ 174 InOrderTraverse((BiTree)T->lchild); 175 printf("%c,%d ", ((BiTNode*)T)->data.key, ((BiTNode*)T)->data.weight); 176 InOrderTraverse((BiTree)T->rchild); 177 } 178 return 0; 179 } 180 181 int PostOrderTraverse(BiTree T){ 182 if(T){ 183 PostOrderTraverse((BiTree)T->lchild); 184 PostOrderTraverse((BiTree)T->rchild); 185 printf("%c,%d ", ((BiTNode*)T)->data.key, ((BiTNode*)T)->data.weight); 186 } 187 return 0; 188 }
运行

