183.Wood Cut【hard】
Given n pieces of wood with length L[i] (integer array). Cut them into small pieces to guarantee you could have equal or more than k pieces with the same length. What is the longest length you can get from the n pieces of wood? Given L & k, return the maximum length of the small pieces.
Notice
You couldn't cut wood into float length.
If you couldn't get >= k pieces, return 0.
For L=[232, 124, 456], k=7, return 114.
O(n log Len), where Len is the longest length of the wood.
这个题一上来一点思路没有,参考:https://algorithm.yuanbin.me/zh-hans/binary_search/wood_cut.html里面的思路
这道题要直接想到二分搜素其实不容易,但是看到题中 Challenge 的提示后你大概就能想到往二分搜索上靠了。首先来分析下题意,题目意思是说给出 n 段木材L[i], 将这 n 段木材切分为至少 k 段,这 k 段等长,求能从 n 段原材料中获得的最长单段木材长度。以 k=7 为例,要将 L 中的原材料分为7段,能得到的最大单段长度为114, 232/114 = 2, 124/114 = 1, 456/114 = 4, 2 + 1 + 4 = 7。
理清题意后我们就来想想如何用算法的形式表示出来,显然在计算如2, 1, 4等分片数时我们进行了取整运算,在计算机中则可以使用下式表示: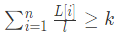
其中 l 为单段最大长度,显然有 1 ≤ l ≤ max(L[i]). 单段长度最小为1,最大不可能超过给定原材料中的最大木材长度。
Warning 注意求和与取整的顺序,是先求
L[i]/l的单个值,而不是先对L[i]求和。
分析到这里就和题 sqrt(x) 差不多一样了,要求的是 l 的最大可能取值,同时 l 可以看做是从有序序列[1, max(L[i])]的一个元素,典型的二分搜素!
代码参考了:http://www.jiuzhang.com/solution/wood-cut/
解法一:
1 public class Solution { 2 /** 3 *@param L: Given n pieces of wood with length L[i] 4 *@param k: An integer 5 *return: The maximum length of the small pieces. 6 */ 7 public int woodCut(int[] L, int k) { 8 int max = 0; 9 for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++) { 10 max = Math.max(max, L[i]); 11 } 12 13 // find the largest length that can cut more than k pieces of wood. 14 int start = 1, end = max; 15 while (start + 1 < end) { 16 int mid = start + (end - start) / 2; 17 if (count(L, mid) >= k) { 18 start = mid; 19 } else { 20 end = mid; 21 } 22 } 23 24 if (count(L, end) >= k) { 25 return end; 26 } 27 if (count(L, start) >= k) { 28 return start; 29 } 30 return 0; 31 } 32 33 private int count(int[] L, int length) { 34 int sum = 0; 35 for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++) { 36 sum += L[i] / length; 37 } 38 return sum; 39 } 40 }
对于上面发现还有可以优化的地方,那就是我们二分找长度的时候只需要找所有木块里面最短的即可,就是所谓的木桶原理,那么end上界又可以进一步减少。
解法二:
1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 /* 4 * @param L: Given n pieces of wood with length L[i] 5 * @param k: An integer 6 * @return: The maximum length of the small pieces 7 */ 8 int woodCut(vector<int> &L, int k) { 9 if (L.empty() || k <= 0) { 10 return 0; 11 } 12 //get min 13 int min = INT_MIN; 14 for (int i = 0; i < L.size(); ++i) { 15 min = (min < L[i] ? L[i] : min); 16 } 17 18 int start = 1; 19 int end = min; 20 21 while (start + 1 < end) { 22 int mid = start + (end - start) / 2; 23 24 if (cal(L, mid) >= k) { 25 start = mid; 26 } 27 else { 28 end = mid; 29 } 30 } 31 32 if (cal(L, end) >= k) { 33 return end; 34 } 35 else if (cal(L, start) >= k) { 36 return start; 37 } 38 else { 39 return 0; 40 } 41 } 42 43 int cal(vector<int> & L, int len) { 44 int sum = 0; 45 for (int i = 0; i < L.size(); ++i) { 46 sum += L[i] / len; 47 } 48 49 return sum; 50 } 51 };