下文的代码可能展示不全,详情请下载文件:用cpp遍历ndarray.rar
问题背景:
现在我有一张二值图test.npy,需要对其闭区域进行孔洞填充,如下图所示:
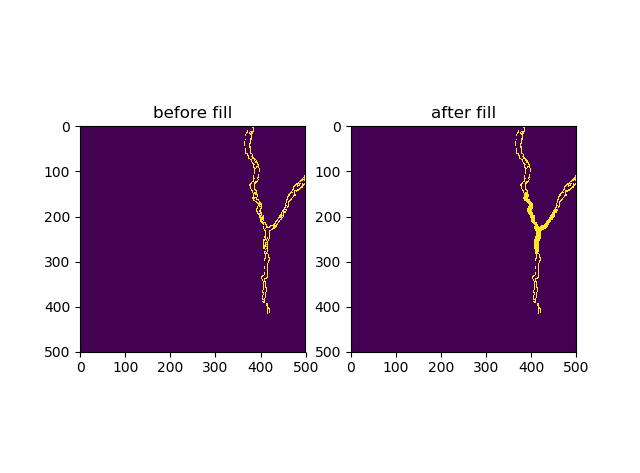
文件下载链接:用cpp遍历ndarray.rar
用python实现BFS:
def bfs1(im, vis, x, y, xb, yb): def legal(tx, ty): if tx < xb and tx >= 0 and ty < yb and ty >= 0: return True else: return False dx = [0, 0, 1, -1] dy = [1, -1, 0, 0] q = Queue() ls = [] q.put((x, y)) flag = True while not q.empty(): tmp = q.get() cx, cy = tmp vis[cx][cy] = 1 for i in range(0, 4): tx = cx + dx[i] ty = cy + dy[i] if (legal(tx, ty)): if im[tx][ty] == 0 and vis[tx][ty] == 0: q.put((tx, ty)) ls.append((tx, ty)) vis[tx][ty] = 1 else: flag = False if flag: for pt in ls: tx, ty = pt im[tx][ty] = 255 def fillHolePy(im): x, y = im.shape[:2] ans=im.copy() vis = np.zeros([x, y]) for i in range(0, x): for j in range(0, y): if vis[i][j] == 0: # and im[i][j]==0 bfs1(ans, vis, i, j, x, y) return ans
程序执行了0.914秒
用C++实现BFS:(因为python向cpp传参只能用一维数组,这涉及到多维数组到一维数组的映射,详见我的另一篇博客:numpy中多维数组的绝对索引)
int x_s,y_s; inline int MAP(int x,int y){ return y_s*x + y; } int dx[4]={0, 0, 1, -1}; int dy[4]={1, -1, 0, 0}; int vis[1000*1000]; typedef struct Pt { int x,y; Pt(int x,int y):x(x),y(y){ } }Pt; bool legal(int x,int y){ if(x<x_s && x>=0 && y<y_s && y>=0) return true; return false; } void bfs(int *img,int x,int y){ queue<Pt> q; vector<Pt> v; q.push(Pt(x,y)); bool flag=1; int i; while(!q.empty()){ Pt pt=q.front(); q.pop(); vis[MAP(x,y)]=1; int cx=pt.x,cy=pt.y; FF(i,4){ int tx=cx+dx[i]; int ty=cy+dy[i]; if(legal(tx,ty)){ if(img[MAP(tx,ty)]==0 && vis[MAP(tx,ty)]==0){ q.push(Pt(tx,ty)); v.push_back(Pt(tx,ty)); vis[MAP(tx,ty)]=1; } }else{ flag=0; } } if(flag){ int sz=v.size(); FF(i,sz){ int & tx=v[i].x; int & ty=v[i].y; img[MAP(tx,ty)]=255; } } } } void fillHole(int * img,int X,int Y){ x_s=X,y_s=Y; int i,j; FF(i,x_s)FF(j,x_s)if(!vis[MAP(i,j)]){ bfs(img,i,j); } }
下面我们看怎样用python调用cpp。
在上文的cpp中,对想要执行的函数fillHole进行声明:
extern "C" { __declspec(dllexport) void fillHole(int * img,int X,int Y) ; }
用g++(mingw64位)编译为dll:
g++ bfs.cpp -shared -o bfs.dll -Wl,--out-implib,bfs.lib pause
在python中使用numpy的封装加载DLL并且传参调用:
import numpy.ctypeslib as npct def fillHoleCpp(im): array_2d_int32 = npct.ndpointer(dtype=np.int32, ndim=2, flags='CONTIGUOUS') dll = npct.load_library("bfs.dll",".") bfs=dll.fillHole bfs.restype = None bfs.argtypes = [array_2d_int32, c_int, c_int] im=im.astype(dtype=np.int32) if not im.flags['C_CONTIGUOUS']: im = np.ascontiguous(im, dtype=im.dtype) X, Y=im.shape bfs(im,X,Y) return im
查看测试结果:
程序执行了0.058秒
根据测试cpp比python快了15倍。
cpp完整代码:

#include <stdio.h> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; #define FF(a,b) for(a=0;a<b;a++) extern "C" { __declspec(dllexport) void fillHole(int * img,int X,int Y) ; } int x_s,y_s; inline int MAP(int x,int y){ return y_s*x + y; } int dx[4]={0, 0, 1, -1}; int dy[4]={1, -1, 0, 0}; int vis[1000*1000]; typedef struct Pt { int x,y; Pt(int x,int y):x(x),y(y){ } }Pt; bool legal(int x,int y){ if(x<x_s && x>=0 && y<y_s && y>=0) return true; return false; } void bfs(int *img,int x,int y){ queue<Pt> q; vector<Pt> v; q.push(Pt(x,y)); bool flag=1; int i; while(!q.empty()){ Pt pt=q.front(); q.pop(); vis[MAP(x,y)]=1; int cx=pt.x,cy=pt.y; FF(i,4){ int tx=cx+dx[i]; int ty=cy+dy[i]; if(legal(tx,ty)){ if(img[MAP(tx,ty)]==0 && vis[MAP(tx,ty)]==0){ q.push(Pt(tx,ty)); v.push_back(Pt(tx,ty)); vis[MAP(tx,ty)]=1; } }else{ flag=0; } } if(flag){ int sz=v.size(); FF(i,sz){ int & tx=v[i].x; int & ty=v[i].y; img[MAP(tx,ty)]=255; } } } } void fillHole(int * img,int X,int Y){ x_s=X,y_s=Y; int i,j; FF(i,x_s)FF(j,x_s)if(!vis[MAP(i,j)]){ bfs(img,i,j); } } //int main() { // return 0; //}
python完整代码:

import numpy as np import numpy.ctypeslib as npct import pylab as plt from queue import Queue import datetime from ctypes import * def bfs1(im, vis, x, y, xb, yb): def legal(tx, ty): if tx < xb and tx >= 0 and ty < yb and ty >= 0: return True else: return False dx = [0, 0, 1, -1] dy = [1, -1, 0, 0] q = Queue() ls = [] q.put((x, y)) flag = True while not q.empty(): tmp = q.get() cx, cy = tmp vis[cx][cy] = 1 for i in range(0, 4): tx = cx + dx[i] ty = cy + dy[i] if (legal(tx, ty)): if im[tx][ty] == 0 and vis[tx][ty] == 0: q.put((tx, ty)) ls.append((tx, ty)) vis[tx][ty] = 1 else: flag = False if flag: for pt in ls: tx, ty = pt im[tx][ty] = 255 def fillHolePy(im): x, y = im.shape[:2] ans=im.copy() vis = np.zeros([x, y]) for i in range(0, x): for j in range(0, y): if vis[i][j] == 0: # and im[i][j]==0 bfs1(ans, vis, i, j, x, y) return ans import numpy.ctypeslib as npct def fillHoleCpp(im): array_2d_int32 = npct.ndpointer(dtype=np.int32, ndim=2, flags='CONTIGUOUS') dll = npct.load_library("bfs.dll",".") bfs=dll.fillHole bfs.restype = None bfs.argtypes = [array_2d_int32, c_int, c_int] im=im.astype(dtype=np.int32) if not im.flags['C_CONTIGUOUS']: im = np.ascontiguous(im, dtype=im.dtype) X, Y=im.shape bfs(im,X,Y) return im if __name__ == '__main__': img=np.load('test.npy') plt.subplot(121) plt.title('before fill') plt.imshow(img) starttime = datetime.datetime.now() img=fillHoleCpp(img) #使用BFS(广度优先搜索算法)对原图像进行处理 endtime = datetime.datetime.now() print("程序执行了%.03f秒" % ((endtime - starttime).microseconds / 1000000)) # exit(0) plt.subplot(122) plt.title('after fill') plt.imshow(img) plt.show()
参考资料:
