前言
Fragment是一种可以嵌入在activity当中的UI片段,它能让程序更加合理和充分地利用大屏幕的空间,因而在平板上用的非常广泛。
Fragment和activity非常像,同样能包含layout、同样有自己的生命周期。你甚至把fragment理解成一个迷你型的activity。
那么fragment在平板上的设计和在手机上有什么区别呢? 或者说fragment如何充分利用平板空间呢?

Fragment的使用方式
Fragment的简单用法
-
创建要在fragment中使用的布局。这里叫left_fragment.xml和right_fragment.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:text="Button"/> </LinearLayout> -
针对上面的布局创建相应的Fragment继承类,使用LayoutInflater动态加载布局:
/** * 这里使用LayoutInflater的inflate方法将刚才定义的left_fragment布局动态加载进来的。 */ public class LeftFragment extends Fragment{ @Nullable @Override public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.left_fragment, container, false); return view; } } -
最后main_activity.xml中引入fragment
<fragment android:id="@+id/left_fragment" android:name="com.ssozh.firstfragment.LeftFragment" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="1"/> <fragment android:id="@+id/right_fragment" android:name="com.ssozh.firstfragment.RightFragment" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="1"/>
动态加载Fragment
fragment真正的强大之处在于它可以在程序运行时动态地添加到活动当中。
动态添加fragment主要分为五步:
- 创建待添加fragment的实例
- 获取fragmentManager,在activity中可以直接调用getSupportFragmentManager方法获取。
- 向容器内添加或替换fragment,一般使用replace()方法实现,需要传入容器的id和待添加的fragment实例。
- 提交事务,调用commit方法来完成。
/**
* 创建一个manager
* 通过manager开启一个事务transaction
* 向容器内添加或替换fragment
* 提交事务
* @param fragment
*/
private void replaceFragment(Fragment fragment) {
FragmentManager manager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction = manager.beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.right_layout,fragment);
transaction.commit();
}
在Fragment中实现返回栈
上面动态添加的fragment不能通过back键退出,而是直接退出。因此需要在fragment中实现返回栈。
FragmentTransaction中提供了一个addToBackStack方法,
transaction.replace(R.id.right_layout,fragment);
transaction.addToBackStack(null);
transaction.commit();
fragment和activity之间的交互
实际上fragment和activity没那么紧密的关系,如果想要在activity中调用fragment里面的方法,或者反之操作,可以使用manager来从布局文件中获取fragment的实例。
FragmentManager manager = getSupportFragmentManager();
manager.findFragmentById()
Fragment的生命周期
和activity一样,fragment也有自己的生命周期。
fragment的状态和回调
4个状态:
- 运行状态:当一个fragment关联的activity正处于运行状态,则该fragment也处于。
- 暂停状态:当一个activity进入暂停状态时,与他相关联的fragment就会进入暂停状态。
- 停止状态:当activity进入停止状态,则与他相关的fragment就会进入停止状态,或者通过fragmenttransaction的remove、replace方法将fragment从activity中移除。
- 销毁状态:fragment总是依附于activity而存在的。activity被销毁,则fragment也被销毁,或者调用了remove、replace也是销毁了。
回调:
- onAttach:当fragment和activity建立关联时调用
- onCreateView:为fragment创建视图(加载布局)时调用。
- onActivityCreated:确保与fragment相关联的activity已经创建完毕时调用。
- onDestroyView:当与fragment关联的视图被移除时候调用
- onDetach:当fragment和activity解除关联时候调用
体验fragment的生命周期
略
动态加载布局的技巧
使用限定符
如何判断运行的程序应该使用单页模式还是双页模式?这就应该借助限定符(Qualifiers)来实现了。
具体而言就是在src下创建一个layout-large文件夹即可,如果是双页就调用这个文件夹下的layout而单页局调用layout下的。
Android的创建限定符包括:
- 大小:small、 normal、 large、 xlarge
- 分辨率:ldpi、 mdpi、hdpi、xhdpi、xxhdpi
- 方向:land(横屏)、port(竖屏)
注意:
<fragment
android:id="@+id/left_fragment"
android:name="com.ssozh.firstfragment.LeftFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<!-- <Fragment-->
<!-- android:id="@+id/right_fragment"-->
<!-- android:name="com.ssozh.firstfragment.RightFragment"-->
<!-- android:layout_width="0dp"-->
<!-- android:layout_height="match_parent"-->
<!-- android:layout_weight="1"/>-->
<!--主要问题在与这个Fragment和fragment的区别!-->
<fragment
android:id="@+id/right_fragment"
android:name="com.ssozh.firstfragment.RightFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="3"/>
使用最小宽度限定符
如果文件夹名字为layout-sw600dp这就意味着当程序运行在屏幕宽度W大于等于600dp的设备上时,会加载这个文件夹下的layout。
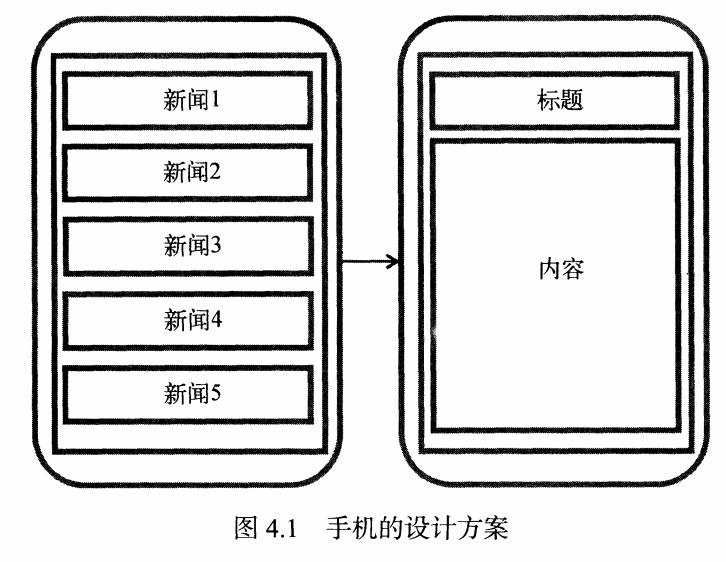
Fragment的最佳实践:一个简易版的新闻应用
两个部分:
-
手机版本通过intent传递点击title阅读content
-
平板版本在一个layout中放两个fragment。点击左边的fragment显示(刷新)右边的fragment(内容是content)
主要的布局(fragment):
-
至少应该包括news_content_frag和news_title_frag。
-
同时为了把title直接展示在主页面,应该包括news_item。
-
使用点击展示content应该包括activity_news_content。
-
两个activity_main。
平板版本
两个fragment及其所对应的Fragment继承类:
title fragment的xml(本质是一个recyclerview)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/news_title_recycer_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
content fragment的xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/content_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:visibility="invisible">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/news_title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:textSize="20sp"/>
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1dp"
android:background="#000"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/news_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:padding="15dp"
android:textSize="18sp"/>
</LinearLayout>
<View
android:layout_width="1dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:background="#000"/>
</RelativeLayout>
正如上面所说因为title fragment是一个recyclerview,因此其逻辑较为复杂,需要将RecyclerView.Adapter也写在其中,包括:
- fragment相关:
- onCreateView
- onActivityCreated
- RecyclerView相关:
- RecyclerView.Adapter类及其方法
- onCreateViewHolder
- onBindViewHolder
- getItemCount
- onCreateViewHolder中关于click的回调函数。
- RecyclerView.Adapter内部类ViewHolder
- RecyclerView.Adapter类及其方法
public class NewsTitleFragment extends Fragment {
private boolean isTwoPane;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.news_title_frag, container, false);
RecyclerView newsTitleRecycerView = (RecyclerView) view.findViewById(R.id.news_title_recycer_view);
LinearLayoutManager layoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager(getActivity());
newsTitleRecycerView.setLayoutManager(layoutManager);
NewsTitleFragment.NewsAdapter newsAdapter = new NewsAdapter(getNews());
newsTitleRecycerView.setAdapter(newsAdapter);
return view;
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
isTwoPane = getActivity().findViewById(R.id.news_content_layout) !=null;
}
private List<News> getNews(){
List<News> newsList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1;i<=50;i++) {
News news = new News();
news.setTitle("This is news title:" + i);
news.setContent(getRandomLengthContent("This is news content:" + i + "."));
newsList.add(news);
}
return newsList;
}
private String getRandomLengthContent(String content) {
Random random = new Random();
int len = random.nextInt(20)+1;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) {
sb.append(content);
}
return sb.toString();
}
class NewsAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<NewsAdapter.ViewHolder> {
private List<News> mNewsList;
class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder{
TextView newsTitleText;
public ViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
newsTitleText = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.news_title);
}
}
public NewsAdapter(){}
public NewsAdapter(List<News> mNewsList) {
this.mNewsList = mNewsList;
Log.d("RecyclerView", mNewsList.toString());
}
@NonNull
@Override
public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext())
.inflate(R.layout.news_item,parent,false);
final ViewHolder holder = new ViewHolder(view);
view.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
News news = mNewsList.get(holder.getAdapterPosition());
if(isTwoPane) {
// 是双页模式
NewsContentFragment newsContentFragment = (NewsContentFragment) getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.news_content_fragment);
newsContentFragment.refresh(news.getTitle(),news.getContent());
}else {
// 如果是单页模式 则直接启动activity并传递数据
NewsContentActivity.actionStart(getActivity(),news.getTitle(),news.getContent());
}
}
});
return holder;
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull NewsAdapter.ViewHolder holder, int position) {
News news = mNewsList.get(position);
holder.newsTitleText.setText(news.getTitle());
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return mNewsList.size();
}
}
}
相比较而言content的fragment实现类会简单很多:除了需要重写的方法onCreateView,还有就是refresh方法【用于title fragment这个fragment的】。
public class NewsContentFragment extends Fragment {
private View view;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.news_content_frag,container,false);
return view;
}
/**
* 用于将新闻的标题和内容显示子在我们刚刚定义好的界面上。
* @param newsTitle
* @param newsContent
*/
public void refresh(String newsTitle,String newsContent) {
View contentLayout = view.findViewById(R.id.content_layout);
contentLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
TextView newsTitleText = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.news_title);
newsTitleText.setText(newsTitle);
TextView newsContentText = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.news_content);
newsContentText.setText(newsContent);
}
}
手机版本
首先应该可以复用平板版本的content fragment和title fragment。
main里面只包含title:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/news_title_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/news_title_fragment"
android:name="com.ssozh.fragmentbestpractice.NewsTitleFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</FrameLayout>
点击title后显示content fragment:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".NewsContentActivity">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/news_content_fragment"
android:name="com.ssozh.fragmentbestpractice.NewsContentFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
相关逻辑代码:
都写在NewsTitleFragment的代码中(其实这里有点过于耦合):
@NonNull
@Override
public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext())
.inflate(R.layout.news_item,parent,false);
final ViewHolder holder = new ViewHolder(view);
view.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
News news = mNewsList.get(holder.getAdapterPosition());
if(isTwoPane) {
// 是双页模式
NewsContentFragment newsContentFragment = (NewsContentFragment) getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.news_content_fragment);
newsContentFragment.refresh(news.getTitle(),news.getContent());
}else {
// 如果是单页模式 则直接启动activity并传递数据
NewsContentActivity.actionStart(getActivity(),news.getTitle(),news.getContent());
}
}
});
return holder;
}
不同于平板版本的NewsContentFragment,这里的手机版本主要是NewsContentActivity类:
public class NewsContentActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
public static void actionStart(Context context, String newsTitle, String newsContent) {
Intent intent = new Intent(context,NewsContentActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("news_title", newsTitle);
intent.putExtra("news_content",newsContent);
context.startActivity(intent);
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_news_content);
String newsTitle = getIntent().getStringExtra("news_title");
String newsContent = getIntent().getStringExtra("news_content");
// 通过supporter 使得activity获取fragment
NewsContentFragment newsContentFragment = (NewsContentFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.news_content_fragment);
// 使用fragment的刷新方法 把fragment刷新
newsContentFragment.refresh(newsTitle,newsContent);
}
}
通过intent方法传递activity,从而显示切换不同的content,区别于平板版本的fragment的切换。
手机和平板的比较
复用部分:
title_frag.xml以及NewsTitleFragment
没有复用部分,实际上也就是页面显示的不同开始的地方:
content_frag.xml和activity_content
相应的实现也分别是
- fragment通过getFragmentManager获取fragment,然后调用fragment的静态方法refresh
- activity通过actionStart实现activity的切换,并传递news.title和content从而显示切换。
实现位置是通过私有变量isTwoPane判断是平板还是手机,进而选择实现方式=>实现代码同样在NewsTitleFragment中。
=>引申问题,那种更耗费资源呢?
几个问题
-
当在平板上使用fragment的时候 一定要注意layout_width和layout_weight,否则容易一个fragment占用整个activity的layout。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <!--因为使用了两个fragment 所以这个地方的layout_width不是match_parent--> <fragment android:id="@+id/news_title_fragment" android:name="com.ssozh.fragmentbestpractice.NewsTitleFragment" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="1"/> <FrameLayout android:id="@+id/news_content_layout" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_weight="3"> <fragment android:id="@+id/news_content_fragment" android:name="com.ssozh.fragmentbestpractice.NewsContentFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"/> </FrameLayout> </LinearLayout> -
在使用
RecyclerView的时候,其中的adapter的layout子项,包括layout在内的height或者width其中一个不能是match_parent。否则以为一页就是一个item子项class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder{ TextView newsTitleText; public ViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) { super(itemView); newsTitleText = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.news_title); } }<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/news_title" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:maxLines="1" android:ellipsize="end" android:textSize="18sp" android:paddingLeft="10dp" android:paddingRight="10dp" android:paddingTop="15dp" android:paddingBottom="15dp"/> </LinearLayout>