双指针
- 首先可以使用快慢指针来判断该链表是否是环形链表,如果快指针能追上慢指针则是环形链表。
- 假设环的节点数为n,用两个指针指向头节点,一个指针先向前移动n步,这时移动第二个指针,当第二个指针到达环的入口节点时,第一个指针恰好在环中走了一圈,这时就找到环的入口结点了。
- 现在要解决的问题就是如何得到环的节点数:
当快指针追上慢指针后返回它们相遇的节点,在此节点的基础上在环中遍历,使用计数器计数,当再次遇到该节点时计数结束,这样就得到了环的节点数。
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
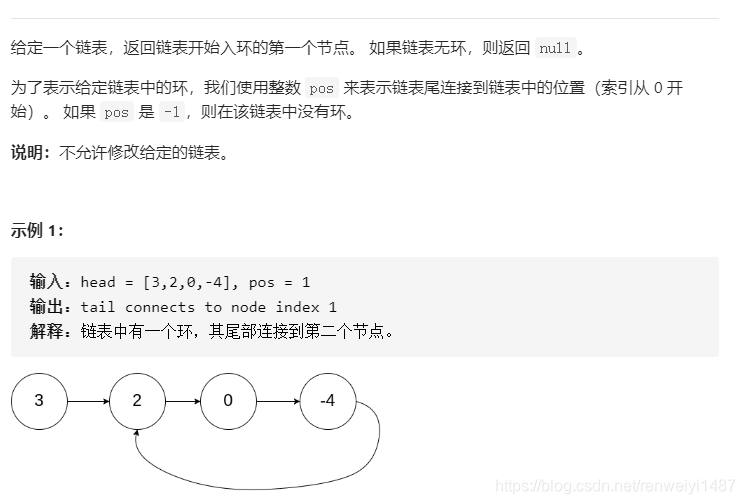
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode meetingNode = meetingNode(head);
if(meetingNode == null) return null;
int nodeInLoop = 1;
ListNode pNode1 = meetingNode;
while(pNode1.next != meetingNode){
++nodeInLoop;
pNode1 = pNode1.next;
}
System.out.println(nodeInLoop);
pNode1 = head;
for(int i = 0; i < nodeInLoop; i++){
pNode1 = pNode1.next;
}
ListNode pNode2 = head;
while(pNode1 != pNode2){
pNode1 = pNode1.next;
pNode2 = pNode2.next;
}
return pNode2;
}
private ListNode meetingNode(ListNode head){
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode pSlow = head;
ListNode pFast = head.next;
if(pFast == null)
return null;
while(pSlow != null && pFast != null){
if(pSlow == pFast)
return pFast;
pSlow = pSlow.next;
pFast = pFast.next;
if(pFast != null)
pFast = pFast.next;
}
return null;
}
}
