线性回归
算法优缺点:
- 优点:结果易于理解,计算不复杂
- 缺点:对非线性数据拟合不好
- 适用数据类型:数值型和标称型
算法思想:
这里是采用了最小二乘法计算(证明比较冗长略去)。这种方式的优点是计算简单,但是要求数据矩阵X满秩,并且当数据维数较高时计算很慢;这时候我们应该考虑使用梯度下降法或者是随机梯度下降(同Logistic回归中的思想完全一样,而且更简单)等求解。这里对估计的好坏采用了相关系数进行度量。
数据说明:
这里的txt中包含了x0的值,也就是下图中前面的一堆1,但是一般情况下我们是不给出的,也就是根据一个x预测y,这时候我们会考虑到计算的方便也会加上一个x0。
数据是这样的

函数:
loadDataSet(fileName):
读取数据。standRegres(xArr,yArr)
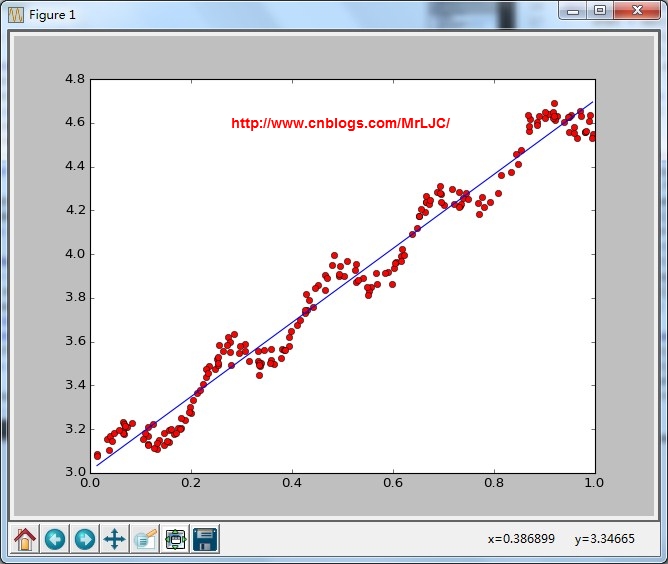
普通的线性回归,这里用的是最小二乘法
![]()
plotStandRegres(xArr,yArr,ws)
画出拟合的效果calcCorrcoef(xArr,yArr,ws)
计算相关度,用的是numpy内置的函数
结果:
局部加权线性回归(Locally Weighted Linear Regression)
算法思想:
这里的想法是:我们赋予预测点附近每一个点以一定的权值,在这上面基于最小均方差来进行普通的线性回归。这里面用“核”(与支持向量机相似)来对附近的点赋予最高的权重。这里用的是高斯核:
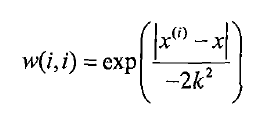
函数:
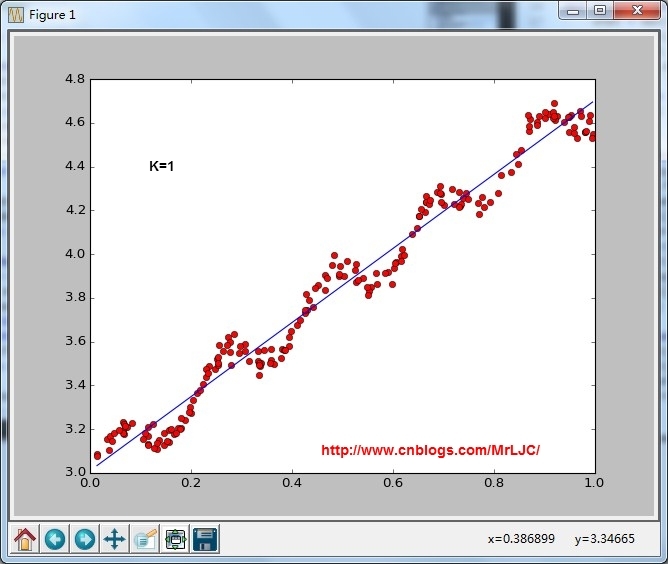
lwlr(testPoint,xArr,yArr,k=1.0)
根据计算公式计算出再testPoint处的估计值,这里要给出k作为参数,k为1的时候算法退化成普通的线性回归。k越小越精确(太小可能会过拟合)求解用最小二乘法得到如下公式:
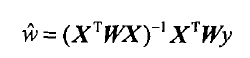
lwlrTest(testArr,xArr,yArr,k=1.0)
因为lwlr需要指定每一个点,这里把整个通过循环算出来了lwlrTestPlot(xArr,yArr,k=1.0)
将结果绘制成图像
结果:
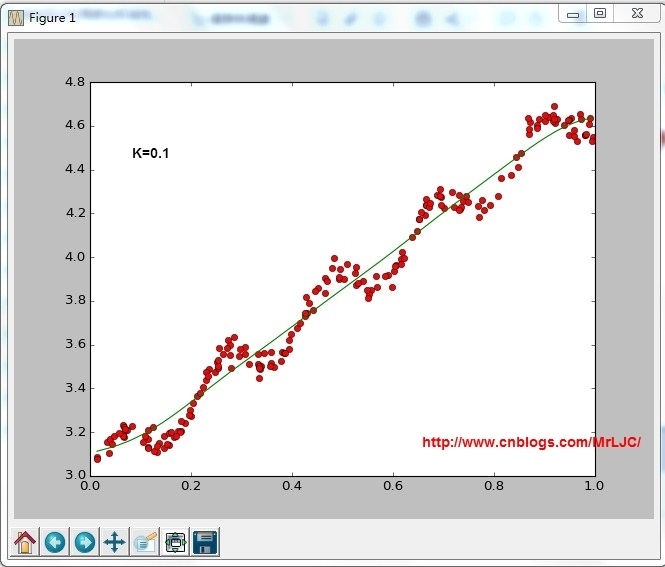
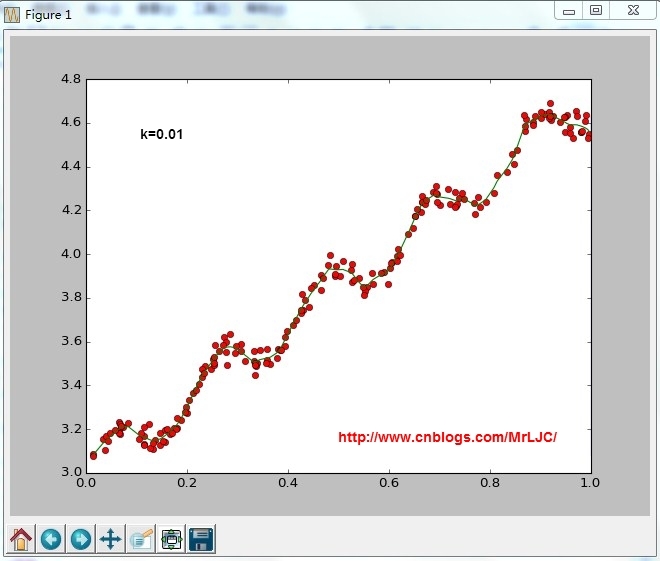
-
1 from numpy import * 2 def loadDataSet(fileName): 3 numFeat = len(open(fileName).readline().split(' ')) - 1 4 dataMat = []; labelMat = [] 5 fr = open(fileName) 6 for line in fr.readlines(): 7 lineArr =[] 8 curLine = line.strip().split(' ') 9 for i in range(numFeat): 10 lineArr.append(float(curLine[i])) 11 dataMat.append(lineArr) 12 labelMat.append(float(curLine[-1])) 13 return dataMat,labelMat 14 def standRegres(xArr,yArr): 15 xMat = mat(xArr) 16 yMat = mat(yArr).T 17 xTx = xMat.T * xMat 18 if linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0: 19 print 'This matrix is singular, cannot do inverse' 20 return 21 ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T * yMat) 22 return ws 23 def plotStandRegres(xArr,yArr,ws): 24 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 25 fig = plt.figure() 26 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 27 ax.plot([i[1] for i in xArr],yArr,'ro') 28 xCopy = xArr 29 print type(xCopy) 30 xCopy.sort() 31 yHat = xCopy*ws 32 ax.plot([i[1] for i in xCopy],yHat) 33 plt.show() 34 def calcCorrcoef(xArr,yArr,ws): 35 xMat = mat(xArr) 36 yMat = mat(yArr) 37 yHat = xMat*ws 38 return corrcoef(yHat.T, yMat) 39 def lwlr(testPoint,xArr,yArr,k=1.0): 40 xMat = mat(xArr); yMat = mat(yArr).T 41 m = shape(xMat)[0] 42 weights = mat(eye((m))) 43 for j in range(m): 44 diffMat = testPoint - xMat[j,:] 45 weights[j,j] = exp(diffMat*diffMat.T/(-2.0*k**2)) 46 xTx = xMat.T * (weights * xMat) 47 if linalg.det(xTx) == 0.0: 48 print "This matrix is singular, cannot do inverse" 49 return 50 ws = xTx.I * (xMat.T * (weights * yMat)) 51 return testPoint * ws 52 def lwlrTest(testArr,xArr,yArr,k=1.0): 53 m = shape(testArr)[0] 54 yHat = zeros(m) 55 for i in range(m): 56 yHat[i] = lwlr(testArr[i],xArr,yArr,k) 57 return yHat 58 def lwlrTestPlot(xArr,yArr,k=1.0): 59 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 60 yHat = zeros(shape(yArr)) 61 xCopy = mat(xArr) 62 xCopy.sort(0) 63 for i in range(shape(xArr)[0]): 64 yHat[i] = lwlr(xCopy[i],xArr,yArr,k) 65 fig = plt.figure() 66 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) 67 ax.plot([i[1] for i in xArr],yArr,'ro') 68 ax.plot(xCopy,yHat) 69 plt.show() 70 #return yHat,xCopy 71 def rssError(yArr,yHatArr): #yArr and yHatArr both need to be arrays 72 return ((yArr-yHatArr)**2).sum() 73 def main(): 74 #regression 75 xArr,yArr = loadDataSet('ex0.txt') 76 ws = standRegres(xArr,yArr) 77 print ws 78 #plotStandRegres(xArr,yArr,ws) 79 print calcCorrcoef(xArr,yArr,ws) 80 #lwlr 81 lwlrTestPlot(xArr,yArr,k=1) 82 if __name__ == '__main__': 83 main()