一、简介
spring事件是观察者设计模式的实现,主要有三个元素:
- 事件 spring事件由ApplicationEvent定义
- 监听者 由ApplicationListener定义
- 发布者 由ApplicationEventPublisher定义,而ApplicationContext继承自ApplicationEventPublisher
简单示例:
自定义事件
public class TestEvent extends ApplicationEvent { private String message; public TestEvent(Object source) { this(source, "default message"); } public TestEvent(Object source, String msg) { super(source); this.message = msg; } public String getMessage() { return message; } }
监听者
@Component public class TestListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { if (event instanceof TestEvent) { System.out.println(((TestEvent)event).getMessage()); } } }
XML配置
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.matt.event"/>
测试
public class EventTest { @Test public void testCustomEvent() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring-context.xml"); context.publishEvent(new TestEvent("", "hello matt")); } }
补充:
定义监听者时,可通过泛型指定监听事件类型,因此,上例监听者可定义如下:
@Component public class TestListener implements ApplicationListener<TestEvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(TestEvent event) { System.out.println(((TestEvent) event).getMessage()); } }
二、spring容器事件
spring为容器启动各阶段定义了相关事件,实现如图:
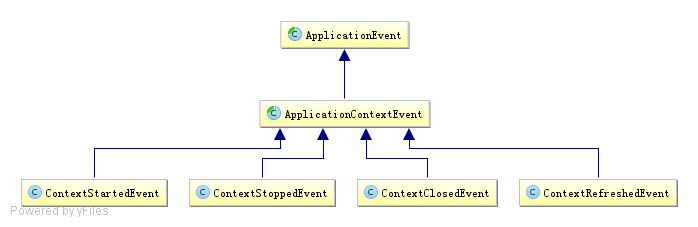
事件说明:
- ContextStartedEvent:ApplicationContext启动后触发的事件(调用start方法)
- ContextStoppedEvent:ApplicationContext停止后触发的事件(调用stop方法)
- ContextClosedEvent:ApplicationContext关闭后触发的事件
- ContextRefreshedEvent:ApplicationContext初始化或刷新完成后触发的事件(容器初始化(如bean的实例化、依赖注入)完成后调用)
使用示例
@Component public class ApplicationStartUpListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) { System.out.println("spring context inited"); } }
三、事件的执行机制
spring事件的执行机制默认使用单线程同步执行,异步执行可使用@Async注解实现,示例如下(新用户注册):
定义事件
public class RegisterEvent extends ApplicationEvent { public RegisterEvent(User user) { super(user); } }
定义监听者
// 发生邮件
@Component public class EmailRegisterListener implements ApplicationListener<RegisterEvent> { @Async public void onApplicationEvent(final RegisterEvent event) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + " **** 注册成功,发送确认邮件给:" + ((User)event.getSource()).getUsername()); } }
// 赠送积分 @Component public class PointRegisterListener implements ApplicationListener<RegisterEvent> { @Async public void onApplicationEvent(final RegisterEvent event) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + " **** 注册成功,赠送积分给:" + ((User)event.getSource()).getUsername()); } }
// 赠送大礼包 @Component public class PresentRegisterListener implements ApplicationListener<RegisterEvent> { @Async public void onApplicationEvent(final RegisterEvent event) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId() + " **** 注册成功,赠送大礼包给:" + ((User)event.getSource()).getUsername()); } }
用户类与业务类
public class User implements Serializable { private String username; private String password; public User(String username, String password) { this.username = username; this.password = password; } public String getUsername() { return username; } }
@Service public class RegisterService { @Autowired private ApplicationContext applicationContext; public void register(String username, String password) { System.out.println(username + "注册成功!"); publishRegisterEvent(new User(username, password)); } private void publishRegisterEvent(User user) { applicationContext.publishEvent(new RegisterEvent(user)); } }
配置
<context:component-scan base-package="com.sishuok"/> <!-- 任务调度器 --> <task:scheduler id="scheduler" pool-size="10"/> <!-- 任务执行器 --> <task:executor id="executor" pool-size="10"/> <!--开启注解调度支持 @Async @Scheduled--> <task:annotation-driven executor="executor" scheduler="scheduler" proxy-target-class="true"/>
测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:spring-config-register.xml"}) public class RegisterServiceIT { @Autowired private RegisterService registerService; @Test public void testRegister() { registerService.register("long", "123"); } } // 输出: // long注册成功! // 15 **** 注册成功,发送确认邮件给:long // 17 **** 注册成功,赠送积分给:long // 18 **** 注册成功,赠送大礼包给:long
参考: