链表和递归
5-1 Leetcode中和链表相关的问题
Java类的递归,包含的成员变量有该类本身。
ListNode

//Definition for singly-linked list. public class ListNode { public int val; public ListNode next; public ListNode(int x) { val = x; } }
/// Leetcode 203. Remove Linked List Elements
/// https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
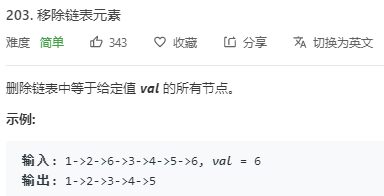
Solution

/// Leetcode 203. Remove Linked List Elements /// https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/ class Solution { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { while(head != null && head.val == val){ ListNode delNode = head; head = head.next; delNode.next = null; } if(head == null) return head; ListNode prev = head; while(prev.next != null){ if(prev.next.val == val) { ListNode delNode = prev.next; prev.next = delNode.next; delNode.next = null; } else prev = prev.next; } return head; } }
Solution2

/// Leetcode 203. Remove Linked List Elements /// https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/ class Solution2 { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { while(head != null && head.val == val) head = head.next; if(head == null) return head; ListNode prev = head; while(prev.next != null){ if(prev.next.val == val) prev.next = prev.next.next; else prev = prev.next; } return head; } }
Solution3

/// Leetcode 203. Remove Linked List Elements /// https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/ class Solution3 { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); dummyHead.next = head; ListNode prev = dummyHead; while(prev.next != null){ if(prev.next.val == val) prev.next = prev.next.next; else prev = prev.next; } return dummyHead.next; } }
5-2 测试自己的Leetcode链表代码

//Definition for singly-linked list. public class ListNode { public int val; public ListNode next; public ListNode(int x) { val = x; } // 链表节点的构造函数 // 使用arr为参数,创建一个链表,当前的ListNode为链表头结点 public ListNode(int[] arr){ if(arr == null || arr.length == 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("arr can not be empty"); this.val = arr[0]; ListNode cur = this; for(int i = 1 ; i < arr.length ; i ++){ cur.next = new ListNode(arr[i]); cur = cur.next; } } // 以当前节点为头结点的链表信息字符串 @Override public String toString(){ StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); ListNode cur = this; while(cur != null){ s.append(cur.val + "->"); cur = cur.next; } s.append("NULL"); return s.toString(); } }
class Solution3

class Solution3 { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(-1); dummyHead.next = head; ListNode prev = dummyHead; while(prev.next != null){ if(prev.next.val == val) prev.next = prev.next.next; else prev = prev.next; } return dummyHead.next; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {1, 2, 6, 3, 4, 5, 6}; ListNode head = new ListNode(nums); System.out.println(head); ListNode res = (new Solution3()).removeElements(head, 6); System.out.println(res); } }
5-3 递归基础与递归的宏观语意
本质上,将原来的问题,转化为更小的同一问题。
递归函数就是一个函数,完成一个功能。


public class Sum { public static int sum(int[] arr){ return sum(arr, 0); } // 计算arr[l...n)这个区间内所有数字的和 private static int sum(int[] arr, int l){ if(l == arr.length) return 0; return arr[l] + sum(arr, l + 1); } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}; System.out.println(sum(nums)); } }
5-4 链表的天然递归结构性质
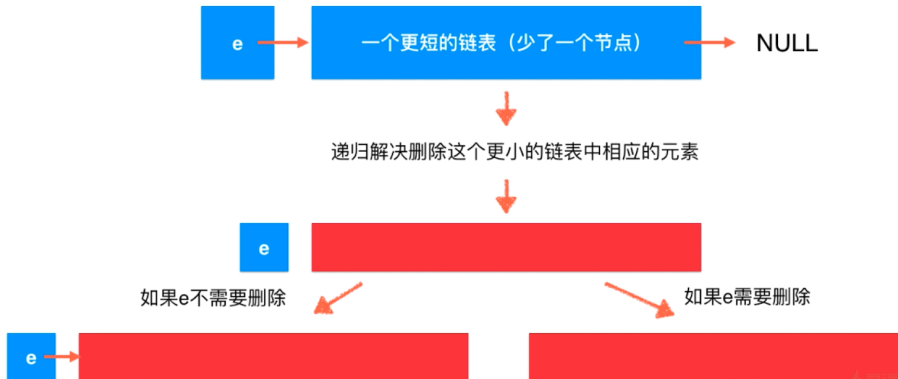

class Solution4 { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { if(head == null) return head; ListNode res = removeElements(head.next, val); if(head.val == val) return res; else{ head.next = res; return head; } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {1, 2, 6, 3, 4, 5, 6}; ListNode head = new ListNode(nums); System.out.println(head); ListNode res = (new Solution4()).removeElements(head, 6); System.out.println(res); } }
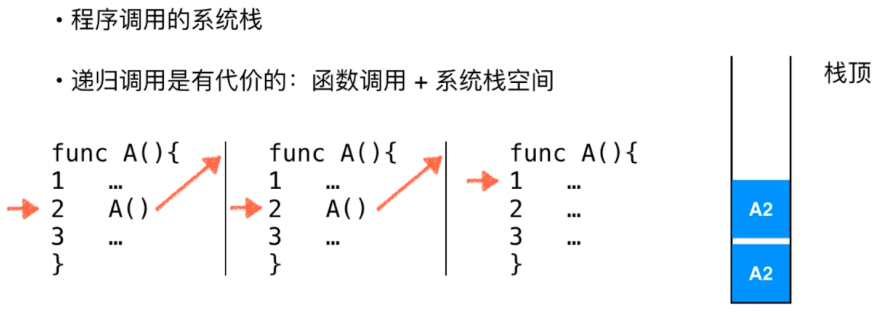
5-5 递归运行的机制:递归的微观解读