关于inflate问题,我想很多人多多少少都了解一点,网上也有很多关于这方面介绍的文章,但是枯燥的理论或者翻译让很多小伙伴看完之后还是一脸懵逼,so,我今天想通过三个案例来让小伙伴彻底的搞清楚这个东东。
0.获取inflater
在 实际开发中LayoutInflater这个类还是非常有用的,它的作用类似于findViewById()。不同点是LayoutInflater是用 来找res/layout/下的xml布局文件,并且实例化;而findViewById()是找xml布局文件下的具体widget控件(如 Button、TextView等)。 具体作用:
1、对于一个没有被载入或者想要动态载入的界面,都需要使用LayoutInflater.inflate()来载入;
2、对于一个已经载入的界面,就可以使用Activiyt.findViewById()方法来获得其中的界面元素。
LayoutInflater 是一个抽象类,在文档中如下声明:
public abstract class LayoutInflater extends Object
获得 LayoutInflater 实例的三种方式
LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater(); //调用Activity的getLayoutInflater()
LayoutInflater localinflater =(LayoutInflater)context.getSystemService (Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
其实,这三种方式本质是相同的,从源码中可以看出:
getLayoutInflater():
Activity 的 getLayoutInflater() 方法是调用 PhoneWindow 的getLayoutInflater()方法,看一下该源代码:
可以看出它其实是调用 LayoutInflater.from(context)。
public PhoneWindow(Context context) {
super(context);
mLayoutInflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
} LayoutInflater.from(context):
可以看出它其实调用 context.getSystemService()。
public static LayoutInflater from(Context context) {
LayoutInflater LayoutInflater =
(LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
if (LayoutInflater == null) {
throw new AssertionError("LayoutInflater not found.");
}
return LayoutInflater;
} inflate方法从大范围来看,分两种,三个参数的构造方法和两个参数的构造方法。
在这两类中又有细分,OK,那我们就把各种情况都来演示一遍。
1.三个参数的inflate方法
方法头如下:
public View inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)
好,这里主要分为三种情况,分别来看:
1.1 root不为null,attachToRoot为true
当root不为null,attachToRoot为true时,表示将resource指定的布局添加到root中,添加的过程中resource所指定的的布局的根节点的各个属性都是有效的。比如下面一个案例,我的Activity的布局如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:id="@+id/ll"
tools:context="org.sang.layoutinflater.MainActivity">
</LinearLayout>
我还有一个布局linearlayout.xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/ll"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
我现在想把这个linearlayout.xml布局文件添加到我的activity的布局中,那么我可以这么做:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LinearLayout ll = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll);
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
inflater.inflate(R.layout.linearlayout, ll,true);
}
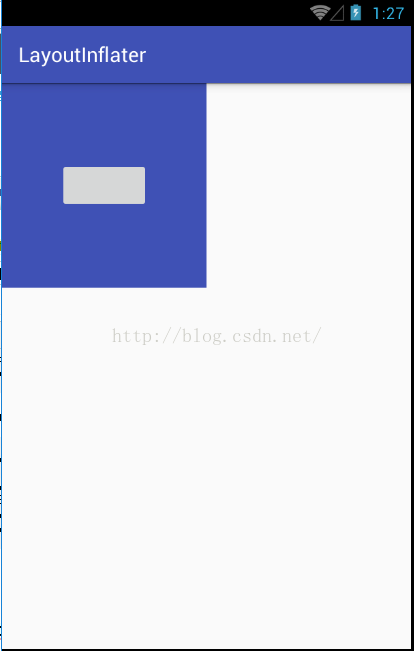
小伙伴们注意到,这里我都没写将inflate出来的View添加到ll中的代码,但是linearlayout布局文件就已经添加进来了,这就是因为我第三个参数设置为了true,表示将第一个参数所指定的布局添加到第二个参数的View中。最终显示效果如下:
如果我作死多写这么一行代码,如下:
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LinearLayout ll = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll);
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.linearlayout, ll, true);
ll.addView(view);
}
这个时候再运行,系统会抛如下异常:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: The specified child already has a parent. You must call removeView() on the child's parent first.
原因就是因为当第三个参数为true时,会自动将第一个参数所指定的View添加到第二个参数所指定的View中。
1.2 root不为null,attachToRoot为false
如果root不为null,而attachToRoot为false的话,表示不将第一个参数所指定的View添加到root中,那么这个时候有的小伙伴可能就有疑问了,既然不添加到root中,那我还写这么多干嘛?我第二个参数直接给null不就可以了?其实不然,这里涉及到另外一个问题:我们在开发的过程中给控件所指定的layout_width和layout_height到底是什么意思?该属性的表示一个控件在容器中的大小,就是说这个控件必须在容器中,这个属性才有意义,否则无意义。这就意味着如果我直接将linearlayout加载进来而不给它指定一个父布局,则inflate布局的根节点的layout_width和layout_height属性将会失效(因为这个时候linearlayout将不处于任何容器中,那么它的根节点的宽高自然会失效)。如果我想让linearlayout的根节点有效,又不想让其处于某一个容器中,那我就可以设置root不为null,而attachToRoot为false。这样,指定root的目的也就很明确了,即root会协助linearlayout的根节点生成布局参数,只有这一个作用。OK,还是上面的布局文件,如果我想将之添加到activity的布局中又该如何呢?
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LinearLayout ll = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll);
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.linearlayout, ll, false);
ll.addView(view);
}
大家注意,这个时候我需要手动的将inflate加载进来的view添加到ll容器中,因为inflate的最后一个参数false表示不将linealayout添加到ll中。显示效果和上文一样,不再贴图。
1.3 root为null
当root为null时,不论attachToRoot为true还是为false,显示效果都是一样的。当root为null表示我不需要将第一个参数所指定的布局添加到任何容器中,同时也表示没有任何容器来来协助第一个参数所指定布局的根节点生成布局参数。我还是使用上文提到的linearlayout,我们来看下面一段代码:
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LinearLayout ll = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll);
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.linearlayout, null, false);
ll.addView(view);
}
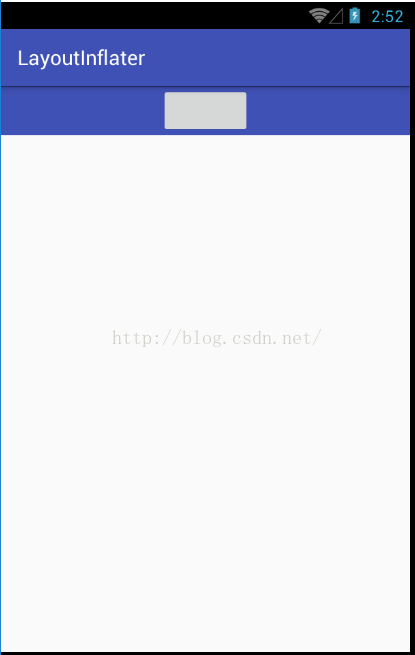
当第二个参数为null,第三个参数为false时(即使为true显示效果也是一样的,这里以false为例),由于在inflate方法中没有将linearlayout添加到某一个容器中,所以我需要手动添加,另外由于linearlayout并没有处于某一个容器中,所以它的根节点的宽高属性会失效,显示效果如下:
小伙伴们注意,这个时候不管我给linearlayout的根节点的宽高设置什么,都是没有效果的,它都是包裹button,如果我修改button,则button会立即有变化,因为button是处于某一个容器中的。
2.两个参数的inflate方法
两个参数的inflate方法就很简单了,我们来稍微看一点点源码:
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, @Nullable ViewGroup root) {
return inflate(parser, root, root != null);
}
这是两个参数的inflate方法,大家注意两个参数实际上最终也是调用了三个参数。
两个参数的inflate方法分为如下两种情况:
1.root为null,等同于1.3所述情况。
2.root不为null,等同于1.1所述情况。
3.为什么Activity布局的根节点的宽高属性会生效?
inflate方法我们已经说完了,小伙伴们可能有另外一个疑问,那为什么Activity布局的根节点的宽高属性会生效?其实原因很简单,大部分情况下我们一个Activity页面由两部分组成(Android的版本号和应用主题会影响到Activity页面组成,这里以常见页面为例),我们的页面中有一个顶级View叫做DecorView,DecorView中包含一个竖直方向的LinearLayout,LinearLayout由两部分组成,第一部分是标题栏,第二部分是内容栏,内容栏是一个FrameLayout,我们在Activity中调用setContentView就是将View添加到这个FrameLayout中,所以给大家一种错觉仿佛Activity的根布局很特殊,其实不然。
OK,以上就是对LayoutInflater中inflate方法的一个简单介绍,希望能够帮助到还没弄懂这个的小伙伴。