25、自动装配-@Profile根据环境注册bean
- 指定组件在哪个环境的情况下才能被注册到容器中
- 加了环境标识的,只有这个环境被激活才能注册到组件中
- 默认是default环境
- 写在类上,整个配置类的激活的时候才能生效
- 没有标注环境标识的bean,在任何环境下都是加载的
package org.springframework.context.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.env.AbstractEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.Profiles;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(ProfileCondition.class)
public @interface Profile {
/**
* 指定组件在哪个环境的情况下才能被注册到容器中
* The set of profiles for which the annotated component should be registered.
*/
String[] value();
}
25.1 实现
package com.hw.springannotation.config;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.EmbeddedValueResolverAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringValueResolver;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
/**
* @Description Profile
* @Author hw
* @Date 2018/11/29 19:25
* @Version 1.0
*/
@Component
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:/datasource.properties"})
public class MainConfigOfProfile implements EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
@Value("${db.username}")
private String username;
private String driveClassName;
private StringValueResolver resolver;
public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) {
this.resolver = resolver;
this.driveClassName = this.resolver.resolveStringValue("${db.driveClassName}");
}
@Profile("default")
@Bean
public DataSource dataSourceTest(@Value("${db.password}") String password) throws PropertyVetoException {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test");
dataSource.setDriverClass(driveClassName);
return dataSource;
}
@Profile("dev")
@Bean
public DataSource dataSourceDev(@Value("${db.password}") String password) throws PropertyVetoException {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysql");
dataSource.setDriverClass(driveClassName);
return dataSource;
}
@Profile("prod")
@Bean
public DataSource dataSourceProd(@Value("${db.password}") String password) throws PropertyVetoException {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/qm_dmp");
dataSource.setDriverClass(driveClassName);
return dataSource;
}
}
运行:
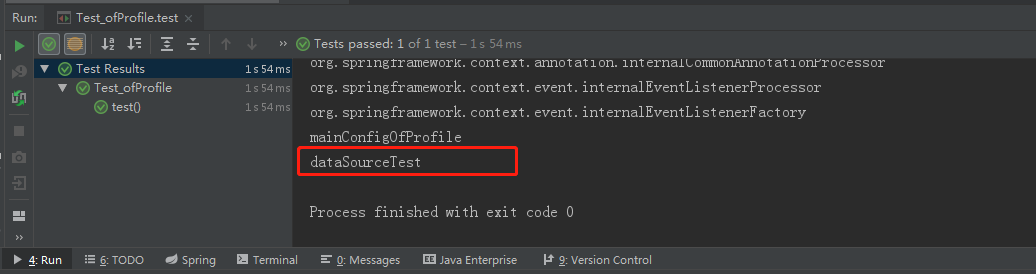
25.2 切换环境-使用命令行动态参数
- 在运行时指定
-Dspring.profiles.active=prod
25.3 切换环境-使用代码的方式
- 之前使用的是有参构造器,配置加载完,容器就刷新了,所以使用无参构造器
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... annotatedClasses) {
this();
register(annotatedClasses);
refresh();
}
步骤
- 构造IOC容器
- 设置需要激活的环境
- 注入配置类
- 启动刷新容器
@Test
public void test() {
// 1. 构造IOC容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
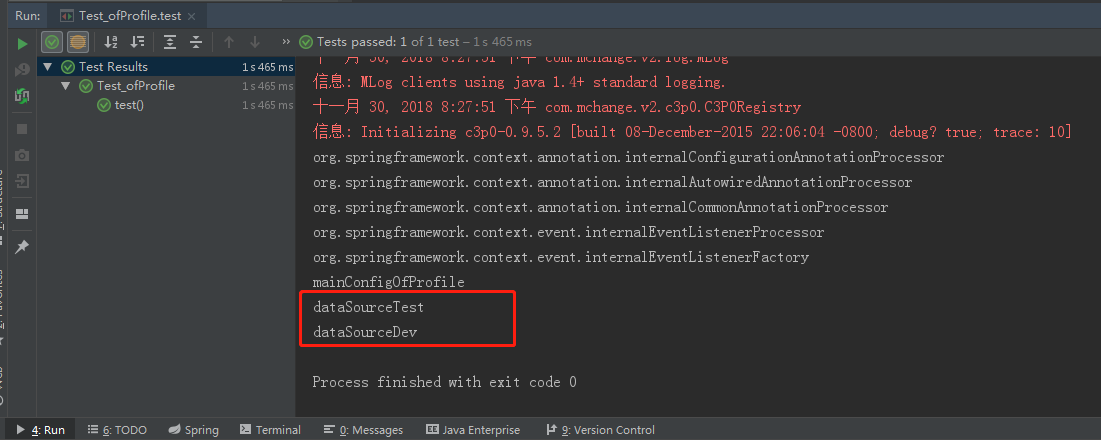
// 2. 设置需要激活的环境(可以同时激活多个)
applicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("test", "dev");
// 3. 注入配置类
applicationContext.register(MainConfigOfProfile.class);
// 4. 启动刷新容器
applicationContext.refresh();
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}