1.gcc的有关知识
运行环境:
Vbox and redhat 6.4
1.1 gcc特点:
Gcc(GNU C Compiler)是GNU推出的功能强大、性能优越的多平台编译器,是GNU的代表作之一。Gcc可以在多种硬体平台上编译出可执行程序,其执行效率与一般的编译器相比平均效率要高20%~30%。
1.2 gcc基本用法:
Gcc最基本的用法是:
Gcc [options] filenames
Options:编译器所需要的编译选项。
Filenames:要编译的文件名。
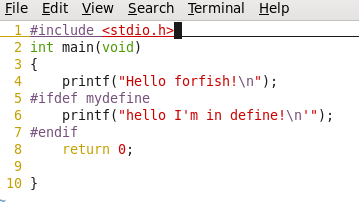
新建一个hello.c文件,内容如下:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("Hello forfish! ");
return 0;
}
编辑的过程如下:

1.3
2.1编译的流程:
Gcc编译器能将C/C++语言源程序、汇编程序形成可执行文件。整个形成过程可以被细分为四个阶段:

1.预处理:

Hello.i的内容:
# 1 "hello.c"
# 1 "<built-in>"
# 1 "<command-line>"
# 1 "hello.c"
# 1 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 1 3 4
# 28 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/features.h" 1 3 4
# 361 "/usr/include/features.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 1 3 4
# 365 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/wordsize.h" 1 3 4
# 366 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 2 3 4
# 362 "/usr/include/features.h" 2 3 4
# 385 "/usr/include/features.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs.h" 1 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/wordsize.h" 1 3 4
# 5 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs-32.h" 1 3 4
# 8 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs.h" 2 3 4
# 386 "/usr/include/features.h" 2 3 4
# 29 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-redhat-linux/4.4.7/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4
# 211 "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-redhat-linux/4.4.7/include/stddef.h" 3 4
typedef unsigned int size_t;
# 35 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 1 3 4
# 28 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/wordsize.h" 1 3 4
# 29 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 2 3 4
typedef unsigned char __u_char;
typedef unsigned short int __u_short;
typedef unsigned int __u_int;
typedef unsigned long int __u_long;
typedef signed char __int8_t;
typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
typedef signed short int __int16_t;
typedef unsigned short int __uint16_t;
typedef signed int __int32_t;
typedef unsigned int __uint32_t;
__extension__ typedef signed long long int __int64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long long int __uint64_t;
__extension__ typedef long long int __quad_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long long int __u_quad_t;
# 131 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/typesizes.h" 1 3 4
# 132 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 2 3 4
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __dev_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __uid_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __gid_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long int __ino_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __ino64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __mode_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __nlink_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __off_t;
__extension__ typedef __quad_t __off64_t;
__extension__ typedef int __pid_t;
__extension__ typedef struct { int __val[2]; } __fsid_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __clock_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long int __rlim_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __rlim64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __id_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __time_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __useconds_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __suseconds_t;
__extension__ typedef int __daddr_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __swblk_t;
__extension__ typedef int __key_t;
__extension__ typedef int __clockid_t;
__extension__ typedef void * __timer_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __blksize_t;
__extension__ typedef long int __blkcnt_t;
__extension__ typedef __quad_t __blkcnt64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __fsblkcnt64_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt_t;
__extension__ typedef __u_quad_t __fsfilcnt64_t;
__extension__ typedef int __ssize_t;
typedef __off64_t __loff_t;
typedef __quad_t *__qaddr_t;
typedef char *__caddr_t;
__extension__ typedef int __intptr_t;
__extension__ typedef unsigned int __socklen_t;
# 37 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 45 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
struct _IO_FILE;
typedef struct _IO_FILE FILE;
# 65 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
typedef struct _IO_FILE __FILE;
# 75 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/libio.h" 1 3 4
# 32 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/_G_config.h" 1 3 4
# 15 "/usr/include/_G_config.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-redhat-linux/4.4.7/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4
# 16 "/usr/include/_G_config.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/wchar.h" 1 3 4
# 83 "/usr/include/wchar.h" 3 4
typedef struct
{
int __count;
union
{
unsigned int __wch;
char __wchb[4];
} __value;
} __mbstate_t;
# 21 "/usr/include/_G_config.h" 2 3 4
typedef struct
{
__off_t __pos;
__mbstate_t __state;
} _G_fpos_t;
typedef struct
{
__off64_t __pos;
__mbstate_t __state;
} _G_fpos64_t;
# 53 "/usr/include/_G_config.h" 3 4
typedef int _G_int16_t __attribute__ ((__mode__ (__HI__)));
typedef int _G_int32_t __attribute__ ((__mode__ (__SI__)));
typedef unsigned int _G_uint16_t __attribute__ ((__mode__ (__HI__)));
typedef unsigned int _G_uint32_t __attribute__ ((__mode__ (__SI__)));
# 33 "/usr/include/libio.h" 2 3 4
# 53 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-redhat-linux/4.4.7/include/stdarg.h" 1 3 4
# 40 "/usr/lib/gcc/i686-redhat-linux/4.4.7/include/stdarg.h" 3 4
typedef __builtin_va_list __gnuc_va_list;
# 54 "/usr/include/libio.h" 2 3 4
# 170 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
struct _IO_jump_t; struct _IO_FILE;
# 180 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
typedef void _IO_lock_t;
struct _IO_marker {
struct _IO_marker *_next;
struct _IO_FILE *_sbuf;
int _pos;
# 203 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
};
enum __codecvt_result
{
__codecvt_ok,
__codecvt_partial,
__codecvt_error,
__codecvt_noconv
};
# 271 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
struct _IO_FILE {
int _flags;
char* _IO_read_ptr;
char* _IO_read_end;
char* _IO_read_base;
char* _IO_write_base;
char* _IO_write_ptr;
char* _IO_write_end;
char* _IO_buf_base;
char* _IO_buf_end;
char *_IO_save_base;
char *_IO_backup_base;
char *_IO_save_end;
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
int _fileno;
int _flags2;
__off_t _old_offset;
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
# 319 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
__off64_t _offset;
# 328 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
void *__pad1;
void *__pad2;
void *__pad3;
void *__pad4;
size_t __pad5;
int _mode;
char _unused2[15 * sizeof (int) - 4 * sizeof (void *) - sizeof (size_t)];
};
typedef struct _IO_FILE _IO_FILE;
struct _IO_FILE_plus;
extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdin_;
extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdout_;
extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stderr_;
# 364 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
typedef __ssize_t __io_read_fn (void *__cookie, char *__buf, size_t __nbytes);
typedef __ssize_t __io_write_fn (void *__cookie, __const char *__buf,
size_t __n);
typedef int __io_seek_fn (void *__cookie, __off64_t *__pos, int __w);
typedef int __io_close_fn (void *__cookie);
# 416 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
extern int __underflow (_IO_FILE *);
extern int __uflow (_IO_FILE *);
extern int __overflow (_IO_FILE *, int);
# 460 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
extern int _IO_getc (_IO_FILE *__fp);
extern int _IO_putc (int __c, _IO_FILE *__fp);
extern int _IO_feof (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int _IO_ferror (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int _IO_peekc_locked (_IO_FILE *__fp);
extern void _IO_flockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern void _IO_funlockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int _IO_ftrylockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
# 490 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4
extern int _IO_vfscanf (_IO_FILE * __restrict, const char * __restrict,
__gnuc_va_list, int *__restrict);
extern int _IO_vfprintf (_IO_FILE *__restrict, const char *__restrict,
__gnuc_va_list);
extern __ssize_t _IO_padn (_IO_FILE *, int, __ssize_t);
extern size_t _IO_sgetn (_IO_FILE *, void *, size_t);
extern __off64_t _IO_seekoff (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int, int);
extern __off64_t _IO_seekpos (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int);
extern void _IO_free_backup_area (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
# 76 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
typedef __gnuc_va_list va_list;
# 91 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
typedef __off_t off_t;
# 103 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
typedef __ssize_t ssize_t;
typedef _G_fpos_t fpos_t;
# 161 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/stdio_lim.h" 1 3 4
# 162 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
extern struct _IO_FILE *stdin;
extern struct _IO_FILE *stdout;
extern struct _IO_FILE *stderr;
extern int remove (__const char *__filename) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int rename (__const char *__old, __const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int renameat (int __oldfd, __const char *__old, int __newfd,
__const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern FILE *tmpfile (void) ;
# 208 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern char *tmpnam (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
extern char *tmpnam_r (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
# 226 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern char *tempnam (__const char *__dir, __const char *__pfx)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__malloc__)) ;
extern int fclose (FILE *__stream);
extern int fflush (FILE *__stream);
# 251 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fflush_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
# 265 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *fopen (__const char *__restrict __filename,
__const char *__restrict __modes) ;
extern FILE *freopen (__const char *__restrict __filename,
__const char *__restrict __modes,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
# 294 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 305 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *fdopen (int __fd, __const char *__modes) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
# 318 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *fmemopen (void *__s, size_t __len, __const char *__modes)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
extern FILE *open_memstream (char **__bufloc, size_t *__sizeloc) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
extern void setbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int setvbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
int __modes, size_t __n) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern void setbuffer (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
size_t __size) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern void setlinebuf (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int fprintf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
__const char *__restrict __format, ...);
extern int printf (__const char *__restrict __format, ...);
extern int sprintf (char *__restrict __s,
__const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int vfprintf (FILE *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg);
extern int vprintf (__const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg);
extern int vsprintf (char *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int snprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
__const char *__restrict __format, ...)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 3, 4)));
extern int vsnprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
__const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 3, 0)));
# 416 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int vdprintf (int __fd, __const char *__restrict __fmt,
__gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 2, 0)));
extern int dprintf (int __fd, __const char *__restrict __fmt, ...)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 2, 3)));
extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
__const char *__restrict __format, ...) ;
extern int scanf (__const char *__restrict __format, ...) ;
extern int sscanf (__const char *__restrict __s,
__const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
# 447 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream, __const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_fscanf")
;
extern int scanf (__const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_scanf")
;
extern int sscanf (__const char *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_sscanf")
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
# 467 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0))) ;
extern int vscanf (__const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 1, 0))) ;
extern int vsscanf (__const char *__restrict __s,
__const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0)));
# 498 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vfscanf")
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0))) ;
extern int vscanf (__const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vscanf")
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 1, 0))) ;
extern int vsscanf (__const char *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vsscanf")
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0)));
# 526 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fgetc (FILE *__stream);
extern int getc (FILE *__stream);
extern int getchar (void);
# 554 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int getc_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
extern int getchar_unlocked (void);
# 565 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fgetc_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
extern int fputc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putchar (int __c);
# 598 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fputc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putchar_unlocked (int __c);
extern int getw (FILE *__stream);
extern int putw (int __w, FILE *__stream);
extern char *fgets (char *__restrict __s, int __n, FILE *__restrict __stream)
;
extern char *gets (char *__s) ;
# 660 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern __ssize_t __getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern __ssize_t getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern __ssize_t getline (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern int fputs (__const char *__restrict __s, FILE *__restrict __stream);
extern int puts (__const char *__s);
extern int ungetc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern size_t fread (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern size_t fwrite (__const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __s) ;
# 732 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern size_t fread_unlocked (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern size_t fwrite_unlocked (__const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern int fseek (FILE *__stream, long int __off, int __whence);
extern long int ftell (FILE *__stream) ;
extern void rewind (FILE *__stream);
# 768 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fseeko (FILE *__stream, __off_t __off, int __whence);
extern __off_t ftello (FILE *__stream) ;
# 787 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fgetpos (FILE *__restrict __stream, fpos_t *__restrict __pos);
extern int fsetpos (FILE *__stream, __const fpos_t *__pos);
# 810 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 819 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern void clearerr (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int feof (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
extern int ferror (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
extern void clearerr_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int feof_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
extern int ferror_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
extern void perror (__const char *__s);
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/sys_errlist.h" 1 3 4
# 27 "/usr/include/bits/sys_errlist.h" 3 4
extern int sys_nerr;
extern __const char *__const sys_errlist[];
# 849 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
extern int fileno (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
extern int fileno_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
# 868 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *popen (__const char *__command, __const char *__modes) ;
extern int pclose (FILE *__stream);
extern char *ctermid (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
# 908 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern void flockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int ftrylockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) ;
extern void funlockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
# 938 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 2 "hello.c" 2
int main(void)
{
printf("Hello forfish! ");
return 0;
}
2.编译生成汇编文件hello.s:
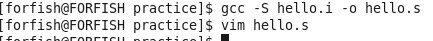
Hello.s 的内容:
.file "hello.c"
.section .rodata
.LC0:
.string "Hello forfish!"
.text
.globl main
.type main, @function
main:
pushl %ebp
movl %esp, %ebp
andl $-16, %esp
subl $16, %esp
movl $.LC0, (%esp)
call puts
movl $0, %eax
leave
ret
.size main, .-main
.ident "GCC: (GNU) 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-4)"
.section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
3.汇编:
打开看不见代码,因为是2进制文件。
4.链接运行:

2.1 gcc编译流程
Gcc通过后缀来区别输入文件的类别,常见类型有:
v .c为后缀的文件: C语言源代码文件
v .a为后缀的文件: 是由目标文件构成的库文件
v .C,.cc或.cxx 为后缀的文件: 是C++源代码文件
v .h为后缀的文件: 头文件
v .o为后缀的文件: 是编译后的目标文件
v .s为后缀的文件: 是汇编语言源代码文件
2.2 gcc编译选项
掌握Gcc的使用方法,最重要的是掌握Gcc的编译选项,Gcc编译器的编译选项大约有100多个,其中多数我们根本就用不到,这里只介绍其中最基本、最常用的参数。
-o output_filename:确定可执行文件的名称为output_filename。如果不给出这个选项,gcc就给出预设的可执行文件a.out。
-O,对程序进行优化编译、链接,采用这个选项,整个源代码会在编译、连接过程中进行优化处理,这样产生的可执行文件的执行效率可以提高,但是,编译、连接的速度就相应地要慢一些。
-O2,比-O更好的优化编译、连接,当然整个编译、连接过程会更慢。
实例:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
double counter;
double result;
double temp;
for(counter = 0; counter< 2000.0*2000.0*2000.0 / 20.0 + 2020;
counter += (5-1)/4){
temp = counter/1979;
result = counter;
}
printf("Result is %lf ",result);
return 0;
}
在上面的程序中result是没有用到的变量,该程序优化与否的时间差:
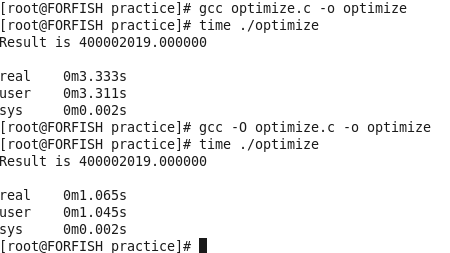
-c:条件是不链接。编译器只是由输入的.c等源代码文件编译生成.o为后缀的中间文件。
-g:条件是产生调试工具(GNU的gdb)所需要的符号信息,要想对编译出的程序进行调试,就必须加入这个选项。
加上-g的调试信息与否的文件大小:
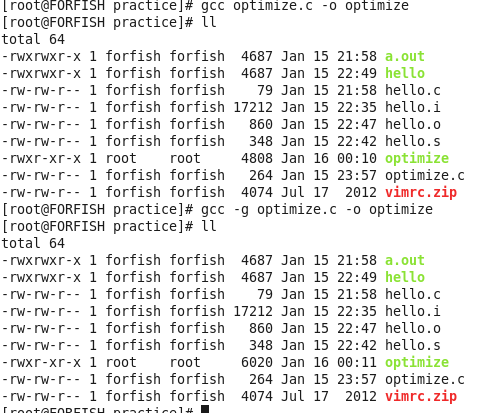
-I dirname:将dirname所指向的目录作为编译器寻找头文件的标准路径。
C程序中的头文件包含两种情况:
#include <a.h>
#include "b.h"
对于<>,gcc在系统预设的头文件目录/usr/include中寻找相应的文件;而对于"",gcc在当前目录中搜索头文件。-I选项的作用是告诉gcc,如果在当前目录中没有找到需要的文件,就到指定的dirname目录中去寻找。
例如:gcc hello.c –I /home/include –o hello

编译错误与编译警告都是我们的程序设计中经常遇到的问题。编译错误一般是代码中出现语法错误,程序无法编译执行,必须修改。编译错误是编译器发现程序中不合理地方(比如类型不匹配),建议最后修改,但不修改也可以编译执行。
-Wall:生成所有警告信息
-w:不生成任何警告信息。
-Dmydefi:定义mydefi宏,等效于在程序中使用#define mydefi.

如果在文件里没有定义需要的宏,可以在编译的时候用-D参数指定宏: