表不支持随机查找,通常是使用next指针进行操作。
206. 反转链表


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
//时间:O(n) 只遍历了一遍链表
//空间:O(1) 开了三个指针的空间
class Solution {
public:
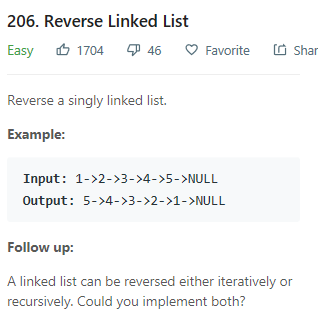
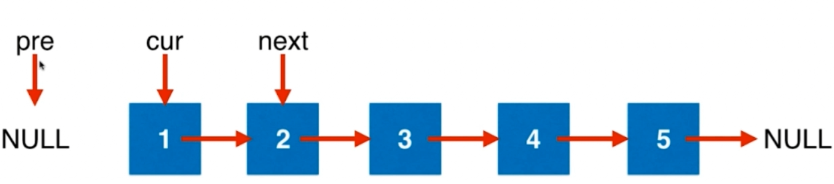
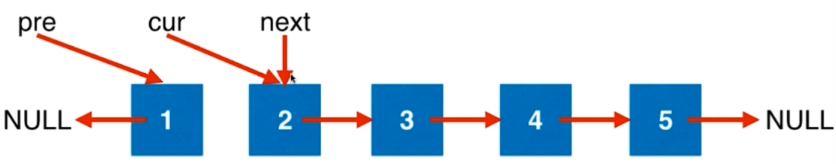
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
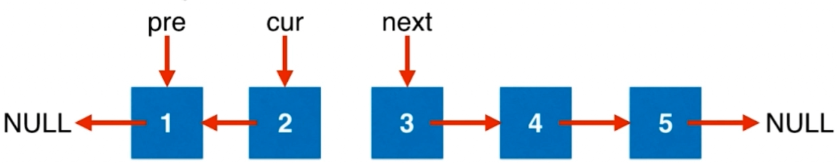
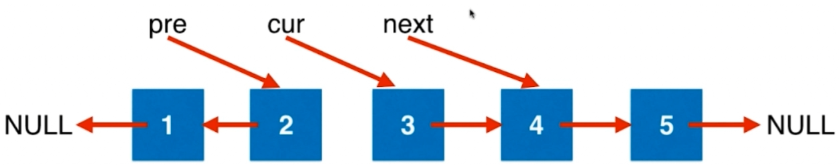
ListNode* pre = NULL, *cur = head, *next = NULL; //head为头指针指向链表中的第一个元素
while(cur != NULL){
//直到cur指向为空,循环结束。即pre指向链表的最后一个结点,也是新链表的头结点
next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};


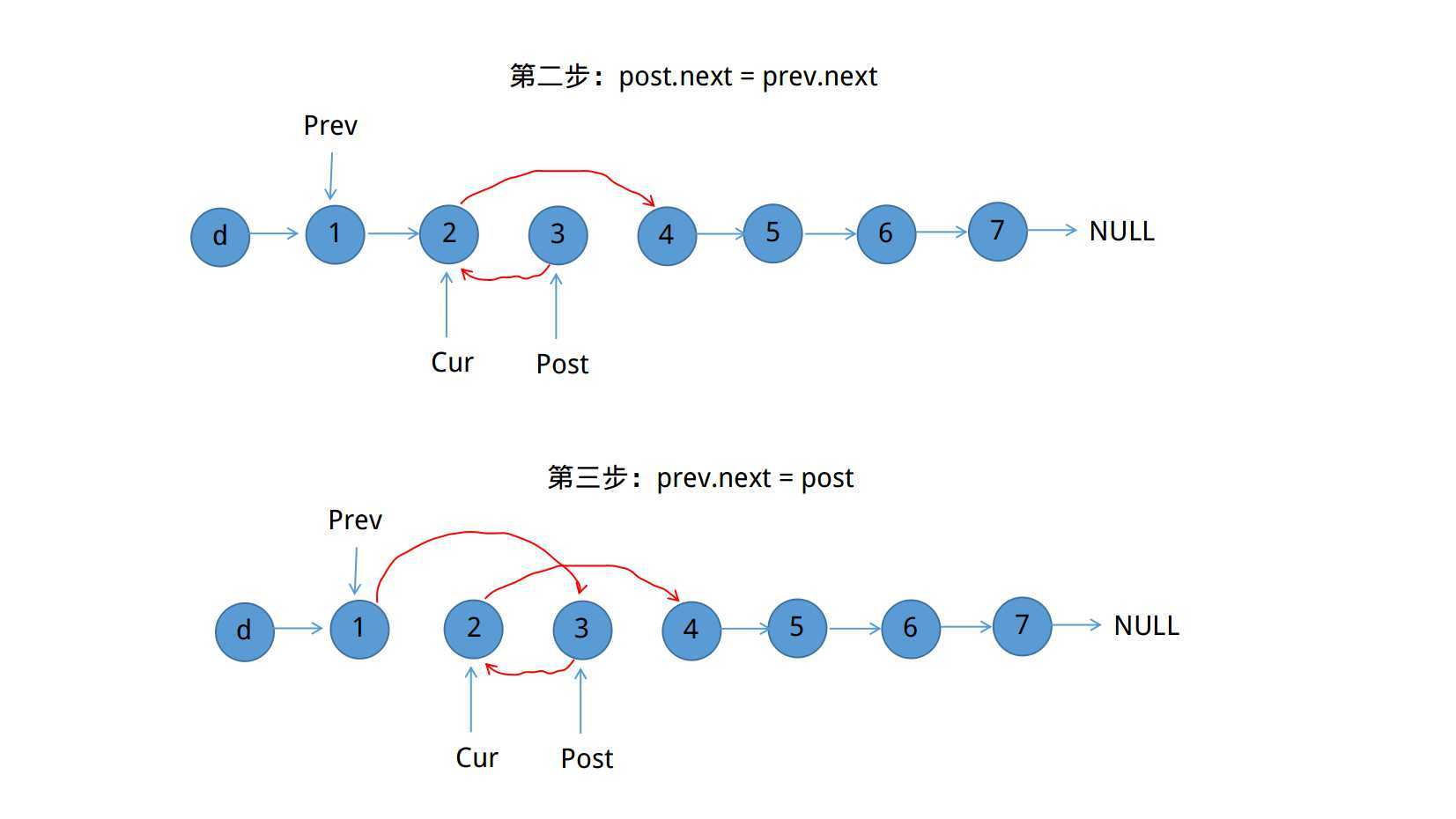
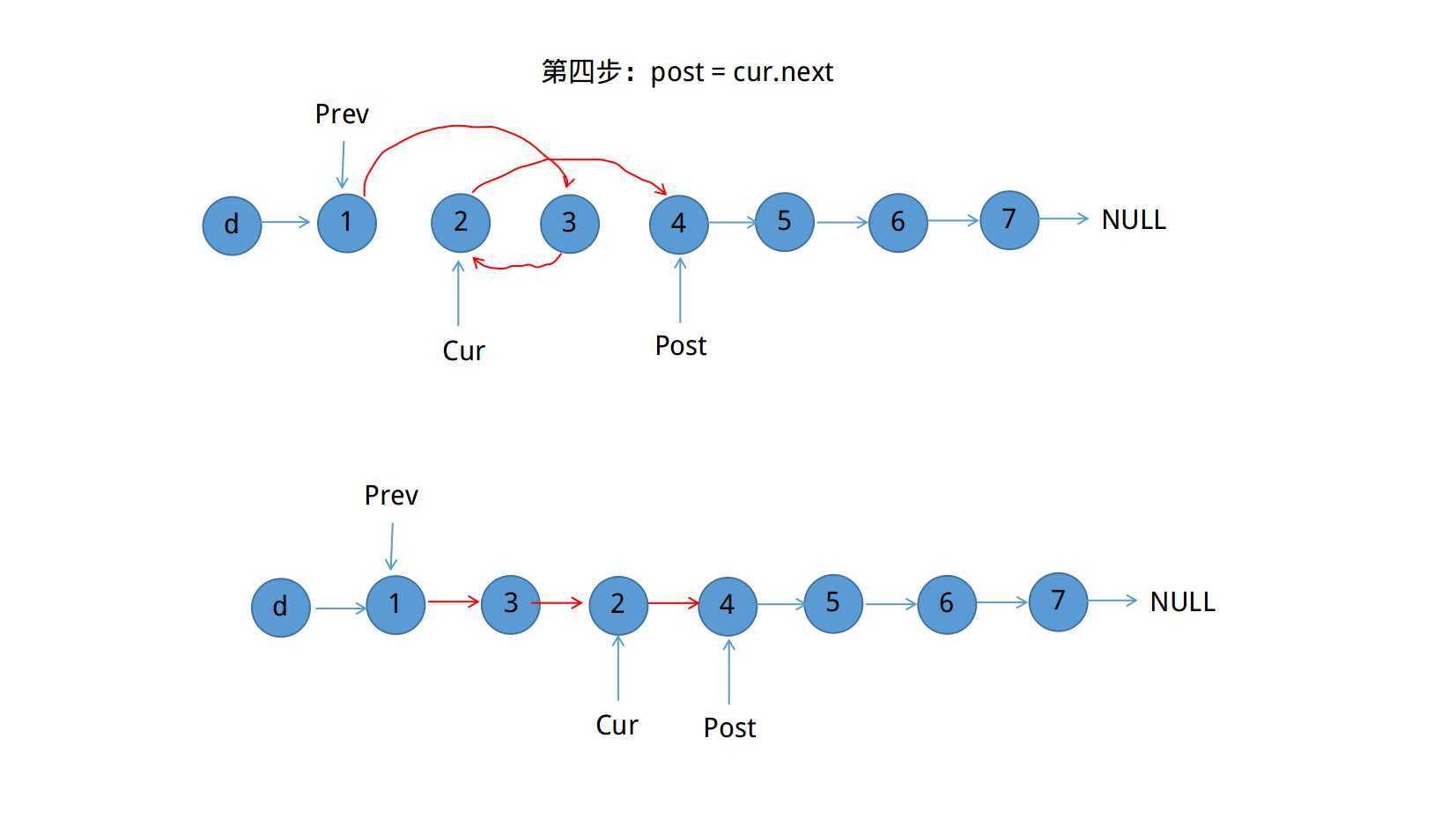
需要考虑以上两个问题,在本题中已经假定1 <= m <= n <= length of list
思路:



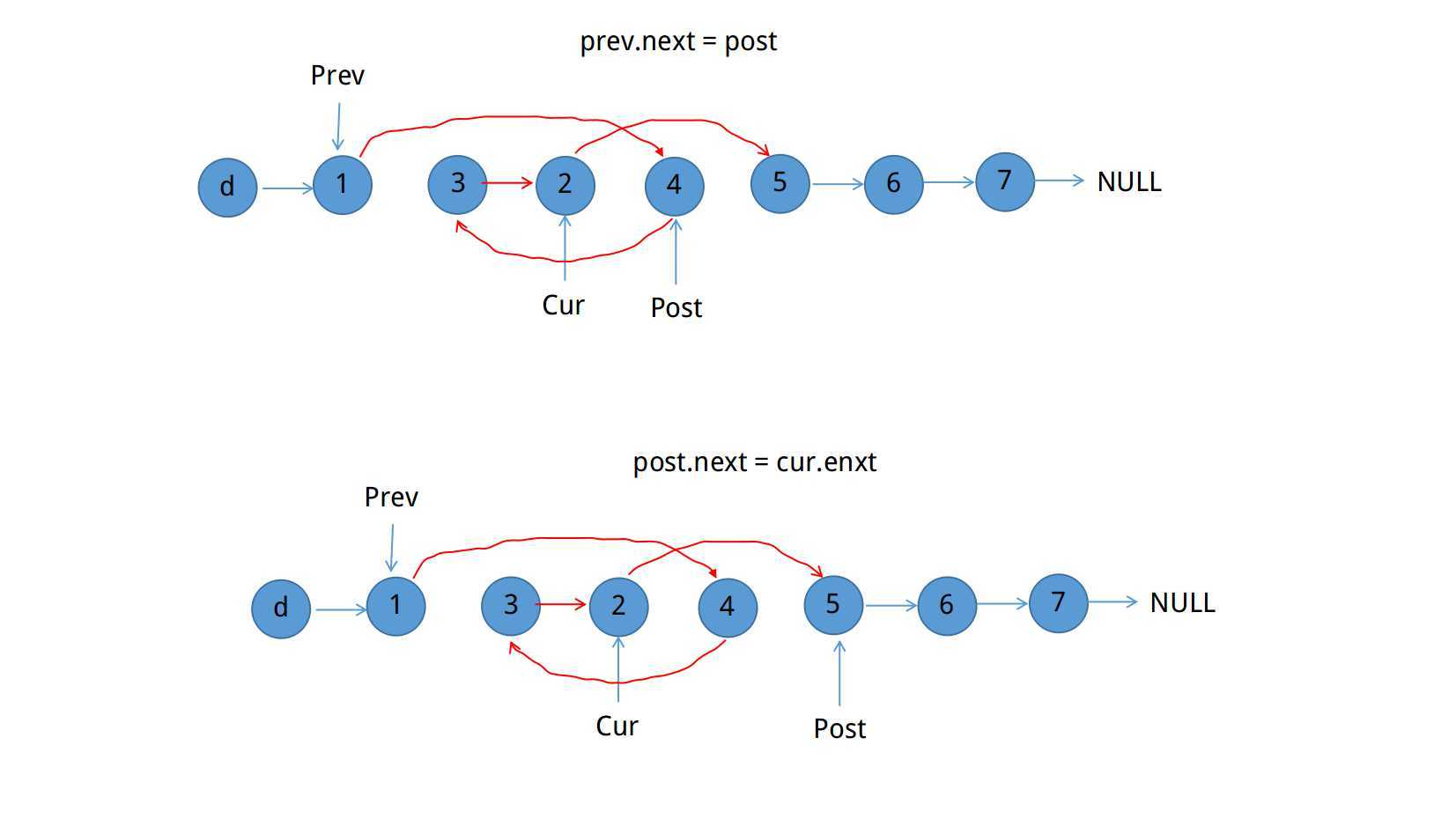
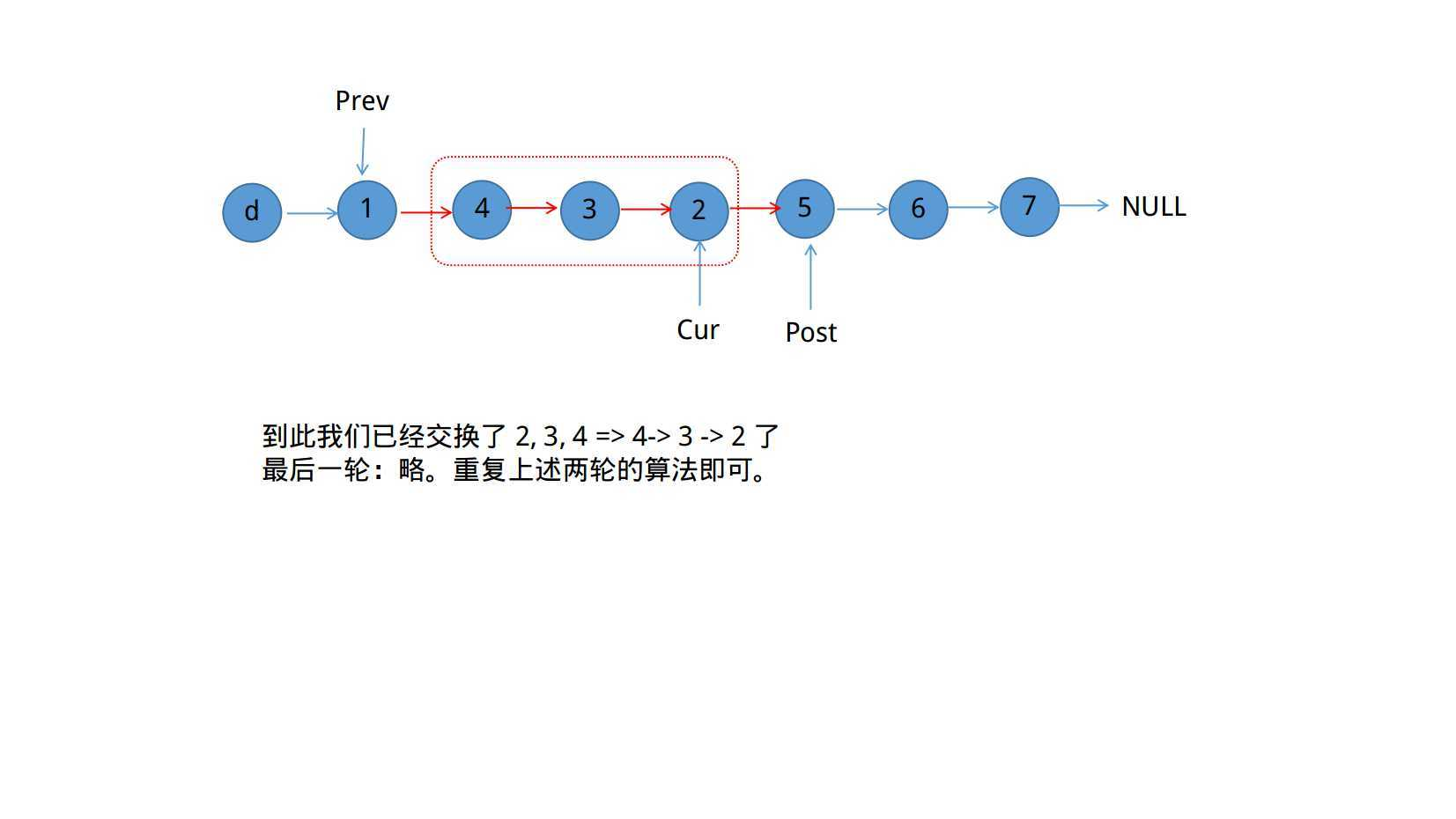
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
ListNode *guard = new ListNode(-1);
guard -> next = head;
ListNode *pre = guard;
for(int i=1;i<=m-1;i++)
pre = pre->next; //pre指向需要翻转链表的前一个结点
ListNode *cur = pre->next; //i指向翻转链表的第一个结点
ListNode *post = cur->next;
for(int i=1;i<=n-m;i++){
cur->next = post->next;
post->next = pre->next;
pre->next = post;
post = cur->next;
}
return guard -> next;
}
};
完整的翻转链表程序:
// list.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//
#include "pch.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
*/
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
// 根据n个元素的数组arr创建一个链表, 并返回链表的头
ListNode* createLinkedList(int arr[], int n) {
if (n == 0)
return NULL;
ListNode* head = new ListNode(arr[0]);
ListNode* curNode = head;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
curNode->next = new ListNode(arr[i]);
curNode = curNode->next;
}
return head;
}
// 打印以head为头结点的链表信息内容
void printLinkedList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* curNode = head;
while (curNode != NULL) {
cout << curNode->val << " -> ";
curNode = curNode->next;
}
cout << "NULL" << endl;
return;
}
// 释放以head为头结点的链表空间
void deleteLinkedList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* curNode = head;
while (curNode != NULL) {
ListNode* delNode = curNode;
curNode = curNode->next;
delete delNode;
}
return;
}
// 206. Reverse Linked List
// https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
// 时间复杂度: O(n)
// 空间复杂度: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* pre = NULL;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != NULL) {
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
int main() {
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);
ListNode* head = createLinkedList(arr, n);
printLinkedList(head);
ListNode* head2 = Solution().reverseList(head);
printLinkedList(head2);
deleteLinkedList(head2);
return 0;
}


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur && cur->next){
ListNode* post = cur->next;
if(post->val == cur->val){
cur->next = post->next;
delete post;
}
else
cur = cur->next;
}
return head;
}
};


思路:在链表中,可以通过创建两个新的头结点指针,来分别指向小于x的结点和大于等于x的结点,遍历结束之后,再将两个新的链表重新连接起来。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
ListNode *l_head = NULL, *l_tail = NULL;
ListNode *r_head = NULL, *r_tail = NULL;
ListNode *p = head;
while(p){
if(p->val < x){
if(l_tail){
l_tail->next = p;
l_tail = l_tail->next;
}
else
l_head = l_tail = p;
}
else{
if(r_tail){
r_tail->next = p;
r_tail = r_tail->next;
}
else
r_head = r_tail = p;
}
p = p->next;
}
if(r_tail)
r_tail->next = NULL;
if(l_tail)
l_tail->next = r_head;
return l_head?l_head:r_head;
}
};


思路:先将偶数索引的第一个节点记录下来,然后将奇数索引和偶数索引分开为两个链表,最后将奇数索引的最后一个节点指向偶数索引的第一个节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if(head==NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
ListNode* odd = head;
ListNode* even = head->next;
ListNode* t = even;
while(even!=NULL && even->next!=NULL){
odd->next = even->next;
odd = odd->next;
even->next = odd->next;
even = even->next;
}
odd->next = t;
return head;
}
};



本题中是两个非负整数,且数字除0外前面不会有0。
思路:
1.首先用两个指针,分别同时遍历两个链表,按位相加,设置相应进位标志。
2.当两个链表长度不一致时,结束按位相加的遍历之后,将剩余元素链接接上。(所以需要判断链表当前要计算的结点是否存在)
3.需要注意连续进位。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* res = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* p = res;
int add = 0;
while(l1 || l2 || add){
int n1 = l1 ? l1->val : 0;
int n2 = l2 ? l2->val : 0;
int sum = n1 + n2 + add;
add = sum/10;
p->next = new ListNode(sum%10);
p = p->next;
if(l1) l1 = l1->next;
if(l2) l2 = l2->next;
}
return res->next;
}
};


思路:使用栈的先进后出结构来实现从链表的后面往前面取数字。res记录当前两个结点的和,然后新建一个进位结点head赋值为sum/10,若没有进位就是0。把head的后继连到res,再把res指向head。直到循环退出后,返回res(返回时要判断res为0则返回res->next)。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
stack<int> s1, s2;
while(l1){
s1.push(l1->val);
l1 = l1->next;
}
while(l2){
s2.push(l2->val);
l2 = l2->next;
}
int sum = 0;
ListNode* res = new ListNode(0);
while(!s1.empty() || !s2.empty()){
if(!s1.empty()){
sum += s1.top();
s1.pop();
}
if(!s2.empty()){
sum += s2.top();
s2.pop();
}
res->val = sum % 10;
ListNode* head = new ListNode(sum/10);
head->next = res;
res = head;
sum /= 10;
}
return res->val == 0 ? res->next : res;
}
};