The solution for the problem can be divided into three cases:
case 1: if the delete node is leaf node, then we can simply remove it
case 2: if the delete node is has single side or substree
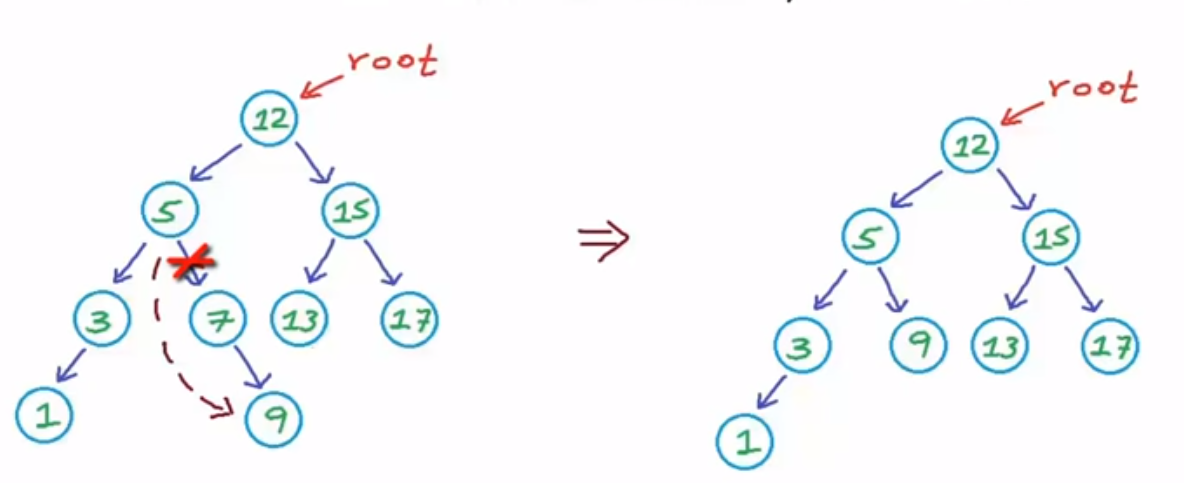
case 3: it has two children, then to keep it as a valid binary search tree, we can copy the min value from right subtree to delete node, to convert the problem into case 2
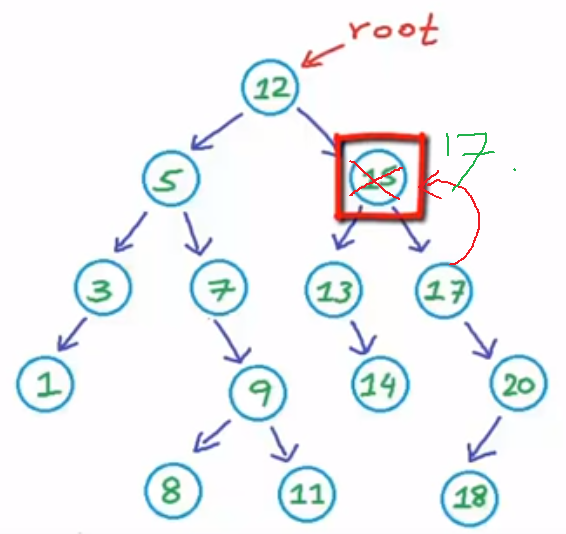
function Node(val) { return { val, left: null, right: null }; } function Tree() { return { root: null, addLeft(val, root) { const node = Node(val); root.left = node; return root.left; }, addRight(val, root) { const node = Node(val); root.right = node; return root.right; } }; } const tree = new Tree(); const root = Node(12); tree.root = root; const n1 = tree.addLeft(5, root); const n2 = tree.addRight(15, root); const n3 = tree.addLeft(3, n1); const n4 = tree.addRight(7, n1); tree.addLeft(1, n3); tree.addRight(9, n4); const n5 = tree.addLeft(13, n2); tree.addRight(14, n5); const n6 = tree.addRight(17, n2); const n7 = tree.addRight(20, n6); tree.addLeft(18, n7); /** * 12 / 5 15 / / 3 7 13 17 / 1 9 14 20 / 18 Delete 15 First copy 17 to 15 12 / 5 17 / / 3 7 13 17 / 1 9 14 20 / 18 Then remove original 17 12 / 5 17 / / 3 7 13 20 / / 1 9 14 18 */ function deleteNode(root, val) { // base case, if leaf node, return if (root === null) { return root; } else if (val > root.val) { // if delete value is larger than root, search on right side of tree root.right = deleteNode(root.right, val); } else if (val < root.val) { // if delete value is smaller than root, search on left side of tree root.left = deleteNode(root.left, val); } else { // if found the delete value and it is leaf node if (root.left === null && root.right === null) { // set leaf node to null root = null; } // if found the delete node and its right side has children // set root to null and link to its right node else if (root.left === null && root.right !== null) { let temp = root.right; root = null; root = temp; } // if found the delete node and its left side and children // set root to null and link to its left node else if (root.left !== null && root.right === null) { let temp = root.left; root = null; root = temp; } // the found node has children on both sides // then pick the min value from rgiht side (or max value from left side) // copy to current node // reset it right side (or left side) else { const temp = root.right; // get the min on the right side or max on the left side root.val = temp.val; root.right = deleteNode(root.right, temp.val); } return root; } } deleteNode(tree.root, 15); console.log(JSON.stringify(tree.root.left, null, 2));