上一博客学习了下基本的约定配置,留下几个遗漏的,这篇就是学习下遗漏一复杂类型。
一、什么是复杂类型?
书中说道:“复杂类型也可视作值类型(?)可以作为附加属性添加到其他类。复杂类型与实体类型的区别在于复杂类型没有其自己的键。它是依赖于其"宿主"类型跟踪变化 和持久化。一个没有Key属性的类型,并且作为属性映射到一个或多个类型中,Code First就会将其视作为复杂类型。Code First将预设复杂类型的属性出现在宿主类型映射到数据库的表中。”
说简单一点就是,项目中有个类A,这个A,会被其他类引用到比如:实体类B 和 实体类C,但是建立数据库的时候,我们不想为这个分割类A建立表,而是把A类中的属性等建立到 B 和 C 映射的表中,这时候,我们管 A 叫做复杂类型。
二、复杂类型和实体类型的区别
首先还是定义两个类Person类和IDCard类还有数据库上下文。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Data.Entity; using EFCodeFirstModels; using System.Configuration; namespace EFCodeFirstDataAccess { public class EFCodeFirstDbContext:DbContext { public EFCodeFirstDbContext() : base("MyStrConn") { } public DbSet<Person> Persons { get; set; } } }
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace EFCodeFirstModels { public enum SexType { Male, Female } [Table("Person")] public class Person { [Key] public string PersonId { get; set; } //姓名 public string Name { get; set; } //性别 public SexType Sex { get; set; } //年龄 public int Age { get; set; } public IDCard Card { get; set; } public Person(string personId, string name, SexType sex, int age,IDCard card) { PersonId = personId; Name = name; Sex = sex; Age = age; Card = card; } public Person() { } } }
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; namespace EFCodeFirstModels { public class IDCard { //法定出生日期 public DateTime BirthDate { get; set; } } }
在上面的IDCard中并没有主键,这个是需要留意的,然后呢新增一个Person对象在数据库上下文中。
using (var db=new EFCodeFirstDbContext()) { IDCard card = new IDCard(); card.BirthDate = DateTime.Now; Person p = new Person("0001","cuiyanwei",SexType.Female,25,card); db.Persons.Add(p); db.SaveChanges(); Console.WriteLine("Scueess"); }
此时会生成下面的表结构。

上面可以看到Person表中增加了一个Card_BirthDate列,但是如果在IDCard类中增加一个主键,结果就会不一样。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; namespace EFCodeFirstModels { public class IDCard { [Key] public int CardId { get; set; } //法定出生日期 public DateTime BirthDate { get; set; } } }
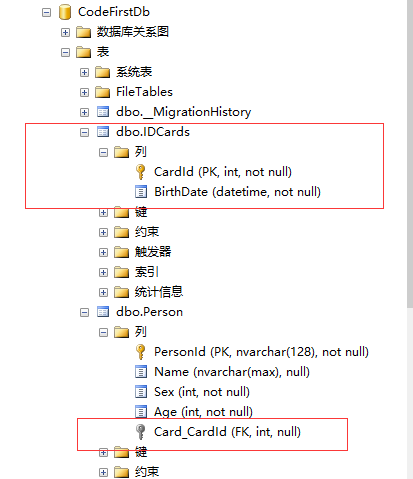
可以看到,数据库中多生成了一个表。Person表中增加了一个外键Card_CardId.
三、复杂类型嵌套
看到这你可能会问这也没提到复杂类型几个字啊,哪来的复杂类型了。上面的例子中IDCard虽然也是复杂类型,由于IDCard类中属性比较简单,没有嵌套这其他的类,所以EF就默认映射到Person表中了,但是假如IDCard类中有其他的类,属于类型嵌套的话那就麻烦了。首先看下如果有嵌套不指定会怎么样?
可以在IDCard类中增加一个属性,用来表示出生地方的经纬度(做个比喻,不可能人出生在一个经纬度的点上,也是大致的位置)。经纬度用Location类表示。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace EFCodeFirstModels { //[ComplexType] public class Location { //经度 public double Longitude { get; set; } //纬度 public double Latitude { get; set; } } }
public class IDCard { //法定出生日期 public DateTime BirthDate { get; set; } //出生地的位置 经纬度 public Location BirthPlace { get; set; } }
同样新增一个Person对象,此时就会报下面的错误。
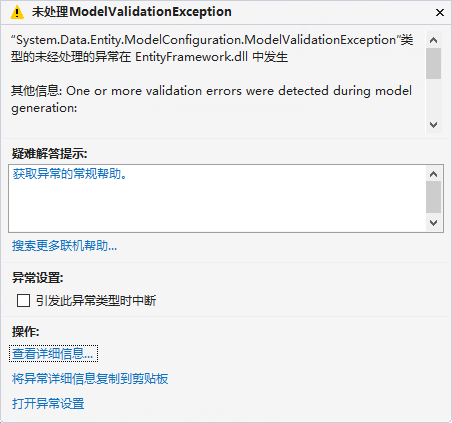
这是为什么呢?因为系统识别不了IDCard类是复杂类型。那怎么解决呢,很简单。只需指定IDCard是复杂类型就ok了。
[ComplexType] public class IDCard
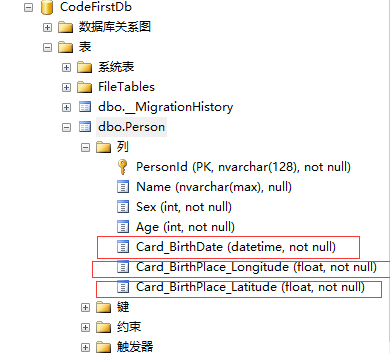
而在Location类上并没有指定复杂类型,这也将Location类认为是复杂类型。