json,pickle模块
1. 什么是序列化
序列化指的是将内存中的数据类型转换成一种中间格式,该格式可以用来存到硬盘中或者基于网络传输
1. 什么是序列化
序列化指的是将内存中的数据类型转换成一种中间格式,该格式可以用来存到硬盘中或者基于网络传输
2. 为何要序列化
1. 持久化(把某一时刻程序的运行状态永久保存下来)
2. 基于网络传输,可以扩平台交互数据
1. 持久化(把某一时刻程序的运行状态永久保存下来)
2. 基于网络传输,可以扩平台交互数据
3. 如何序列化
json:(t模式文本)rt,wt,at 写进硬盘 格式任意 读一定要满足json的格式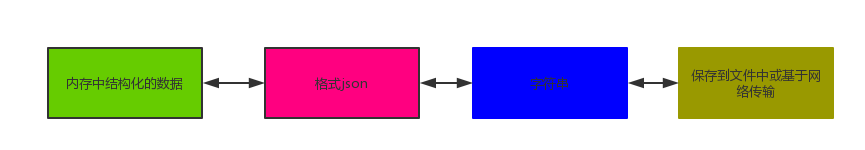 优点:兼容所有语言,可以扩平台交互数据
优点:兼容所有语言,可以扩平台交互数据
缺点:不能支持所有的python数据类型
pickle:(b模式二进制读写)rb,wb,ab
json:(t模式文本)rt,wt,at 写进硬盘 格式任意 读一定要满足json的格式
json.dump([1,2],open('a.txt','wt',encoding='utf-8',),ensure_ascii=False)默认为True
 优点:兼容所有语言,可以扩平台交互数据
优点:兼容所有语言,可以扩平台交互数据缺点:不能支持所有的python数据类型
pickle:(b模式二进制读写)rb,wb,ab
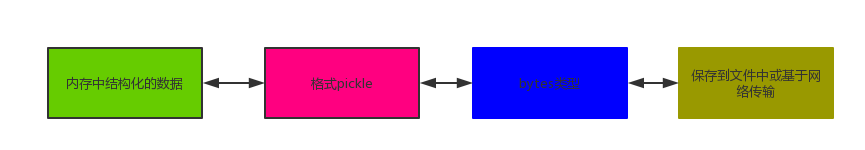
优点:可以支持所有的python数据类型
缺点:不能跨平台
json.dumps(数据类型) json.loads(json格式的字符串)
json.dump(数据类型,文件对象) json.load(文件对象)
json.dump(数据类型,文件对象) json.load(文件对象)
shelve模块(pickle底层功能的封装)
info={'name':'egon','age':18,'hobby':['piao','smoking','drinking']}
存
f=shelve.open(r'sheve.txt') 不用指定模式可读可写
f['st']=info
f.close()
取
f=shelve.open(r'sheve.txt')
print(f['st']['name'])
f.close()
改
f=shelve.open(r'sheve.txt',writeback=True) #改:全部重新写到硬盘
f['st']['name']='alex'
f.close()
info={'name':'egon','age':18,'hobby':['piao','smoking','drinking']}
存
f=shelve.open(r'sheve.txt') 不用指定模式可读可写
f['st']=info
f.close()
取
f=shelve.open(r'sheve.txt')
print(f['st']['name'])
f.close()
改
f=shelve.open(r'sheve.txt',writeback=True) #改:全部重新写到硬盘
f['st']['name']='alex'
f.close()
xml模块(中间格式) 解析文件
格式:
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein">
<rank updated="yes">2</rank>
<year>2008</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/>
<neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/>
</country>
</data>
就像字典:date={Liechtenstein:{....}}
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml") #整棵树(加载解析文件)
root = tree.getroot() #先拿树根(节点)例如root节点<peple age='18'>wd</people> root.tag,.attrib,.text
查
root.iter('year') #全文搜索
root.find('country') #当前的节点的下一层找(当前为根节点),只找一个
root.findall('country') #当前的节点的下一层找(当前为根节点),找所有
举例res=root.find('country') #country节点
nh=res.find('year') #从country节点开始找下层的year,没有返回None
改
1.找到要改的
2.改
3.tree.write('a.xml',#encoding="utf-8",xml_declaration=True) #把整棵树wt覆盖写回
增
ele=ET.Element('egon')#增加节点
ele.attrib={'nb':'yes'}#属性
ele.text='非常帅'#属性
节点.append(ele) #把节点添加进节点ele
.remove(ele) #
建整棵树
先拿个节点作为根:ele=ET.Element('egon')
tree=ET.ElementTree(ele)
再创建其他子节点:
a=ET.Element('egon1') #a表示节点,egon1是节点的(a.tag)名字
a.text=
a.attrib=
格式:
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein">
<rank updated="yes">2</rank>
<year>2008</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/>
<neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/>
</country>
</data>
就像字典:date={Liechtenstein:{....}}
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse("xmltest.xml") #整棵树(加载解析文件)
root = tree.getroot() #先拿树根(节点)例如root节点<peple age='18'>wd</people> root.tag,.attrib,.text
查
root.iter('year') #全文搜索
root.find('country') #当前的节点的下一层找(当前为根节点),只找一个
root.findall('country') #当前的节点的下一层找(当前为根节点),找所有
举例res=root.find('country') #country节点
nh=res.find('year') #从country节点开始找下层的year,没有返回None
改
1.找到要改的
2.改
3.tree.write('a.xml',#encoding="utf-8",xml_declaration=True) #把整棵树wt覆盖写回
增
ele=ET.Element('egon')#增加节点
ele.attrib={'nb':'yes'}#属性
ele.text='非常帅'#属性
节点.append(ele) #把节点添加进节点ele
.remove(ele) #
建整棵树
先拿个节点作为根:ele=ET.Element('egon')
tree=ET.ElementTree(ele)
再创建其他子节点:
a=ET.Element('egon1') #a表示节点,egon1是节点的(a.tag)名字
a.text=
a.attrib=
b=ET.subElement('父节点',‘子节点’,attrib= ,text=?)
ele.append(a)
最后保存
tree.write('路径文件名')#可以指定编码 还有这个头文件申明就像codeing:utf-8一个道理
图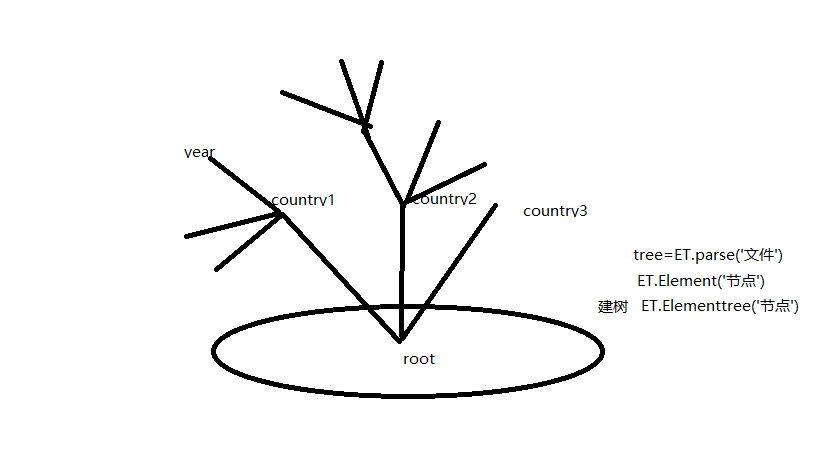
ele.append(a)
最后保存
tree.write('路径文件名')#可以指定编码 还有这个头文件申明就像codeing:utf-8一个道理
图
