1.猜数字游戏:一个类A有一个成员变量v,有一个初值100。定义一个类,对A类的成员变量v进行猜。如果大了则提示大了,小了则提示小了。等于则提示猜测成功。
1 public class A {
2 int v=100;
3 }
4
5
6 //测试类
7
8 import java.util.Scanner;
9
10 public class Test {
11
12 public static void main(String[] args) {
13 A a =new A();
14 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
15 System.out.println("请输入猜测的数字");
16 while(true){
17 int i = input.nextInt();
18 if(i > a.v){
19 System.out.println("猜大了");
20 continue;
21 }
22 if(i < a.v ){
23 System.out.println("猜小了");
24 continue;
25 }
26 if(i == a.v ){
27 System.out.println("猜对了");
28 break;
29 }
30 }
31 }
32 }
2.请定义一个交通工具(Vehicle)的类,其中有:
属性:速度(speed),体积(size)等等
方法:移动(move()),设置速度(setSpeed(int speed)),加速speedUp(),减速speedDown()等等.
最后在测试类Vehicle中的main()中实例化一个交通工具对象,并通过构造方法给它初始化speed,size的值,并且通过打印出来。
另外,调用加速,减速的方法对速度进行改变。
1 public class Vehicle { 2 int size; 3 int speed; 4 double speedUp; 5 double speedDown; 6 int move; 7 void move(int move){ 8 move=move; 9 System.out.println("移动的距离为"+move); 10 } 11 public int getSize() { 12 return size; 13 } 14 public void setSize(int size) { 15 this.size = size; 16 } 17 public int getSpeed() { 18 return speed; 19 } 20 public void setSpeed(int speed) { 21 this.speed = speed; 22 } 23 public void speedUp(){ 24 speedUp=speed+2; 25 System.out.println("加速后的速度"+speedUp); 26 } 27 public void speedDown(){ 28 speedDown = speed-2; 29 System.out.println("减速后的速度"+speedDown); 30 } 31 } 32 33 34 35 36 37 //测试类 38 public class Test1 { 39 40 public static void main(String[] args) { 41 Vehicle v=new Vehicle(); 42 v.setSize(10); 43 v.setSpeed(5); 44 System.out.println("当前体积为"+v.getSize()+"当前速度为"+v.getSpeed()); 45 v.move(10); 46 v.speedUp(); 47 v.speedDown(); 48 } 49 50 }
1 public class Vehicle {
2 int size;
3 int speed;
4 double speedUp;
5 double speedDown;
6 int move;
7 void move(int move){
8 move=move;
9 System.out.println("移动的距离为"+move);
10 }
11 public int getSize() {
12 return size;
13 }
14 public void setSize(int size) {
15 this.size = size;
16 }
17 public int getSpeed() {
18 return speed;
19 }
20 public void setSpeed(int speed) {
21 this.speed = speed;
22 }
23 public void speedUp(){
24 speedUp=speed+2;
25 System.out.println("加速后的速度"+speedUp);
26 }
27 public void speedDown(){
28 speedDown = speed-2;
29 System.out.println("减速后的速度"+speedDown);
30 }
31 }
32
33
34
35
36
37 //测试类
38 public class Test1 {
39
40 public static void main(String[] args) {
41 Vehicle v=new Vehicle();
42 v.setSize(10);
43 v.setSpeed(5);
44 System.out.println("当前体积为"+v.getSize()+"当前速度为"+v.getSpeed());
45 v.move(10);
46 v.speedUp();
47 v.speedDown();
48 }
49
50 }
规范答案:
1 public class Vehicle {
2 int speed;
3 int size;
4 int SpeedUp;
5 int SpeedDown;
6 double move;
7 int ChangeSpeedup;
8 int ChangeSpeeddown;
9 Vehicle() { //构造无参方法
10 }
11
12 Vehicle(int sp, int si) {
13 speed = sp;
14 size = si; //构造有参的方法并将sp的值赋给speed,si的值赋给size
15 }
16 //移动(方法)
17 public void move() {
18 move=1.0;
19 System.out.println("输出移动速度的距离"+move);
20
21 }
22 //设置有参数的速度(方法)
23 public int setSpeed(int speed){
24 speed=speed;
25 return speed;
26 }
27 //设置有参数的体积(方法)
28 public int setSize(int size){
29 size=size;
30 return size;
31 }
32 //加速
33 public int SpeedUp(){
34 System.out.println("输出加速时的速度:"+SpeedUp);
35 return SpeedUp;
36
37 }
38 //减速
39 public int SpeedDown(){
40 System.out.println("输出减速时的速度:"+SpeedDown);
41 return SpeedDown;
42 }
43 //加速后改变的速度
44 public void ChangeSpeedup(){
45 ChangeSpeedup=speed+SpeedUp;
46 System.out.println("输出加速后的速度:"+ChangeSpeedup);
47
48
49 }
50 //减速后改变的速度
51 public void ChangeSpeeddown(){
52 ChangeSpeeddown=speed-SpeedDown;
53 System.out.println("输出减速后的速度:"+ChangeSpeeddown);
54
55
56 }
57 }
58
59 public class Test {
60 public static void main(String[] args) {
61 Vehicle vehicle = new Vehicle(); // 声明对象并为对象分配变量
62 vehicle.speed = 5;// 给速度赋初值
63 vehicle.size = 10;// 给体积赋初值
64 System.out.println("当前速度为:" + vehicle.speed);
65 System.out.println("当前体积为:" + vehicle.size);
66 vehicle.SpeedUp = 4; // 给加速赋初值
67 vehicle.SpeedDown = 1; // 给减速赋初值
68 // 调用方法输出结果
69 vehicle.move();
70 vehicle.SpeedUp();
71 vehicle.SpeedDown();
72 vehicle.ChangeSpeedup();
73 vehicle.ChangeSpeeddown();
74
75 }
76
77 }
3.在程序中,经常要对时间进行操作,但是并没有时间类型的数据。那么,我们可以自己实现一个时间类,来满足程序中的需要。
定义名为MyTime的类,其中应有三个整型成员:时(hour),分(minute),秒(second),为了保证数据的安全性,
这三个成员变量应声明为私有。
为MyTime类定义构造方法,以方便创建对象时初始化成员变量。
再定义diaplay方法,用于将时间信息打印出来。
为MyTime类添加以下方法:
addSecond(int sec)
addMinute(int min)
addHour(int hou)
subSecond(int sec)
subMinute(int min)
subHour(int hou)
分别对时、分、秒进行加减运算。
1 package com.oracle.demo01;
2
3 public class MyTime {
4 private int hour;
5 private int minute;
6 private int second;
7 public MyTime(){
8
9 }
10 public MyTime(int hour,int minute,int second){
11 this.hour=hour;
12 this.minute=minute;
13 this.second=second;
14 huansuan();
15 }
16 public void addSecond(int sec){
17 second+=sec;
18 huansuan();
19 }
20 public void addMinute(int min){
21 minute+=min;
22 huansuan();
23 }
24 public void addHour(int hou){
25 hour+=hou;
26 huansuan();
27 }
28 public void subSecond(int sec){
29 second-=sec;
30 huansuan();
31 }
32 public void subMinute(int min){
33 minute-=min;
34 huansuan();
35 }
36 public void subHour(int hou){
37 hour-=hou;
38 huansuan();
39 }
40 public void display(){
41 String h=null;
42 String m=null;
43 String s=null;
44 if(hour<10){
45 h="0"+hour;
46 }else{
47 h=hour+"";
48 }
49 if(minute<10){
50 m="0"+minute;
51 }else{
52 m=minute+"";
53 }
54 if(second<10){
55 s="0"+second;
56 }else{
57 s=second+"";
58 }
59 System.out.println("当前时间为:"+h+"点"+m+"分"+s+"秒");
60 }
61 public void huansuan(){
62 //对秒进行换算
63 if(second>=60){
64 minute=minute+second/60;
65 second=second%60;
66 }else if(second<0){
67 if(second%60 != 0){
68 minute=minute+(second/60-1);
69 second=second%60+60;
70 }else{
71 minute=minute+second/60;
72 second=second%60;
73 }
74 }
75 //对分钟进行换算
76 if(minute>=60){
77 hour=hour+minute/60;
78 minute=minute%60;
79 }else if(minute<0){
80 if(minute%60 !=0){
81 hour=hour+(minute/60-1);
82 minute=minute%60+60;
83 }else{
84 hour=hour+minute/60;
85 minute=minute%60;
86 }
87 }
88 //对小时进行换算
89 if(hour>=24){
90 hour=hour%24;
91 }else if(hour<0){
92 if(hour%24 !=0){
93 hour=hour%24+24;
94 }else{
95 hour=hour%24;
96 }
97 }
98 }
99 }
测试类:
1 package com.oracle.demo01;
2
3 public class Test2 {
4
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6 MyTime my=new MyTime(20,45,80);
7 my.display();
8 }
9
10 }
运行结果:
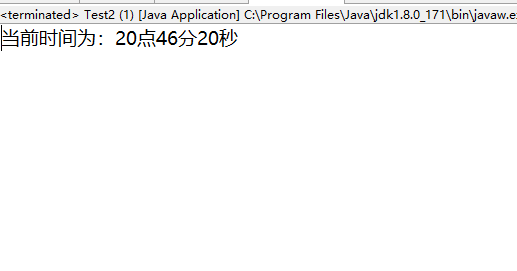
4、
编写Java程序,模拟简单的计算器。
定义名为Number的类,其中有两个整型数据成员n1和n2,应声明为私有。编写构造方法,赋予n1和n2初始值,
再为该类定义加(addition)、减(subtration)、乘(multiplication)、除(division)等公有成员方法,
分别对两个成员变量执行加、减、乘、除的运算。
在main方法中创建Number类的对象,调用各个方法,并显示计算结果。
public class Number { private int n1; private int n2; private String n; Number(){ n1=0; n2=0; } Number(int n1,int n2){ this.n1=n1; this.n2=n2; } public int getN1() { return n1; } public void setN1(int n1) { this.n1 = n1; } public int getN2() { return n2; } public void setN2(int n2) { this.n2 = n2; } public void addition(){ p(n1+n2); } public void subtration(){ p(n1-n2); } public void multiplication(){ p(n1*n2);; } public void division(){ p(n1/n2); } public void p(int n){ System.out.println(n); } } public class Test3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Number num=new Number(3,6); num.addition(); num.subtration(); num.multiplication(); num.division(); } }
5:
编写Java程序,用于显示人的姓名和年龄。
定义一个人类(Person),该类中应该有两个私有属性,姓名(name)和年龄(age)。定义构造方法,用来初始化数据成员。再定义显示(display)方法,将姓名和年龄打印出来。
在main方法中创建人类的实例,然后将信息显示。
public class Person { private String name; private int age; Person(){ } Person(String name,int age){ this.name=name; this.age=age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public void display(){ System.out.println(this.name+"的年龄是"+this.age+"岁"); } } public class Test4 { public static void main(String[] args) { Person p=new Person(); p.setName("薛之谦"); p.setAge(33); p.display(); } }
6:
定义一个名为Vehicles(交通工具)的基类,该类中应包含String类型的成员属性brand(商标)和color(颜色),还应包含成员方法run(行驶,在控制台显示“我已经开动了”)和showInfo(显示信息,在控制台显示商标和颜色),并编写构造方法初始化其成员属性。
编写Car(小汽车)类继承于Vehicles类,增加int型成员属性seats(座位),还应增加成员方法showCar(在控制台显示小汽车的信息),并编写构造方法。
编写Truck(卡车)类继承于Vehicles类,增加float型成员属性load(载重),还应增加成员方法showTruck(在控制台显示卡车的信息),并编写构造方法。
在main方法中测试以上各类。
public class Vehicles {
private String brand;
private String color;
//构造方法
public Vehicles(String brand, String color) {
this.brand = brand;
this.color = color;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("我已经开动了");
}
public void showinfo() {
System.out.println("商标: " + brand);
System.out.println("颜色: " + color);
}
}
public class Car extends Vehicles {
private int seats;
// 构造方法
public Car(String brand, String color, int seats) {
super(brand, color);
this.seats = seats;
}
public void showCar() {
super.showinfo();
System.out.println("座位: " + seats + " 个");
}
}
public class Truck extends Vehicles {
private float load;
public Truck(String brand, String color, float load) {
super(brand, color);
this.load = load;
}
public void showTruck() {
super.showinfo();
System.out.println("载重 :" + load + "吨");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vehicles vehicle = new Vehicles("奥迪","黑色");
vehicle.showinfo();
Car car = new Car("桑塔纳","红色", 5);
car.showCar();
Truck truck = new Truck("解放","蓝色",10);
truck.showTruck();
}
}
7.定义一个网络用户类,要处理的信息有用户ID、用户密码、email地址。在建立类的实例时,把以上三个信息都作为构造函数的参数输入,其中用户ID和用户密码时必须的,缺省的email地址是用户ID加上字符串"@gameschool.com"
1 public class User {
2 private String id;
3 private String password;
4 private String Email;
5 User(){
6
7 }
8 User(String id,String password,String Email){
9 super();
10 this.id=id;
11 this.password=password;
12 this.Email=Email;
13 }
14 User(String id,String password){
15 super();
16 this.id=id;
17 this.password=password;
18 this.Email=id+"@gameschool.com";
19 }
20 void shuchu(){
21 System.out.println("用户id为"+this.id+"
"+"用户密码为"+this.password+"
"+"用户地址为"+this.Email);
22 }
23 }
//测试类
1 public class Test6 {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 User u=new User("李四","123456");
5 u.shuchu();
6 }
7
8 }
规范答案:
1 public class User {
2 private String id;
3 private String email;
4 private String password;
5 public User(){
6
7 }
8 public User(String id,String password) {
9 this.password = password;
10 this.id = id;
11 this.email=id+"@gameschool.com";
12 }
13 public User(String id,String password,String email) {
14 this.password = password;
15 this.id = id;
16 this.email=email;
17 }
18
19 void show(){
20 System.out.println("id:"+id+",password:"+password+",email:"+email);
21 }
22
23 }
24 public class Test {
25 public static void main(String[] args) {
26 User s1 = new User("0001", "1234561234516", "guang");
27 User s2 = new User("0002", "123456", "zhang");
28 User s3 = new User("0003", "123456", "li");
29 s1.show();
30 s2.show();
31 s3.show();
32 }
33
34 }