截至9点之前写完了spark两个实验,这次主要是总结一下关于scala部分的

第一题:

写的时候没有按照要求在REPL模式上运行,因为没弄明白怎么在REPL模式下写for循环和break
package winterTest import scala.io.StdIn import scala.util.control.Breaks object test2 { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { println("Input the number(only Int and > 0)") val num = StdIn.readInt() println("Sn=" + sumSN(num)) } def sumSN(n: Int): Double = { val loop = new Breaks var res: Double = 0.0 var sn: Double = 0.0 loop.breakable { for (i <- 1 to n) { if (res >= n) { loop.break() } sn = (i + 1).toDouble / i res = res + sn } } res } }
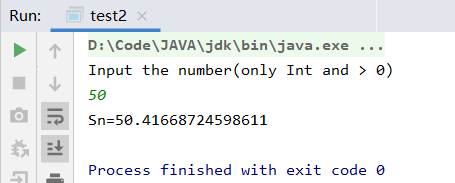
这道题的要点在scala的输入:StdIn,和breakable的使用。
第二题:模拟图形绘制
对于一个图形绘制程序,用下面的层次对各种实体进行抽象。定义一个 Drawable 的特 质,其包括一个 draw 方法,默认实现为输出对象的字符串表示。定义一个 Point 类表示点, 其混入了 Drawable 特质,并包含一个 shift 方法,用于移动点。所有图形实体的抽象类为Shape,其构造函数包括一个 Point 类型,表示图形的具体位置(具体意义对不同的具体图 形不一样)。Shape 类有一个具体方法 moveTo 和一个抽象方法 zoom,其中 moveTo 将图形从 当前位置移动到新的位置, 各种具体图形的 moveTo 可能会有不一样的地方。zoom 方法实 现对图形的放缩,接受一个浮点型的放缩倍数参数,不同具体图形放缩实现不一样。继承 Shape 类的具体图形类型包括直线类 Line 和圆类 Circle。Line 类的第一个参数表示其位置, 第二个参数表示另一个端点,Line 放缩的时候,其中点位置不变,长度按倍数放缩(注意, 缩放时,其两个端点信息也改变了),另外,Line 的 move 行为影响了另一个端点,需要对 move 方法进行重载。Circle 类第一个参数表示其圆心,也是其位置,另一个参数表示其半 径,Circle 缩放的时候,位置参数不变,半径按倍数缩放。另外直线类 Line 和圆类 Circle 都混入了 Drawable 特质,要求对 draw 进行重载实现,其中类 Line 的 draw 输出的信息样式 为“Line:第一个端点的坐标--第二个端点的坐标)”,类 Circle 的 draw 输出的信息样式为 “Circle center:圆心坐标,R=半径”。如下的代码已经给出了 Drawable 和 Point 的定义, 同时也给出了程序入口 main 函数的实现,请完成 Shape 类、Line 类和 Circle 类的定义。
package winterTest //特质Drawable trait Drawable { def draw() { println(this.toString) } } //样例类Point case class Point(var x: Double, var y: Double) extends Drawable { def shift(deltaX: Double, deltaY: Double) { x += deltaX; y += deltaY; } } //抽象类Shape abstract class Shape(var location: Point) { //构造函数包含一个Point类型 //具体方法,移动,更改点坐标 def moveTo(newLocation: Point): Unit = { location = newLocation } //抽象方法,放缩 def zoom(scale: Double) } //Line class Line(beginP: Point, var endP: Point) extends Shape(beginP) with Drawable { //重载draw override def draw() { //Shape中的location,由beginP传入作为起点,终点用endP表示 println(s"Line:(${location.x},${location.y})--(${endP.x},${endP.y})") } //重载moveTo override def moveTo(newLocation: Point): Unit = { //先移动endP endP.shift(newLocation.x - location.x, newLocation.y - location.y) //更改位置 location = newLocation } //重载zoom override def zoom(scale: Double): Unit = { //求出中点,按中点进行缩放 val midPoint = Point((endP.x + location.x) / 2, (endP.y + location.y) / 2) //样例类创建对象可以省略new location.x = midPoint.x + scale * (location.x - midPoint.x) location.y = midPoint.y + scale * (location.y - midPoint.y) endP.x = midPoint.x + scale * (endP.x - midPoint.x) endP.y = midPoint.y + scale * (endP.y - midPoint.y) } } //Circle class Circle(center: Point, var radius: Double) extends Shape(center) with Drawable { //重载draw override def draw() { println(s"Circle center:(${location.x},${location.y}),R=$radius") } //重载zoom override def zoom(scale: Double): Unit = { //只修改半径 radius = scale * radius } } object MyDraw { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val p = new Point(10, 30) p.draw; val line1 = new Line(Point(0, 0), Point(20, 20)) line1.draw line1.moveTo(Point(5, 5)) line1.draw line1.zoom(2) line1.draw val cir = new Circle(Point(10, 10), 5) cir.draw cir.moveTo(Point(30, 20)) cir.draw cir.zoom(0.5) cir.draw } }
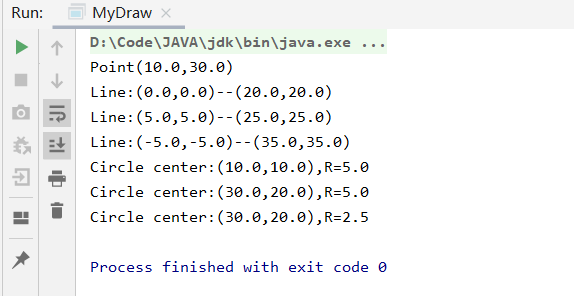
这道题的样例代码中就用到了特质trait和样例类case class,后续主要是继承类与抽象类。
Scala中的trait类似但强于Java中的接口,它可以定义定义属性和方法的实现,还可以实现多重继承,继承多个时使用with连接。
Scala中样例类case class与class的区别在于:自动创建伴生对象,实现子apply方法(初始化可以不用new);默认使用toString,copy,equals,hashCode方法;默认可以序列化;默认构造参数为val类型;伴生对象中会实现unapply方法,从而应用于模式匹配。
第三题:统计学生成绩
首先是测试样例
再附上文字版的:
Id gender Math English Physics
301610 male 80 64 78
301611 female 65 87 58
301612 female 44 71 77
301613 female 66 71 91
301614 female 70 71 100
301615 male 72 77 72
301616 female 73 81 75
301617 female 69 77 75
301618 male 73 61 65
301619 male 74 69 68
301620 male 76 62 76
301621 male 73 69 91
301622 male 55 69 61
301623 male 50 58 75
301624 female 63 83 93
301625 male 72 54 100
301626 male 76 66 73
301627 male 82 87 79
301628 female 62 80 54
301629 male 89 77 72
——————————————————————
然后是代码
package winterTest object scoreDo { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val inputFile = scala.io.Source.fromFile("F:/score.txt") //"\s+"是字符串正则表达式,将每行按空白字符(包括空格/制表符)分开 //originaData的类型为List[Array[String]] val originaData = inputFile.getLines.map { _.split("\s+") }.toList val courseNames = originaData.head.drop(2) //第一行的课程名 val allStudents = originaData.tail //去除第一行后剩下的数据 val couresNum = courseNames.length //统计行 //闭包函数 def statistc(lines: List[Array[String]]) = { //对每门课程生成一个三元组,分别表示总分,最低分和最高分 (for (i <- 2 to couresNum + 1) yield { //取出需要统计的列 val temp = lines map { elem => elem(i).toDouble } (temp.sum, temp.min, temp.max) //map case用法,更改样式,将总分变成平均分 }) map { case (total, min, max) => (total / lines.length, min, max) } } //输出结果函数 def printResult(res: Seq[(Double, Double, Double)]): Unit = { //遍历之前先使用zip方法将课程名容器与结果容器合并,结果为二元组容器 (courseNames zip res) foreach { case (course, result) => println(f"${course + ":"}%-10s${result._1}%5.2f${result._2}%8.2f${result._3}%8.2f") } } //分别用两个函数统计全体学生 val allRes = statistc(allStudents) println("course average min max") printResult(allRes) //按性别划分 val (maleL, femaleL) = allStudents partition { _ (1) == "male" } //分别用两个函数统计男同学 val maleRes = statistc(maleL) println("course average min max(males)") printResult(maleRes) //分别用两个函数统计女同学 val femaleRes = statistc(femaleL) println("course average min max(females)") printResult(femaleRes) } }
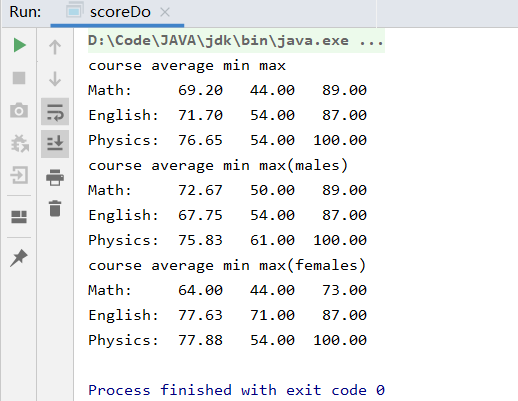
这里使用了大量的map知识点,使用map case更改样式等等。以及zip合成,tuple3的使用(result._1,result._2,result._3),Seq
zip拉链操作:将两个参数缝合成一个pair数组,若其中一个参数过长,多余的参数会被删除。
tuple3:Tuple(元组)操作用于返回多个值,Tuple3就是三元组。
Seq:属于列表,适合有序重复的数据,进行快速插入/删除元素等场景,与Set集合有一定差别。