1. 本周学习总结
1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结多流与文件相关内容。
1、流的划分:输入流:字节流(InputStream)、字符流(reader);
输出流:字节流(OutputStream)、字符流(writer);
2、字节流:读入数据结束返回-1;
子类有:FileInputStream、System.in;
available:检查读入的字节数;
close:关系系统资源;
flush:手动输出缓冲区字符;
3、字符流:基于字节的处理;
一定要在finally中关闭系统资源;
FileReader按系统默认的字符集解码,这边注意会出现乱码;
4、字节字符的相互转换:InputStreamReader(字节->字符)、OutputStreamWriter(字符->字节);
5、缓冲流:字节流(BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream)
字符流(BufferedReader、BufferedWriter)
手动flush;
缓冲区空的时候写入,满的时候读出;
6、scanner:格式化的输出(PrintWriter、PrintStream);
scanner使用完关闭;
printwriter:内部使用缓冲区,flush或close,否则没有真正的输出;
当调用println的时候,设置为autoflush,缓冲区的数据才能被输出;
2. 书面作业
将Student对象(属性:int id, String name,int age,double grade)写入文件student.data、从文件读出显示。
1. 字符流与文本文件:使用 PrintWriter(写),BufferedReader(读)
1.1 生成的三个学生对象,使用PrintWriter的println方法写入student.txt,每行一个学生,学生的每个属性之间用|作为分隔。使用Scanner或者BufferedReader将student.txt的数据读出。(截图关键代码,出现学号)
//201521123065
try
{
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter("D:/student.date");
out.println(student[0].id+"|"+student[0].name+"|"+student[0].age+"|"+student[0].grade);
out.println(student[1].id+"|"+student[1].name+"|"+student[1].age+"|"+student[1].grade);
out.println(student[2].id+"|"+student[2].name+"|"+student[2].age+"|"+student[2].grade);
out.close();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:/student.date"));
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.println(br.readLine());
}
}catch (IOException exception)
{
exception.printStackTrace();
}
运行结果:
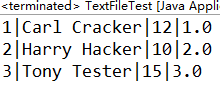

1.2 生成文件大小多少?

1.3 如果调用PrintWriter的println方法,但在后面不close。文件大小是多少?为什么?
close的话文件大小应该为0
因为printwriter中有用到缓冲区
三个学生对象此时被写入的是缓冲区
不使用close或者flush,缓冲区的数据是不会被写入文件中的
参考:本题具体要求见流与文件实验任务书-题目1-2.1
参考代码:TextFileTest.java
2. 缓冲流
2.1 使用PrintWriter往文件里写入1千万行(随便什么内容都行),然后对比使用BufferedReader与使用Scanner从该文件中读取数据的速度(只读取,不输出),使用哪种方法快?请详细分析原因?提示:可以使用junit4对比运行时间
BufferedReaderTest
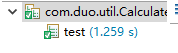
ScannerTeat
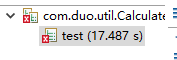
BufferedReader读取数据更快,因为BufferedReader读取数据中使用了缓冲区,并且其容量大于Scanner
2.2 将PrintWriter换成BufferedWriter,观察写入文件的速度是否有提升。记录两者的运行时间。试分析原因。
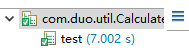
BufferedWriter的读取速度大于PrintWriter
因为BufferedWriter方法中用到了缓冲区的技术,提高了读取效率
参考:本题具体要求见流与文件实验任务书-题目1-2.2到2.3
参考代码:BufferedReaderTest.java
JUnit4常用注解
JUnit4学习
3. 字符编码
3.1 现有EncodeTest.txt 文件,该文件使用UTF-8编码。使用FileReader与BufferedReader将EncodeTest.txt的文本读入并输出。是否有乱码?为什么会有乱码?如何解决?(截图关键代码,出现学号)
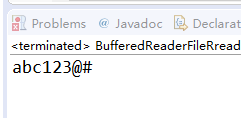
出现了乱码,原因是 FileReader只能按系统默认的字符集(如GBK)来解码 ,但是EncodeTest.txt文件是按照UTF-8进行编码
解决方案:
FileInputStream fis = null;
InputStreamReader isr = null;
BufferedReader br=null;
try {
fis=new FileInputStream("D:/EncodeTest.txt");
isr=new InputStreamReader(fis, "GBK");
br=new BufferedReader(isr);
while(br.readLine() != null){
System.out.println(br.readLine());
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e1){
e1.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if (br!=null){
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
运行结果:
3.2 编写一个方法convertGBK2UTF8(String src, String dst),可以将以GBK编码的源文件src转换成以UTF8编码的目的文件dst。
public static void convertGBK2UTF8(String src, String dst) throws IOException{
try {
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src));
OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(dst));
while(br.readLine()!=null){
osw.write(br.readLine());
}
br.close();
osw.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e1){
e1.printStackTrace();
}
参考:InputStreamReaderTest.java与教学PPT
4. 字节流、二进制文件:DataInputStream, DataOutputStream、ObjectInputStream
4.1 参考DataStream目录相关代码,尝试将三个学生对象的数据写入文件,然后从文件读出并显示。(截图关键代码,出现学号)
//201521123065
static final String dataFile = "Studentsdate";
static final String[] name={"zhang","lin","zheng"};
static final int[] age={21,23,12};
static final double[] score={100,67,89};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DataOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new DataOutputStream(new
BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dataFile)));
for (int i = 0; i < age.length; i ++) {
out.writeUTF(name[i]);
out.writeInt(age[i]);
out.writeDouble(score[i]);
}
} finally {
out.close();
}
DataInputStream in = null;
try {
in = new DataInputStream(new
BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(dataFile)));
String name;
int age;
double score;
try {
while (true) {
name = in.readUTF();
age = in.readInt();
score = in.readDouble();
System.out.println(name+" "+age+" "+score);
}
} catch (EOFException e) { }
}
finally {
in.close();
}
}
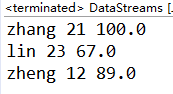
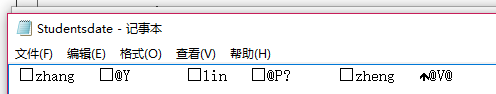
** 4.2生成的文件有多大?分析该文件大小?将该文件大小和题目1生成的文件对比是大了还是小了**

文件有55字节
name共13个字符(17字节)
age是整型,共12字节;
score是double型,共24字节
正文结束标志2字节
一共是55字节
和题目一相比更大
因为题目一是用字符流写入的,数字只占一个字节,而这里是用DataOutputStream 写入的,数字就占4个字节
4.3 使用wxMEdit的16进制模式(或者其他文本编辑器的16进制模式)打开student.data,分析数据在文件中是如何存储的。
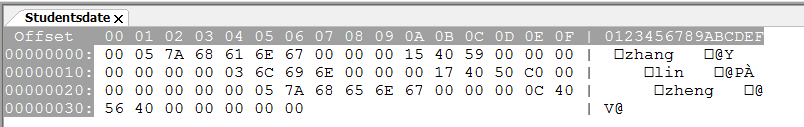

根据上面阴影部分
前00 -06 存储的是zhang这个字符
以此类推,根据图可以看出
4.4 使用ObjectInputStream(读), ObjectOutputStream(写)读写学生。(截图关键代码,出现学号) //参考ObjectStreamTest目录
//201521123065
static final String dataFile = "Studentsdate";
static final String[] name={"zhang","lin","zheng"};
static final int[] age={21,23,12};
static final BigDecimal[] score={new BigDecimal("100.00"),
new BigDecimal("67.00"),
new BigDecimal("89.00")};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException , ClassNotFoundException{
ObjectOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new ObjectOutputStream(new
BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dataFile)));
for (int i = 0; i < age.length; i ++) {
out.writeUTF(name[i]);
out.writeInt(age[i]);
out.writeObject(score[i]);
}
} finally {
out.close();
}
ObjectInputStream in = null;
try {
in = new ObjectInputStream(new
BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(dataFile)));
String name;
int age;
BigDecimal score;
try {
while (true) {
name = in.readUTF();
age = in.readInt();
score = (BigDecimal)in.readObject();
System.out.println(name+" "+age+" "+score);
}
} catch (EOFException e) { }
}
finally {
in.close();
}
}
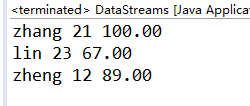
运行结果:
参考:本题具体要求见流与文件实验任务书-题目1-1
5. Scanner基本概念组装对象
编写public static List
public static List<Student> readStudents(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName));
List<Student> list=new ArrayList<>();
try {
while(br.readLine()!=null){
String name=br.readLine();
int age=br.read();
double score=br.read();
Student e=new Student(name,age,score);
list.add(e);
}
return list;
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
br.close();
}
}
IO用到的有:BufferedReader、FileReader
用BufferedReader是因为其有缓冲流的技术,对于文件较大时,存取效率快;
实验文件:Students.txt
参考:TextFileTest目录下TextFileTest.java
7. 文件操作
编写一个程序,可以根据指定目录和文件名,搜索该目录及子目录下的所有文件,如果没有找到指定文件名,则显示无匹配,否则将所有找到的文件名与文件夹名显示出来。
7.1 编写public static void findFile(String path,String filename)函数,以path指定的路径为根目录,在其目录与子目录下查找所有和filename相同的文件名,一旦找到就马上输出到控制台。(截图关键代码,出现学号)
//201521123065
public class FileTest {
public static void findFile(String path,String filename){
File file=new File(path);
String[] Filename=file.list();
for (int i = 0; i < Filename.length; i++) {
if(Filename[i].equals(filename)){
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
}
8. 正则表达式
8.1 如何判断一个给定的字符串是否是10进制数字格式?尝试编程进行验证。(截图关键代码,出现学号)
public boolean Test(String string){
Pattern p=null;
p=Pattern.compile("\d");//判断0-9的数字
for (int i = 0; i < string.length(); i++) {
Matcher m=p.matcher(string);
if(!m.matches()){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
3. 码云及PTA
3.1. 码云代码提交记录
3.2 上周PTA已完成