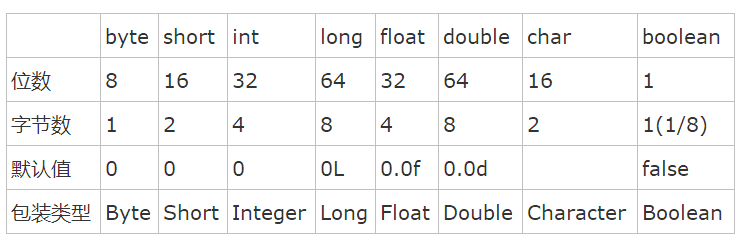
JAVA中的8种基本数据类型:byte short int long float double char boolean
特别说明:
1)char类型占2个字节,可以表示汉字。汉字和英文字符都占2个字节。
2)boolean类型理论上占1个bit,但实际中按1个byte(字节)处理。
3)基本数据类型之间的转换:低级向高级自动转换,高级向低级需要显示(强制)转换。
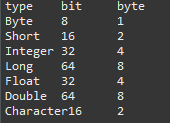
1 public class ByteAndBit { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 System.out.println("type "+"bit "+"byte"); 6 System.out.println("Byte "+Byte.SIZE+" "+Byte.BYTES); 7 System.out.println("Short "+Short.SIZE+" "+Short.BYTES); 8 System.out.println("Integer "+Integer.SIZE+" "+Integer.BYTES); 9 System.out.println("Long "+Long.SIZE+" "+Long.BYTES); 10 System.out.println("Float "+Float.SIZE+" "+Float.BYTES); 11 System.out.println("Double "+Double.SIZE+" "+Double.BYTES); 12 System.out.println("Character"+Character.SIZE+" "+Character.BYTES); 13 14 } 15 }
输出:
包装类:
为满足Java语言面相对对象的特性,上述8种基本数据类型在java.lang包中都有对应的包装类。
包装类可以分为3大类,Character,Boolean和Number(Short,Integer,Long,Float,Double)
包装类的一些特性:
1)所有包装类都可以将与之对应的基本数据类型作为参数来创建它们的实例对象
2)除了Character类之外,其他包装类都可以将一个字符串作为参数来构造它们的实例
3)Boolean类的构造方法参数为String类型时,若该字符串为true(不论大小写),则该对象表示true,否则表示false
4)当包装类Number构造方法的参数为String类型时,字符串不能为null,并且该字符串必须能够解析为基本类型的数据
public static void main(String[] args) { // 1)所有包装类都可以将与之对应的基本数据类型作为参数来创建它们的实例对象 Byte b=new Byte((byte) 2); Short s=new Short((short) 3); Integer a=new Integer(4); Double d = new Double(5.0d); Character c=new Character('A'); Boolean bb=new Boolean(false); Long l=new Long(4L); Float f=new Float(4.7f); System.out.println(b+" "+s+" "+a+" "+d+" "+c+" " +bb); // output: 2 3 4 5.0 A false // 2)除了Character类之外,其他包装类都可以将一个字符串作为参数来构造它们的实例 Byte b1=new Byte("2"); Short s1=new Short("3"); Integer a1=new Integer("4"); Double d1 = new Double("5.0d"); Character c1=new Character('A'); Boolean bb1=new Boolean("false"); System.out.println(b1+" "+s1+" "+a1+" "+d1+" "+c1+" " +bb1); // output: 2 3 4 5.0 A false // 3)Boolean类的构造方法参数为String类型时,若该字符串为true(不论大小写),则该对象表示true,否则表示false Boolean n1 = new Boolean("True"); Boolean n2 = new Boolean("TrUE"); Boolean n3 = new Boolean("hello"); System.out.println(n1+" "+n2+" "+n3); // output: true true false // 4)当包装类Number构造方法的参数为String类型时,字符串不能为null,并且该字符串必须能够解析为基本类型的数据 Integer a2 = new Integer(" "); //Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: " " Integer a3 = new Integer(""); // Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "" Integer a4 = new Integer(null); //Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: null Integer a5 = new Integer("abs"); //Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "abs" System.out.println(a2+" "+a3+" "+a4+" "+a5); // byte bbb=2; short ss=3; int ii=4; long ll=5; float ff=6.67f; // 必须加f double dd=7.7d; //可以不加d dd=bbb; dd=ss; dd=ii; dd=ll; ff=bbb; ff=ss; ff=ii; ff=ll; ff=(float)dd; ll=bbb; ll=ss; ll=ii; ll=(long)ff; ll=(long)dd; ii=bbb; ii=ss; ii=(int)ll; ii=(int)ff; ii=(int)dd; ss=bbb; ss=(short)ii; ss=(short)ll; ss=(short)ff; ss=(short)dd; bbb=(byte)ss; bbb=(byte)ii; bbb=(byte)ll; bbb=(byte)ff; bbb=(byte)dd; }
包装类的作用:
1)集合中不允许存放基本数据类型,故常用包装类
2)包含了每种基本数据类型的相关属性,如最大值、最小值、所占位数等
3)作为基本数据类型对应的类类型,提供了一系列实用的对象操作,如类型转换、进制转换等等
public static void main(String[] args) { //Byte System.out.println(Byte.MAX_VALUE); //127 System.out.println(Byte.MIN_VALUE); //-128 System.out.println(Byte.hashCode((byte)2)); System.out.println(Byte.valueOf((byte)2));//返回Byte类型 System.out.println(Byte.valueOf("2")); //返回Byte类型 System.out.println(Byte.toString((byte) 4)); System.out.println(Byte.parseByte("2")); //返回byte类型 System.out.println(); //Integer System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE); //(2^31)-1 2147483647 System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE); //-(2^31) -2147483648 System.out.println(Integer.hashCode(2)); System.out.println(Integer.valueOf(2)); //返回Integer类型 System.out.println(Integer.valueOf("2")); //返回Integer类型 System.out.println(Integer.max(1, 2)); System.out.println(Integer.min(1, 2)); System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("2")); //2 System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("3",8)); //3 System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(2));//10 System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(2));//2 System.out.println(Integer.toString(3)); //3 Integer i=new Integer(10); int ii=i.intValue(); //Character System.out.println(Character.isDigit('s')); System.out.println(Character.isLetter('e')); System.out.println(Character.isLetterOrDigit('E')); }
从JDK1.5就开始引入了自动拆装箱的语法功能,也就是系统将自动进行基本数据类型和与之相对应的包装类型之间的转换,这使得程序员书写代码更加方便。
public static void main(String[] args) { //自动装箱 int m = 10; Integer in = m; System.out.println(in);//10 //自动拆箱 Integer out = new Integer(10); int n = out; System.out.println(n);//10 }
包装类中==和equals的用法比较:
值得注意的是,包装类中的equals方法和String类一样,都是重写了Object类中的equals方法,因此比较的是内容而不是地址,
而“==”比较的依然是引用变量的地址,只是当包装类型和与之相对应的基本类型进行“==”比较时会先做自动拆箱处理。
public static void main(String[] args) { Integer a=new Integer(-100); Integer b=new Integer(-100); int c=-100; System.out.println(a==b); //false; System.out.println(a==c); //true; System.out.println(a.equals(b));//true; System.out.println(a.equals(c));//true; }
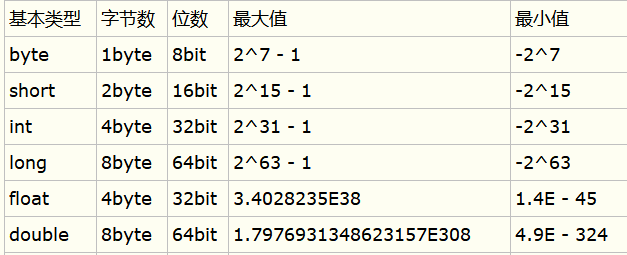
- 基本类型,在Java中所有数字都是带符号的。
类型 长度 范围
一、基本数据类型的特点,位数,最大值和最小值。
1、
基本类型:short 二进制位数:16
包装类:java.lang.Short
最小值:Short.MIN_VALUE=-32768 (-2的15此方)
最大值:Short.MAX_VALUE=32767 (2的15次方-1)
2、
基本类型:int 二进制位数:32
包装类:java.lang.Integer
最小值:Integer.MIN_VALUE= -2147483648 (-2的31次方)
最大值:Integer.MAX_VALUE= 2147483647 (2的31次方-1)
3、
基本类型:long 二进制位数:64
包装类:java.lang.Long
最小值:Long.MIN_VALUE=-9223372036854775808 (-2的63次方)
最大值:Long.MAX_VALUE=9223372036854775807 (2的63次方-1)
4、
基本类型:float 二进制位数:32
包装类:java.lang.Float
最小值:Float.MIN_VALUE=1.4E-45 (2的-149次方)
最大值:Float.MAX_VALUE=3.4028235E38 (2的128次方-1)
5、
基本类型:double 二进制位数:64
包装类:java.lang.Double
最小值:Double.MIN_VALUE=4.9E-324 (2的-1074次方)
最大值:Double.MAX_VALUE=1.7976931348623157E308 (2的1024次方-1) - char 16bit/2byte u0000~uFFFF,unicode编码
- 在计算机中,正数以原码形式存在,负数以补码形式存在。以byte为例:
0000 0001代表数字1,1000 0000 代表数字-1,因此byte的最大值为
0111 1111即数字127,最小值为1111 1111也就是数字-128
借鉴:https://www.cnblogs.com/Wilange/p/7732236.html