| Time Limit: 3500MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 17487 | Accepted: 6643 |
Description
So we all know what a square looks like, but can we find all possible squares that can be formed from a set of stars in a night sky? To make the problem easier, we will assume that the night sky is a 2-dimensional plane, and each star is specified by its x and y coordinates.
Input
Output
Sample Input
4 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 9 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 2 1 2 2 2 0 1 1 1 2 1 4 -2 5 3 7 0 0 5 2 0
Sample Output
1 6 1
Source
大致题意:
有一堆平面散点集,任取四个点,求能组成正方形的不同组合方式有多少。
相同的四个点,不同顺序构成的正方形视为同一正方形。
解题思路:
做本题数学功底要很强= =
直接四个点四个点地枚举肯定超时的,不可取。
普遍的做法是:先枚举两个点,通过数学公式得到另外2个点,使得这四个点能够成正方形。然后检查散点集中是否存在计算出来的那两个点,若存在,说明有一个正方形。
但这种做法会使同一个正方形按照不同的顺序被枚举了四次,因此最后的结果要除以4.
已知: (x1,y1) (x2,y2)
则: x3=x1+(y1-y2) y3= y1-(x1-x2)
x4=x2+(y1-y2) y4= y2-(x1-x2)
或
x3=x1-(y1-y2) y3= y1+(x1-x2)
x4=x2-(y1-y2) y4= y2+(x1-x2)
据说是利用全等三角形可以求得上面的公式
有兴趣的同学可以证明下。。。
再来就是利用hash[]标记散点集了
我个人推荐key值使用 平方求余法
即标记点x y时,key = (x^2+y^2)%prime
此时key值的范围为[0, prime-1]
由于我个人的标记需求,我把公式更改为key = (x^2+y^2)%prime+1
使得key取值范围为[1, prime],则hash[]大小为 hash[prime]
其中prime为 小于 最大区域长度(就是散点个数)n的k倍的最大素数,
即小于k*n 的最大素数 (k∈N*)
为了尽量达到key与地址的一一映射,k值至少为1,
当为k==1时,空间利用率最高,但地址冲突也相对较多,由于经常要为解决冲突开放寻址,使得寻找key值耗时O(1)的情况较少
当n太大时,空间利用率很低,但由于key分布很离散,地址冲突也相对较少,使得寻找键值耗时基本为O(1)的情况
提供一组不同k值的测试数据
K==1, prime=997 1704ms
K==2, prime=1999 1438ms
K==8, prime=7993 1110ms
K==10, prime=9973 1063ms
K==30, prime=29989 1000ms
K==50, prime=49999 1016ms
K==100, prime=99991 1000ms

最后解决的地址冲突的方法,这是hash的难点。我使用了 链地址法
typedef class HashTable
{
public:
int x,y; //标记key值对应的x,y
HashTable* next; //当出现地址冲突时,开放寻址
HashTable() //Initial
{
next=0;
}
}Hashtable;
Hashtable* hash[prime]; //注意hash[]是指针数组,存放地址
//hash[]初始化为NULL (C++初始化为0)
先解释所谓的“冲突”
本题对于一组(x,y),通过一个函数hash(x,y),其实就是上面提到的key的计算公式
key = (x^2+y^2)%prime+1
于是我们得到了一个关于x,y的key值,但是我们不能保证key与每一组的(x,y)都一一对应,即可能存在 hash(x1,y1) = hash(x2,y2) = key
处理方法:
(1) 当读入(x1, y1)时,若hash[key]为NULL,我们直接申请一个临时结点Hashtable* temp,记录x1,y1的信息,然后把结点temp的地址存放到hash[key]中
此后我们就可以利用key访问temp的地址,继而得到x1,y1的信息
(2) 当读入(x2, y2)时,由于hash(x1,y1) = hash(x2,y2) = key,即(x2, y2)的信息同样要存入hash[key],但hash[key]已存有一个地址,怎么办?
注意到hash[key]所存放的temp中还有一个成员next,且next==0,由此,我们可以申请一个新结点存放x2,y2的信息,用next指向这个结点
此后我们利用key访问temp的地址时,先检查temp->x和temp->y是否为我们所需求的信息,若不是,检查next是否非空,若next非空,则检查下一结点,直至 next==0
当检查完所有next后仍然找不到所要的信息,说明信息原本就不存在
就是说hash[key]只保存第一个值为key的结点的地址,以后若出现相同key值的结点,则用前一个结点的next保存新结点的地址,其实就是一个链表
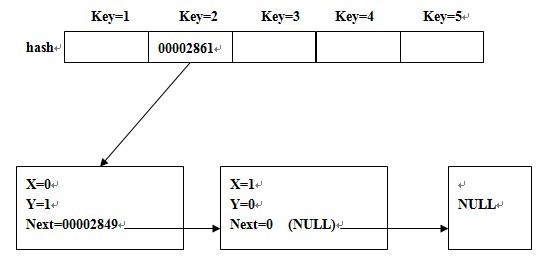
简单的图示为:
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn=10100; const int mod=10007; int ptx[maxn],pty[maxn]; int cur,ans; int first[maxn]; struct node{ int x,y; int next; }que[10100]; void insert(int x,int y){ int h=(x*x+y*y)%mod; que[cur].x=x; que[cur].y=y; que[cur].next=first[h]; first[h]=cur; cur++; } bool find(int tx,int ty){ int h=(tx*tx+ty*ty)%mod; int next=first[h]; while(next!=-1){ if(que[next].x==tx&&que[next].y==ty) return true; next=que[next].next; } return false; } int main(){ int n; while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){ if(n==0) break; cur=0,ans=0; memset(ptx,0,sizeof(ptx)); memset(pty,0,sizeof(pty)); memset(first, -1,sizeof(first)); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d%d",&ptx[i],&pty[i]); insert(ptx[i],pty[i]); } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j){ int x1 = ptx[i] - (pty[i] - pty[j]); int y1 = pty[i] + (ptx[i] - ptx[j]); int x2 = ptx[j] - (pty[i] - pty[j]); int y2 = pty[j] + (ptx[i] - ptx[j]); if (find(x1, y1) && find(x2, y2)) ++ans; } } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j){ int x1 = ptx[i] + (pty[i] - pty[j]); int y1 = pty[i] - (ptx[i] - ptx[j]); int x2 = ptx[j] + (pty[i] - pty[j]); int y2 = pty[j] - (ptx[i] - ptx[j]); if (find(x1, y1) && find(x2, y2)) ++ans; } } ans=ans/4; printf("%d ",ans); } return 0; }