An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
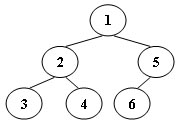
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2 lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
1 //这道题就是已知前序和中序遍历,得到后序遍历 2 //push为前序遍历,pop为中序遍历 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <stack> 6 #include <string> 7 using namespace std; 8 int N; 9 vector<int>preOrder, inOrder, posOrder; 10 struct Node 11 { 12 int val; 13 Node *l, *r; 14 Node(int a = 0) :val(a), l(nullptr), r(nullptr) {}; 15 }; 16 Node* createTree(int preL, int preR, int inL, int inR) 17 { 18 if (preL > preR) 19 return nullptr; 20 Node* root = new Node(preOrder[preL]); 21 int i; 22 for (i = inL; i <= inR; ++i)//找到根节点 23 if (inOrder[i] == preOrder[preL]) 24 break; 25 int num = i - inL; 26 root->l = createTree(preL + 1, preL + num, inL, i - 1); 27 root->r = createTree(preL + num + 1, preR, i + 1, inR); 28 return root; 29 } 30 void posOrderTree(Node *root) 31 { 32 if (root == nullptr) 33 return; 34 posOrderTree(root->l); 35 posOrderTree(root->r); 36 posOrder.push_back(root->val); 37 } 38 int main() 39 { 40 41 cin >> N; 42 string str; 43 stack<int>s; 44 int a; 45 for (int i = 0; i < 2*N; ++i) 46 { 47 cin >> str; 48 if (str == "Push") 49 { 50 cin >> a; 51 s.push(a); 52 preOrder.push_back(a); 53 } 54 else 55 { 56 inOrder.push_back(s.top()); 57 s.pop(); 58 } 59 } 60 Node* root = createTree(0, N - 1, 0, N - 1); 61 posOrderTree(root); 62 for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) 63 cout << posOrder[i] << (i == N - 1 ? "" : " "); 64 return 0; 65 }