一、包的结构与功能介绍
java是一门面向对象的语言,sun公司提供基于面向对象的帮助文档(API Application Program Interface),并针对不同的版本生成的API
API中根据不同的功能分如下包(package)
- java.applet:java的小应用程序
- java.awt和java.swing:java的图形用户界面的包(开发单机版小游戏)
- java.lang.*:java的语言包
- java.util.*:java的工具类包、集合框架包
- java.io.*:java的文件读写包(input Output)
- java.net.*:java的网络编程包(Socket机制相关,URL)
- java.sql./javax.sql.:java的数据库操作
- java.lang.reflect.*:反射相关包
二、java的lang包
1、包装类
定义:java的8个基本数据类型对应的 对象类型,称为它们的包装类;
基本数据类型中不能提供方法,不能与其他引用数据类型转换,此时包装类作为该基本数据类型的对象类型,不仅提供常用的方法,还可以与其他数据类型互相转换和“装箱”、“拆箱”
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类型 | 包装类的默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| byte | Byte | null |
| short | Short | null |
| int | Integer | null |
| long | Long | null |
| float | Float | null |
| double | Double | null |
| char | Character | null |
| boolean | Booleean | null |
| 问题1:基本数据类型、包装类以及字符串的相互转换 | ||
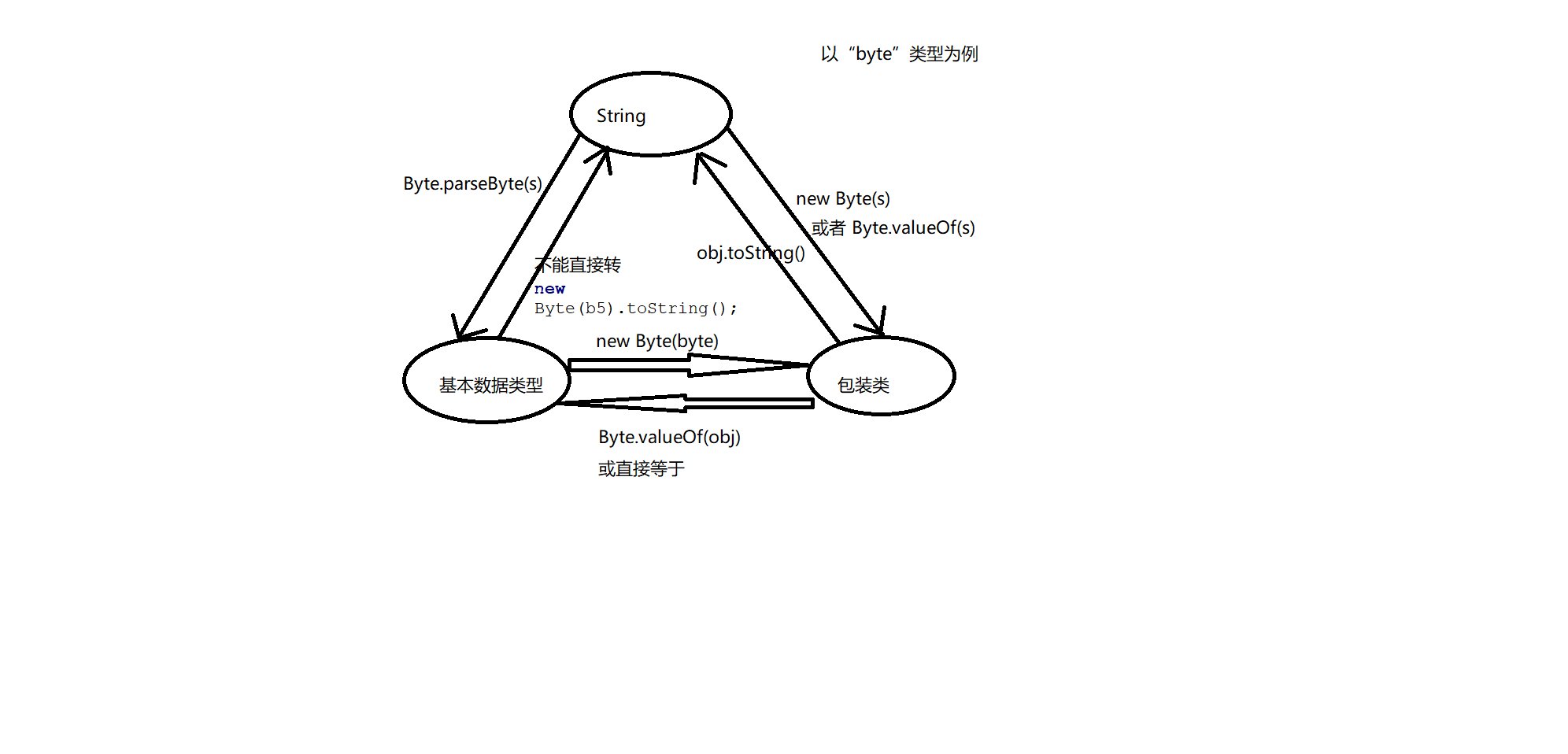 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、byte 的包装类 Byte
// 创建包装类的对象
byte b=123;
Byte obj1 = new Byte(b);
//1、 包装类 转字符串 包装类对象.toString()
String s1 = obj1.toString();
//2、字符串转包装类 new 包装类(s) 或者 包装类.valueOf(s)
String s2="100";
Byte obj2 = new Byte(s2);
// 或者
Byte obj3 = Byte.valueOf(s2);
//3 获取包装类的数值,包装类转基本数据类型 Byte - > byte
// 包装类.valueOf(基本数据类型) 或者 byteValue()
byte b2 = obj2; // 包装类可以直接复制给基本数据类型 ,这个过程 “拆箱”过程
byte b3 = Byte.valueOf(obj2);
// 4、字符串转 基本类型 包装类.paseByte(s)
byte b4 = Byte.parseByte(s2);
byte b5=122;
String s5 = new Byte(b5).toString();
}
再以Integer举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=250;
// 转包装类
Integer obj1 = new Integer(n);
//包装类转基本数据类型
int n3 = Integer.valueOf(obj1);
// 转字符串
String s1 = obj1.toString();
// 字符串再转成 Integer
Integer obj2 = Integer.parseInt(s1);
Integer obj3 = new Integer(s1);
// 字符串转int
int n2 = Integer.valueOf(s1);
// int 转 转字符串
String s3 = new Integer(n2).toString();
System.out.println("-------------Intger的常用方法------");
int num = Integer.bitCount(2); // 个位数 + 高位数的和
System.out.println(num);
// n1>n2 返回1 n1==n2 返回0 n1<n2 -1
//比较两个数是否相等
System.out.println(Integer.compare(100,200));
System.out.println(Integer.decode("123"));
//equals 比较两个数是否相等 对于基本数据类型的包装类比较他们的数值
Integer n1 = new Integer(90);
Integer n4 = new Integer(90);
System.out.println(n1.equals(n4));// 比较两个对象的 值
System.out.println(n1 == n4);// 比较 两个对象的地址
int n5 =100;
int n6 =100;
System.out.println(n5==n6);// 对于基本数据类型 == 比较的值
// 进制转换
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(18));//转成二进制表示形式
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(15));//转成16进制表示形式
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(10));//转成8进制表示
}
问题2:数据类型的装箱和拆箱
装箱:将基本数据类型自动转换后才能它的包装类,可以使用包装类的方法和属性
//自动装箱 100自动转成Integer
Integer num1=100;
拆箱:将包装类型 自动转成 对应的基本数据类型、
// 自动拆箱: Integer 自动转成 int
int num2 = num1;
面试题:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//包装类
//自动装箱 100自动转成Integer
Integer num1=100;
//自动拆箱
int num3=num1;
Integer n1=100;
Integer n2=100;
System.out.println(n1.equals(n2));//true
System.out.println(n1==n2);//true 它们同时指向常量池
Integer n3=150;//等价于 Integer n3=new Integer(150)
Integer n4=150;//等价于 Integer n4=new Integer(150)
System.out.println(n3.equals(n4));//true
System.out.println(n3==n4);//false
Integer n6=new Integer(100);//一定会创建新对象
Integer n7=new Integer(100);//
System.out.println(n6.equals(n7));//true
System.out.println(n6==n7);//false
System.out.println(n6==n1);//false
}
//结论
//对于 -128 <=Integer的值 <=127 之间(byte范围),
// 装箱时不会创建新对象 而是直接引用 常量池中的值
// 如果超出byte 的返回,则自动创建新对象,各自指向新对象的内存
2、Object类
Object类是lang包提供的,对于lang包的类不需要import,所以Object类无处不在,你不需要自己创建
常用方法
a、getClass:返回该对象的类型 任何类都有它的类型
b、equals:java中所有的equals方法都是重写Object的方法
原生的equals比较的时对象的地址,我们通常说的equals比较两个对象的值是因为几乎所有的数据类型(包装类,String)都重写了equals方法的
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
c、hsshCode:返回该对象的hash值
// Object中的hashCode 本身没有实现 ,
/**
* 1、对于基本数据类型的包装类 其值就是其本身
* 2、对于String类型的HashCode ,也是String自己实现的,其算法目的尽可能减少hash冲突
* 3、对于自定义类,需要你自己重写HashCode ,如果不重写 就在程序运行期间 JVM根据内存地址
* 类自动分配。(原则: 根据每个有意义的属性值,计算各自的hashCode 相加等一系列操作得到)
*/
d、fanalize():资源回首调用该方法,当对象地址不再被引用时,会被GC回收,并调用该方法
Object boj=null;
e、toString():返回该对象的字符串表现形式(通常会被子类重写)
f、wait():线程等待
g、notify():唤醒其中一个等待的线程
h、notifyAll:唤醒所有等待中的线程
对象的比较
public class Student {
private int id; //学生编号
private String sname;
private Integer age;
public void showInfo(){
System.out.println( sname +"---"+ age);
}
public Student(){
}
public Student(int id ,String sname ,int age){
this.id = id;
this.sname = sname;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
// 判断类型 是否一致
if(obj instanceof Student){
// 强转
Student stu = (Student)obj;
// 开始比较 id 和 sname
if(this.id == stu.id && this.sname.equals(stu.sname)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return id;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象 比较对象是否相等
// 比较内存相等 或 比较值(对象的属性)相等
Student stu1 = new Student(1001,"敖园",22);
Student stu2 = new Student(1001,"敖园",22);
System.out.println(stu1==stu2); // 比较两个对象的地址 (不相等) false
System.out.println(stu1.equals(stu2)); // true
// 由于equals本身没办法解决
// 两个对象因id 和name相等业务上是同一个对象的问题
// 所以需要重写 equals 和 hashcode 。
// 为什么要重写HashCode呢?
// 回答: 在JMV中如果HashCode不相等,一定不能认为是同一个对象
Student stu3 = stu1; // stu3 的地址于stu1的地址是同一个
}
总结:对象之间的比较通常是比较属性值,如果属性值想的呢个,我们可以认为是同一个对象,此时需要重写equals和hashCode的方法。
为什么要重写HashCode呢?
回答:在JVM中如果HashCode不相等,一定不能认为是同一个对象
3、System类
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System 属于系统类
// System.out; // 获取控制台的打印流
// 设置JVM运行时 系统参数
System.setProperty("encoding","UTF-8");
System.out.println("获取:"+System.getProperty("encoding"));
// 时间从 1970-01-01
System.out.println("获取当前系统的时间毫秒数:"+ System.currentTimeMillis());
System.exit(0); // 0 : 表示JVM正常退出 -1 表示非正常退出
}
4、字符串类
java.lang.String类,java中所有的字符串都会创建该类的实例,它结义队字符串查找、检索、转变大小写、截取等一系列操作,并提供了大量的字符串操作方法。
String类的特点:
它是一个不可变字符串,它的值创建后不能被改变。
String的构造器:
// 创建字符串对象
String s1="abc";
String s2 = new String("abc");
//通过字符数组构建
char [] chars = {'a','b','c'};
String s3 = new String(chars); // 或指定长度构建字符串
String s4 = new String(chars,0,2);
//或根据字节数组构建
byte [] byts = {97,98,99};
String s5 = new String(byts);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
System.out.println(s5);
// 字符串是一个不可变的对象
// class类被JVM装载时,会分配一个存放字符串的常量池(String Pool)
// 在类加载时 先检查常量池中是否有“abc”常量,如果有,直接将ss1指向该常量
// 如果没有,则创建常量abc
// 创建2个对象
String ss1 = "abc";
// abc常量不能改变, 则再创建 abcd的常量,由ss1重新指向
ss1+="d";
// 创建3个对象
String ss2 ="abcd"; // abcd
String ss3 = "aaa"; // aaa
ss2 += ss3; // abcdaaa 重新创建abcdaaa并由ss2重新指向
String a1="abc";
String b1="abc"; // 两个地址同时指向一个常量 “abc”
System.out.println(a1==b1); // true
System.out.println(a1.equals(b1));
String c1=new String("abc");// 堆内存中 对abc包装后的地址
System.out.println(a1==c1); // false
System.out.println(a1.equals(c1));//true
字符串类常用方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = "HELLO";
//boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
System.out.println("-------------");
//boolean equalsIgnoreCose(String str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3));
System.out.println("--------------");
}
4.1、获取功能的方法
- 返回字符串的长度:public int length()
- 将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾:public String concat (String str)
- 返回指定索引处的char值:public char charAt (int index)
- 返回指定字符串第一次出现在该字符串内的索引:public int indexof(String str)
- 返回一个子字符串,从begingIndex开始截取字符串到字符串结尾:public String substring (int beginIndex)
- 返回一个子字符串,从beginIndex到endIndex截取字符串。含beginIndex,不含endIndex public String (int beginIndex,int endIndex)
4.2、转换功能的方法
- 将字符串转换为新的字符数组:public char[] tocharArray()
- 使用平台的默认字符集将改String编码转换为新的字节数组:public byte[] getBytes()
- 将与targer匹配的字符串使用replacement字符串鹈鹕那public String rep;ace (CharSequence targer,CharSequence replacement)
4.3、分割功能的方法
将字符串按照给定的regex(规则)拆分为字符串数组:public String[] split(String regex)
举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "aa|bb|cc";
String[] strArray = s.split("|");
for(int x = 0;x < strArray.length; x++){
System.out.println(strArray[x]);
}
}