最近在弄一个sip网页集成版软电话,为了功能的完善,呼叫中心的工作人员为我们提供了一个http接口,我先在网页中直接打开分析了一下他的返回值,然后又放到js中去访问,结果一放到js中一访问就发现浏览器会提示:

刚开始我百思不得其解,查询过表头中未找到源http://localhost:8080,原本我还以为是在发送的时候我的表头有问题,但是用html5设置表头尝试了几次,发现还是提示一样的问题,于是我又在网上查询了一下0x80070005这个错误代码,网上提示说是属于跨域了,于是我又跟着网上的方法试了一下:
方法一:get方式获取
$.ajax({ dataType:'jsonp',
url:"http://10.0.0.230/asterccinterfaces?EVENT=GetCdr&orgidentity=dc&user=7501&password=7501&pwdtype=plaintext",
date:'get'
success: function(data){ alert(data) } ,
});
对于跨域的访问,只能使用get,并且要设置dataType,有的朋友这个样设置之后就可以成功运行了,但是很可惜也不知道是电脑的设置问题还是什么,反正这个方法在我这里无效,于是我又继续尝试,突然就想到了浏览器的安全权限设置,于是有了方法二
方法二:浏览器安全站点设置
1.将访问地址加入受信任站点:http://10.0.0.230
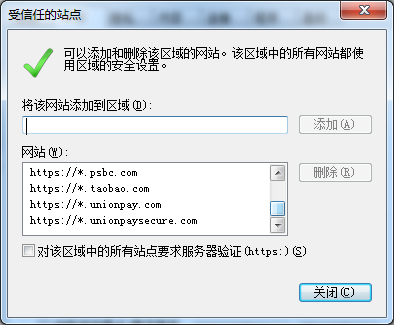
2.点击自定义,将通过域访问数据源设置为启用

这种方法如果是固定电脑使用的话,那还是蛮方便的,但是如果大面积的客户端访问服务器那就不行了,毕竟我们不可能让每一个客户都修改自己的浏览器吧,更何况有的人还不会,特别是一些商业网,这是更不允许的。因此这个方法建议大家视情况而用。
方法三:后台发送请求接收返回数据:参照http://blog.csdn.net/sd0902/article/details/10097457
public class HttpInvoker  {
{
public static final String GET_URL = "http://10.0.0.230/asterccinterfaces";
public static final String POST_URL = "http://10.0.0.230/asterccinterfaces";
public static void readContentFromGet() throws IOException  {
{
// 拼凑get请求的URL字串,使用URLEncoder.encode对特殊和不可见字符进行编码
String getURL = GET_URL + "??EVENT=GetCdr&orgidentity=dc&user=7501&password=7501&pwdtype=plaintext&username=" + URLEncoder.encode("fat man", "utf-8");
URL getUrl = new URL(getURL);
// 根据拼凑的URL,打开连接,URL.openConnection函数会根据URL的类型,
// 返回不同的URLConnection子类的对象,这里URL是一个http,因此实际返回的是HttpURLConnection
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) getUrl.openConnection();
// 进行连接,但是实际上get request要在下一句的connection.getInputStream()函数中才会真正发到
// 服务器
connection.connect();
// 取得输入流,并使用Reader读取
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
connection.getInputStream()));
System.out.println("=============================");
System.out.println("Contents of get request");
System.out.println("=============================");
String lines;
while ((lines = reader.readLine()) != null)  {
{
System.out.println(lines);
}
reader.close();
// 断开连接
connection.disconnect();
System.out.println("=============================");
System.out.println("Contents of get request ends");
System.out.println("=============================");
}
public static void readContentFromPost() throws IOException  {
{
// Post请求的url,与get不同的是不需要带参数
URL postUrl = new URL(POST_URL);
// 打开连接
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) postUrl.openConnection();
// Output to the connection. Default is
// false, set to true because post
// method must write something to the
// connection
// 设置是否向connection输出,因为这个是post请求,参数要放在
// http正文内,因此需要设为true
connection.setDoOutput(true);
// Read from the connection. Default is true.
connection.setDoInput(true);
// Set the post method. Default is GET
connection.setRequestMethod("POST");
// Post cannot use caches
// Post 请求不能使用缓存
connection.setUseCaches(false);
// This method takes effects to
// every instances of this class.
// URLConnection.setFollowRedirects是static函数,作用于所有的URLConnection对象。
// connection.setFollowRedirects(true);
// This methods only
// takes effacts to this
// instance.
// URLConnection.setInstanceFollowRedirects是成员函数,仅作用于当前函数
connection.setInstanceFollowRedirects(true);
// Set the content type to urlencoded,
// because we will write
// some URL-encoded content to the
// connection. Settings above must be set before connect!
// 配置本次连接的Content-type,配置为application/x-www-form-urlencoded的
// 意思是正文是urlencoded编码过的form参数,下面我们可以看到我们对正文内容使用URLEncoder.encode
// 进行编码
connection.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
// 连接,从postUrl.openConnection()至此的配置必须要在connect之前完成,
// 要注意的是connection.getOutputStream会隐含的进行connect。
connection.connect();
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(connection
.getOutputStream());
// The URL-encoded contend
// 正文,正文内容其实跟get的URL中'?'后的参数字符串一致
String content = "firstname=