import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Scanner;
class ATM{
private String zhanghu;
private String name;
private String Date;
private String mima;
private double yuer;
public String getMima(){
return mima;
}
public void cunkuan(){
System.out.println("请输入存款金额:");
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
yuer+=s.nextDouble();
}
public void quluan(){
String qu="";
int quu=0;
boolean f=true,q=true,h=true;
while(q){
Scanner ss=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请选择:1、取款,2、返回,3、退卡。");
int ch=ss.nextInt();
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
while(f){
System.out.println("请输入取款金额:");
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
qu=s.nextLine();
int a=qu.length();
for(int i=0;i<a;i++)
{
if((qu.charAt(i)<'0')||(qu.charAt(i)>'9'))
{
h=false;
break;
}
else
h=true;
}
if(!h){
try{
System.out.println("数字格式异常");
throw new myException();
}
catch(myException e){
System.out.println("请输入数字");
f=true;
}
}
if(h){
quu=Integer.parseInt(qu);
if(quu%100!=0){
try{
System.out.println("数字录入错误,");
throw new myException();
}
catch(myException e){
System.out.println("请输入100的整数倍:");
f=true;
}
}
else
f=false;
}
}
yuer=yuer-quu;
break;
case 2:
q=false;
break;
case 3:
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
public void zhuanzhang(){
boolean f=true;
double zhuan=0;
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入转账账号");
String zhang=s.nextLine();
while(f){
System.out.println("请输入转账金额:");
zhuan=s.nextDouble();
if(zhuan>yuer) //转账超过余额。
try{
throw new myException();
}
catch(myException e){
System.out.println("转账超出余额,请重新输入:");
}
else
f=false;
}
yuer-=zhuan; //当前余额
System.out.println("转账成功!");
}
public void xiugai(){
System.out.println("请输入当前密码:");
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
String mi=s.nextLine();
if(mi.equals(mima))
{
System.out.println("请输入要修改的密码:");
mima=s.nextLine();
}
else
System.out.println("密码错误,无法修改");
}
public void chaxun(){
System.out.println("账户余额为:"+yuer);
}
public void set(String zhanghu,String name,String Date,String mina,double yuer){
this.zhanghu=zhanghu;
this.name=name;
this.Date=Date;
this.mima=mina;
this.yuer=yuer;
}
}
public class AtmException extends ATM {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ATM a=new ATM();
boolean f=false,q=true;
int i=0;
a.set("111111111111", "nasdf", "199508030048", "123456", 20000);
while(q){
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
Scanner aa=new Scanner(System.in);
String ba=aa.nextLine();
i++;
if(!ba.equals(a.getMima()))
System.out.println("密码输入错误。");
else
{
q=false;
f=true;
}
if(q){
if(i>=3)
try{
throw new myException();
}
catch(myException e){
System.out.println("密码输入超过三次,该卡被锁定");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
while(f){
System.out.println("1、取款");
System.out.println("2、存款");
System.out.println("3、转账");
System.out.println("4、查询");
System.out.println("5、退出");
System.out.println("请选择:");
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
int b=s.nextInt();
switch(b){
case 1:
a.quluan();
a.chaxun();
break;
case 2:
a.cunkuan();
a.chaxun();
break;
case 3:
a.zhuanzhang();
a.chaxun();
break;
case 4:
a.chaxun();
case 5:
System.exit(0);
break;
}
}
}
}
class myException extends Exception{
public myException(){
}
}
实验结果截图:



2、成绩输入异常处理
源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Exam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
boolean f=true,h=true,q=true;
int Sc=0;
while(f){
System.out.println("Please input a score:");
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
String ss=s.nextLine();
int a=ss.length();
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
if((ss.charAt(i)<'0')||(ss.charAt(i)>'9'))
break;
else
{
q=false;
h=false;
}
}
if(q){
try{
throw new ScException();
}
catch(ScException e){
System.out.println("格式错误");
}
}
if(!h) //输入的是数字
{
Sc=Integer.parseInt(ss);
if((Sc<0)||(Sc>100))
{
try{
ScException x= new ScException();
throw x;
}
catch(ScException x){
System.out.println("输入异常,请输入整数");
}
}
else
f=false;
}
}
if(Sc<60)
System.out.println("不及格");
else if(Sc<70)
System.out.println("及格");
else if(Sc<80)
System.out.println("中");
else if(Sc<90)
System.out.println("良");
else if((Sc<100)||(Sc==100))
System.out.println("优");
}
}
class ScException extends Exception{
public ScException(){
}
}
实验结果截图:

二 动手动脑
1、请尝试解释以下奇怪的现象。
源代码
import javax.swing.*;
class AboutException {
public static void main(String[] a)
{
int i=1, j=0, k;
k=i/j;
try
{
k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception
//throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!");
}
catch ( ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
if (e instanceof ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("被0除");
else
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
finally
{
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK"+" "+k);
}
}
}
核心代码1:
int i=1,j=0,k;
k=i/j;

代码执行时发生异常
核心代码2:
double i=1,j=0,k;
k=i/j;
代码执行时不发生异常。
jvm在处理浮点数时,生成的是ddiv字节码指令,i/0,0转化为浮点数0.0,而0.0是double类型的,并不精确,所以不会抛出异常。
jvm在处理整数时,生成的是idiv字节码指令,整数除0就是除0,会抛出异常。
第一个程序没有执行finally?
finally 块必须与 try 或 try/catch 块配合使用。因为没有执行try,所以不会执行finally,异常是系统捕获的,try并没有抛出。
此外,不可能退出 try 块而不执行其 finally 块。如果 finally 块存在,则它总会执行。
(无论从那点看,这个陈述都是正确的。有一种方法可以退出 try 块而不执行 finally 块。如果代码在 try 内部执行一条 System.exit(0); 语句,
则应用程序终止而不会执行 finally 执行。另一方面,如果您在 try 块执行期间拨掉电源,finally 也不会执行。)
2、多层的异常捕获
阅读以下代码,输出结果。
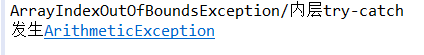
public class CatchWho {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
try {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
public class CatchWho2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { try { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); } throw new ArithmeticException(); } catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); } catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); } } } |
请看以下代码:
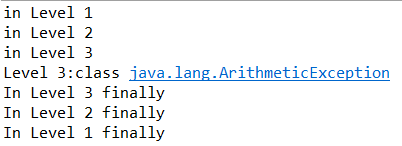
public class EmbededFinally {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int result;
try {
System.out.println("in Level 1");
try {
System.out.println("in Level 2");
// result=100/0; //Level 2
try {
System.out.println("in Level 3");
result=100/0; //Level 3
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 3 finally");
}
// result=100/0; //Level 2
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 2 finally");
}
// result = 100 / 0; //level 1
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
. System.out.println("In Level 1 finally");
}
}
}
总结try catch finally
1)try抛出一个异常之后,程序会跳出try,不再执行try后边的语句,开始对catch进行匹配,处理异常;
2)try嵌套中,抛出的异常只有被处理才可以按顺序抛出下一个异常,如果不处理,程序就终止;
3)try抛出异常之后,就跳出了try语句,内层catch无法捕获就继续向外抛,所以外层也就有异常,外层语句不执行,第二个程序 throw new ArithmeticExcepption没有执行。
4)第三个程序,try第一层第二层没有异常不用捕获,执行完之后到第三层,除0有异常,catch捕获,执行第三层的finally然后,顺序执行第二层,第一层的finally。
3、finally一定会执行吗?
public class SystemExitAndFinally {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try{
System.out.println("in main");
throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main");
//System.exit(0);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.exit(0);
}
finally
{
System.out.println("in finally");
}
}
}
执行结果:

此程序中finally并未执行,原因是catch语句中的 System.exit(0);使得程序退出jvm了,所以finally也就不执行了。
4、总结try catch finally嵌套使用执行顺序。
1)try语句嵌套从外层到内层执行,在try语句中,哪一层出错,哪一层就抛出异常,后边的try语句就不再执行,如果该层存在catch就进行相应的捕获,有该层的finally也执行,除非finally遇到不执行的情况;
2)如果该层没有catch进行捕获,就向外抛出,去找catch,如果没有catch进行捕获,就终止程序。