CSS定位
首先,思考一个问题,如果我们想要某个元素在一个盒子内自由的移动位置,并且压住盒子,应该怎么做?
使用标准流 ,浮动是很难做到如上操作的,那么就需要定位。
标准流常用于多个块级盒子的纵向排列
浮动可以让多个块级盒子在一行内没有缝隙的排列显示,常用于横向排列
而定位可以让盒子自由的在某个盒子中移动位置或固定在屏幕中的某个位置,并且压住其他盒子
定位 = 定位模式 + 边偏移
定位模式 position : (1) relative 相对定位 (2) absolute绝对定位 (3) fixed固定定位
边偏移(指的是定义元素相对于其父元素的边偏移量): top, bottom, left, right
(1)相对定位 relative
1.相对定位指的是元素移动位置的时候,是相对它原来的位置来说的
2.原来在标准流中的位置会继续保存,后面的盒子不会去占据它的位置
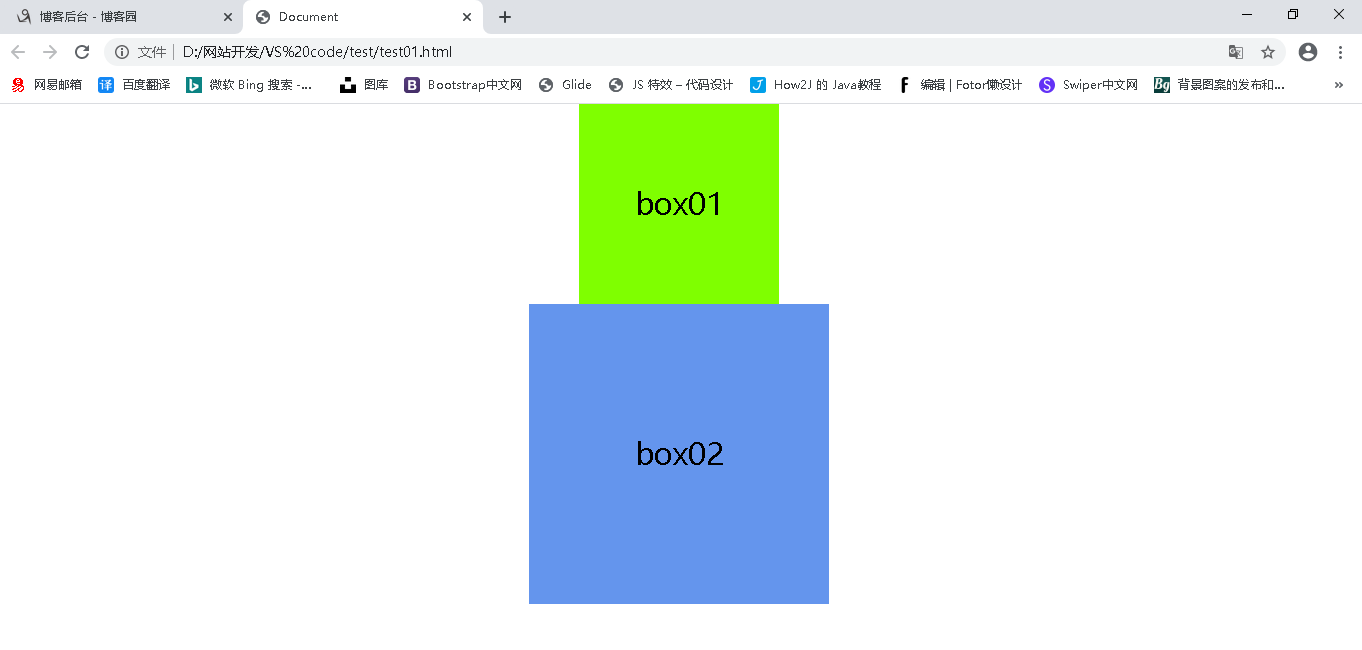
如下代码,初始化盒子1,盒子2
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> 6 <title>Document</title> 7 <style> 8 *{ 9 /* 清除所有元素的内外边距 */ 10 padding:0 ; 11 margin: 0; 12 } 13 .d1{ 14 width: 200px; 15 height: 200px; 16 background-color: chartreuse; 17 margin: 0 auto; 18 font-size: 30px; 19 line-height: 200px; 20 text-align: center; 21 } 22 .d2{ 23 width: 300px; 24 height: 300px; 25 background-color: cornflowerblue; 26 margin: 0 auto; 27 font-size: 30px; 28 line-height: 300px; 29 text-align: center; 30 } 31 </style> 32 </head> 33 <body> 34 <div class="d1">box01</div> 35 <div class="d2">box02</div> 36 </body> 37 </html>
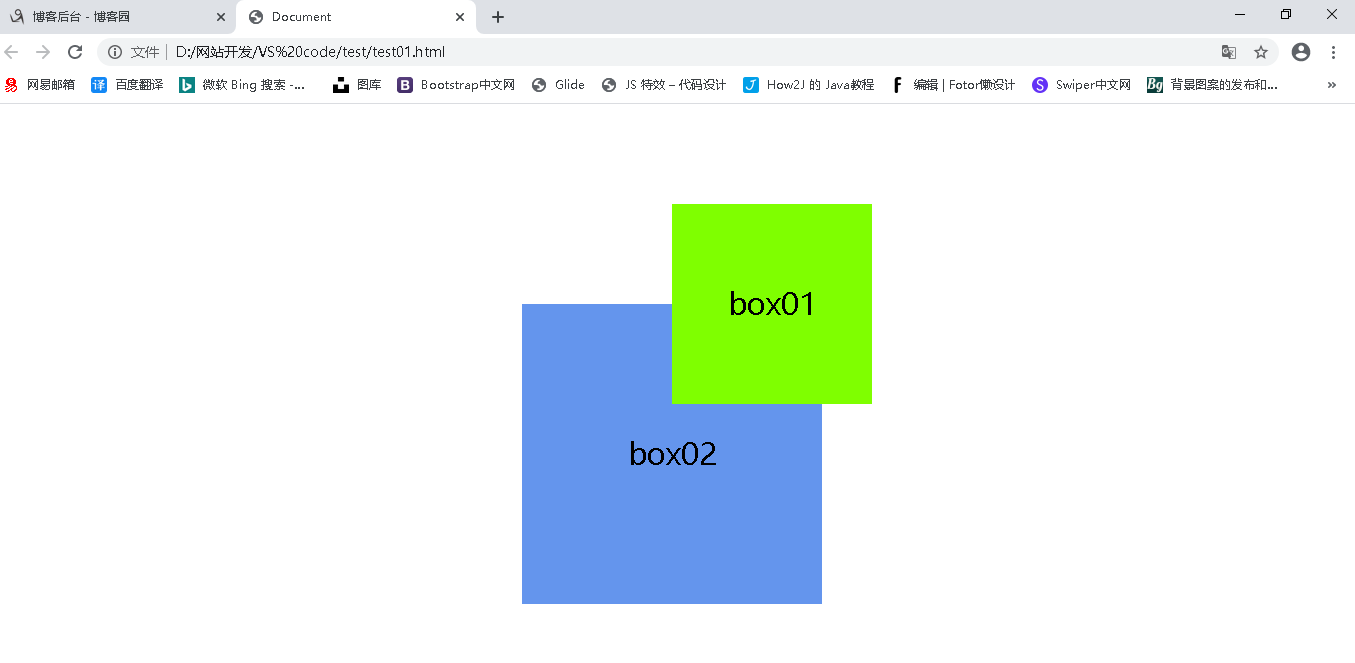
然后给 box01 添加相对定位,相对于其原先的位置向下移动100px ,向右移动100px,由于其仍然保留其在标准流中的位置,所以后面的盒子不会去占据它的位置
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> 6 <title>Document</title> 7 <style> 8 *{ 9 /* 清除所有元素的内外边距 */ 10 padding:0 ; 11 margin: 0; 12 } 13 .d1{ 14 position: relative; 15 top: 100px; 16 left: 100px; 17 width: 200px; 18 height: 200px; 19 background-color: chartreuse; 20 margin: 0 auto; 21 font-size: 30px; 22 line-height: 200px; 23 text-align: center; 24 } 25 .d2{ 26 width: 300px; 27 height: 300px; 28 background-color: cornflowerblue; 29 margin: 0 auto; 30 font-size: 30px; 31 line-height: 300px; 32 text-align: center; 33 } 34 </style> 35 </head> 36 <body> 37 <div class="d1">box01</div> 38 <div class="d2">box02</div> 39 </body> 40 </html>
(2)绝对定位 absolute
绝对定位是元素在移动过程中,是相对于它的祖先元素来说的
1.如果没有祖先元素,或者祖先元素没有定位,那么就是相对于浏览器来移动的
2.如果祖先元素有定位,那么就相对于最近一级的有定位的祖先元素作为参考点
3,绝对定位不再占有原先的位置(脱标)
子绝父相
(1)子级盒子需要绝对定位,不占有位置,可以放在父级盒子的任意一个位置,不影响其他的兄弟盒子
(2)父级盒子需要一个定位,使子级盒子只在父级盒子中移动,且父级盒子应该占有位置,所以用相对定位
示例:绝对定位的盒子水平垂直居中方法
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> 6 <title>Document</title> 7 8 <style> 9 10 *{ 11 margin: 0; 12 padding: 0; 13 } 14 .box{ 15 position: relative; 16 width:500px; 17 height: 500px; 18 background-color: #999; 19 margin: 100px auto; 20 21 } 22 .b1{ 23 position: absolute; 24 /* 水平居中 */ 25 left: 50%; 26 margin-left: -100px; 27 28 /* 垂直居中 */ 29 top:50%; 30 margin-top: -100px; 31 width: 200px; 32 height: 200px; 33 background-color:cyan; 34 } 35 </style> 36 </head> 37 <body> 38 <div class="box"> 39 <div class="b1"></div> 40 </div> 41 </body> 42 </html>

(3)固定定位 fixed
1. 以浏览器的可视窗口为参照点移动元素
2 不再保留位置
案例:使用绝对定位固定到版心右侧位置
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <style> *{ margin: 0; padding: 0; } .d1{ width:500px; height: 3000px; background-color: #999; margin:0 auto; } /* 先用left 移动到页面的中央 再使用 margin 向左移动版心宽度的一半 */ .d2{ position: fixed; bottom: 50px; left:50%; margin-left: 255px; width: 50px; height: 50px; background-color: blue; } </style> </head> <body> <div class='d1'> </div> <div class="d2"></div> </body> </html>

(4)定位的叠放次序
使用定位布局时,可能出现盒子的重叠情况,比如两个固定定位的盒子有一部分相交,那么要决定谁完整的显示出来,此时可以使用
z-index来控制盒子的前后循序。 z-index后面的数值越大,盒子越靠上。
如下代码。两个绝对定位的div盒子 box01 box02,box02压住了 box01
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <style> .box{ position: relative; width: 400px; height: 400px; background-color: #999; margin: 0 auto; } .d1{ position: absolute; top: 100px; left: 100px; width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: darkcyan; font-size: 25px; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; } .d2{ position: absolute; top: 80px; left: 130px; width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color:darkorchid; font-size: 25px; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <div class="d1">box01</div> <div class="d2">box02</div> </div> </body> </html>
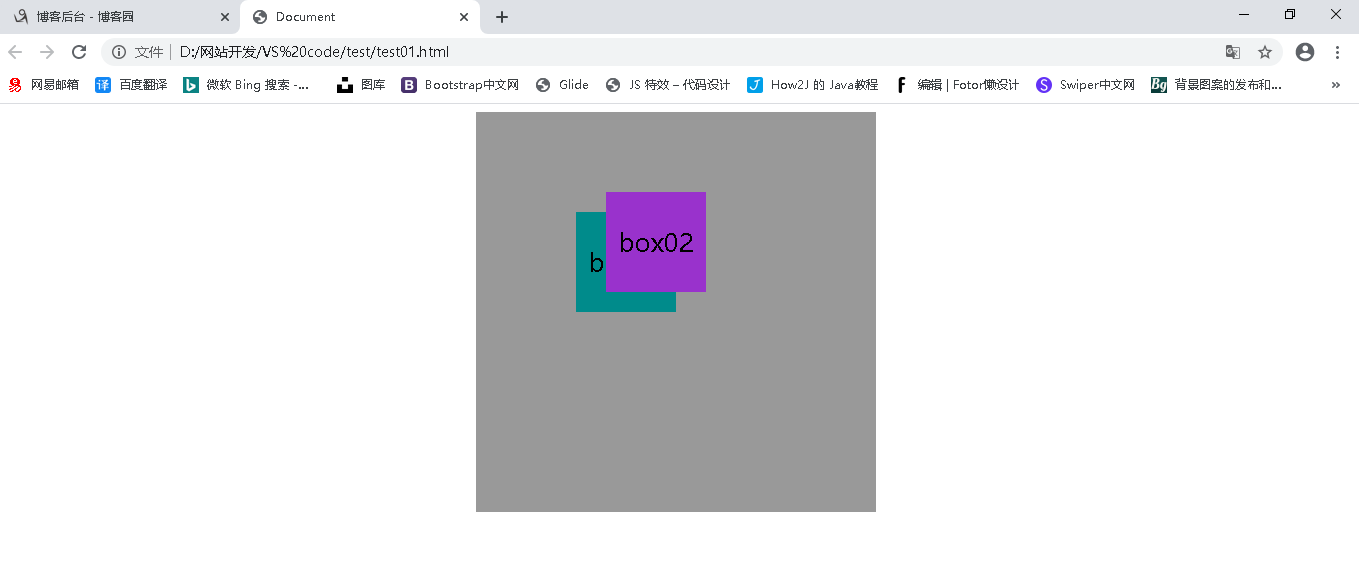
我们给box01盒子添加 z-index 属性,就可以使他浮上来
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <style> .box{ position: relative; width: 400px; height: 400px; background-color: #999; margin: 0 auto; } .d1{ position: absolute; z-index: 1; top: 100px; left: 100px; width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: darkcyan; font-size: 25px; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; } .d2{ position: absolute; top: 80px; left: 130px; width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color:darkorchid; font-size: 25px; text-align: center; line-height: 100px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <div class="d1">box01</div> <div class="d2">box02</div> </div> </body> </html>
