Breaking news from zombie neurology! It turns out that – contrary to previous beliefs – every zombie is born with a single brain, and only later it evolves into a complicated brain structure. In fact, whenever a zombie consumes a brain, a new brain appears in its nervous system and gets immediately connected to one of the already existing brains using a single brain connector. Researchers are now interested in monitoring the brain latency of a zombie. Your task is to write a program which, given a history of evolution of a zombie's nervous system, computes its brain latency at every stage.
The first line of the input contains one number n – the number of brains in the final nervous system (2 ≤ n ≤ 200000). In the second line a history of zombie's nervous system evolution is given. For convenience, we number all the brains by 1, 2, ..., n in the same order as they appear in the nervous system (the zombie is born with a single brain, number 1, and subsequently brains 2, 3, ..., n are added). The second line contains n - 1 space-separated numbers p2, p3, ..., pn, meaning that after a new brain k is added to the system, it gets connected to a parent-brain 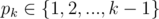 .
.
Output n - 1 space-separated numbers – the brain latencies after the brain number k is added, for k = 2, 3, ..., n.
6
1
2
2
1
5
1 2 2 3 4
题意:
给你一个根节点1,之后每次加一条边,结点的父结点是树中已经得到的结点,问你加完边之后每一次的直径
题解:
新直径与加边之前的直径的关系,假设未加边之前是由X,Y这两点组成的链最长,那么答案必然是 max(dis(i,X),dis(i,Y),dis(X,Y));
这个画图作作假设就看得出
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const int N=4e5+110,mods=20090717,inf=2e9+10; int fa[N][30],dep[N],n,f[N]; vector<int > G[N]; void Lca_dfs(int u,int p,int d) { fa[u][0] = p, dep[u] = d; for(int i = 0; i < G[u].size(); ++i) { int to = G[u][i]; if(to == p) continue; Lca_dfs(to,u,d+1); } } void Lca_init() { Lca_dfs(1,0,0); for(int i = 1; i <= 22; ++i) { for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) { if(fa[j][i-1]) { fa[j][i] = fa[fa[j][i-1]][i-1]; } else { fa[j][i] = 0; } } } } int Lca(int x,int y) { if(dep[x] > dep[y]) swap(x,y); for(int k = 0; k < 22; ++k) { if((dep[y] - dep[x])>>k&1) y = fa[y][k]; } if(x == y) return x; for(int k = 21; k >= 0; --k) { if(fa[x][k] != fa[y][k]) { x = fa[x][k]; y = fa[y][k]; } } return fa[x][0]; } int main() { scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i){ scanf("%d",&f[i]); G[f[i]].push_back(i); } Lca_init(); int ans = 0,x = 1,y = 1; for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) { int ux = Lca(i,x); int uy = Lca(i,y); int nowx,nowy; if(x == ux) { if(ans < dep[i] - dep[x]) { ans = dep[i] - dep[x]; nowx = i;nowy = x; } }else { if(dep[i] + dep[x] - 2*dep[ux] > ans) { ans = dep[i] + dep[x] - 2*dep[ux]; nowx = i; nowy = x; } } if(y == uy) { if(ans < dep[i] - dep[y]) { ans = dep[i] - dep[y]; nowx = i;nowy = y; } } else { if(dep[i] + dep[y] - 2*dep[uy] > ans) { ans = dep[i] + dep[y] - 2*dep[uy]; nowx = i; nowy = y; } } x= nowx; y = nowy; cout<<ans<<" "; } return 0; }