一、实验内容
1、ex 2_28
(1) 用if...else判断
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int main() 4 { 5 char i; 6 cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elect) S(ort) Q(uit), Select one:"; 7 while(cin>>i) 8 { 9 if(i=='A') 10 cout<<"Data has been added."<<endl; 11 else if(i=='D') 12 cout<<"Data has been delected."<<endl; 13 else if(i=='S') 14 cout<<"Data has been sorted."<<endl; 15 else if(i=='Q') exit(0); 16 else 17 cout<<"Have no choice,please select another one."<<endl; 18 cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elect) S(ort) Q(uit), Select one:"; 19 } 20 return 0; 21 }
运行结果如下:
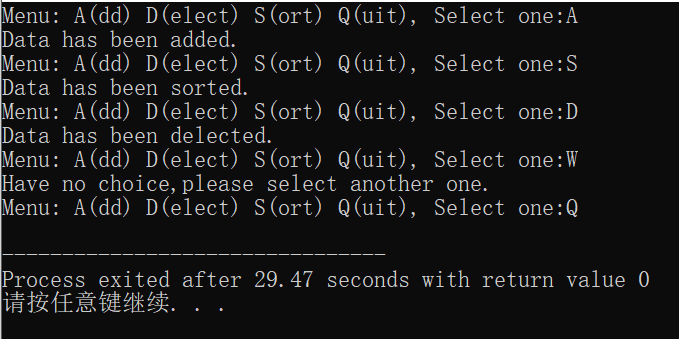
(2)用switch语句
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int main() 4 { 5 char i; 6 cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elect) S(ort) Q(uit), Select one:"; 7 while(cin>>i) 8 { 9 switch(i) 10 { 11 case 'A':cout<<"Data has been added."<<endl;break; 12 case 'D':cout<<"Data has been delected."<<endl;break; 13 case 'S':cout<<"Data has been sorted."<<endl;break; 14 case 'Q':exit(0); 15 default:cout<<"have no choice,please select another one."<<endl; 16 } 17 cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elect) S(ort) Q(uit), Select one:"; 18 } 19 return 0; 20 }
结果同上。
2、ex 2_29
(1)while循环
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<iomanip> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 int i=2,j,k=0; 7 while(i<=100) 8 { 9 j=2; 10 while(j<=i) 11 { 12 if(i%j==0) break; 13 j++; 14 } 15 if(i==j) 16 { 17 cout<<setw(5)<<i; 18 k++; 19 } 20 i++; 21 if(k%5==0) cout<<endl; 22 } 23 return 0; 24 }
结果如下:
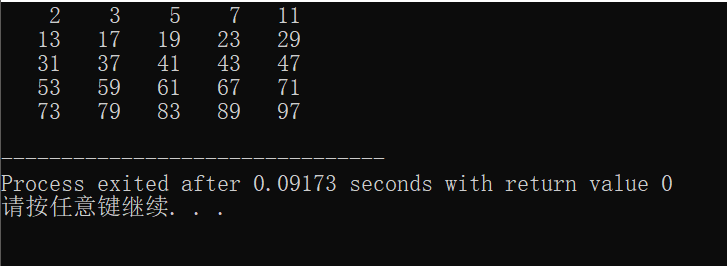
(2)do...while循环
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<iomanip> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 int i=2,j,k=0; 7 do 8 { 9 j=2; 10 do 11 { 12 if(i%j==0) break; 13 j++; 14 }while(j<=i); 15 if(i==j) 16 { 17 cout<<setw(5)<<i; 18 k++; 19 } 20 i++; 21 if(k%5==0) cout<<endl; 22 }while(i<=100); 23 return 0; 24 }
(3)for循环
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<iomanip> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 int i,j,k=0; 7 for(i=2;i<=100;i++) 8 { 9 for(j=2;j<=i;j++) 10 if(i%j==0) break; 11 if(i==j) 12 { 13 cout<<setw(5)<<i; 14 k++; 15 } 16 if(k%5==0) cout<<endl; 17 } 18 return 0; 19 }
3、ex 2_32
(1)while循环
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <ctime> 4 using namespace std; 5 int main() 6 { 7 srand(time(0)); 8 int m=rand()%100+1,n; 9 10 cout<<"Please write down the number you guess:"; 11 while(cin>>n) 12 { 13 if(m<n) 14 cout<<"What you guess is bigger than the number."<<endl; 15 if(m>n) 16 cout<<"What you guess is smaller than the number."<<endl; 17 if(m==n) 18 {cout<<"Congratulation!"<<endl;break;} 19 cout<<"Please write down the number you guess:"; 20 } 21 return 0; 22 }
(2)do...while循环
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <ctime> 4 using namespace std; 5 int main() 6 { 7 srand(time(0)); 8 int m=rand()%100+1,n; 9 10 cout<<"Please write down the number you guess:"; 11 do 12 { 13 cin>>n; 14 if(m<n) 15 cout<<"What you guess is bigger than the number."<<endl; 16 if(m>n) 17 cout<<"What you guess is smaller than the number."<<endl; 18 if(m==n) 19 {cout<<"Congratulation!"<<endl;break;} 20 cout<<"Please write down the number you guess:"; 21 }while(m!=n); 22 return 0; 23 }
效果如下:
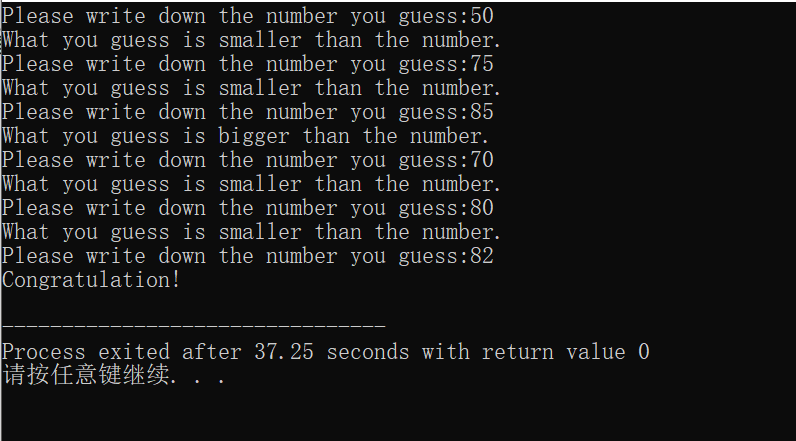
4、ex 2_34
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<iomanip> 3 using namespace std; 4 enum Balls{red,yellow,blue,white,black}; 5 void Print(int a) 6 { 7 switch(a) 8 { 9 case 0:cout<<setw(10)<<"red";break; 10 case 1:cout<<setw(10)<<"yellow";break; 11 case 2:cout<<setw(10)<<"blue";break; 12 case 3:cout<<setw(10)<<"white";break; 13 case 4:cout<<setw(10)<<"black";break; 14 } 15 } 16 int main() 17 { 18 int n=0,i,j,k; 19 for(i=red;i<=blue;i++) 20 { 21 for(j=i+1;j<=white;j++) 22 { 23 24 for(k=j+1;k<=black;k++) 25 { 26 Print(i);Print(j);Print(k); 27 cout<<endl; 28 n++; 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 cout<<"There are "<<n<<" ways in all."<<endl; 33 return 0; 34 }
效果如下:

二、实验反思
1、注意"A"与'A'的区别,"A"表示字符串,'A'表示字符,比较的是ASCII码。
2、三种循环各具特点,用前应思考其作用,明显看出29题用for循环简洁。
3、生成随机数时,注意头文件cstdlib,ctime;设置域宽时,注意头文件iomanip。
4、使用枚举类型,返回球颜色时,我使用一个了函数将数字与颜色对应。
三、实验小评
https://www.cnblogs.com/fifi1224/p/10555549.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/yinyinzuinihai/p/10556280.html#4213197