变量:引用(指向地址) + 值(该变量指向值所储存的那一片内存)
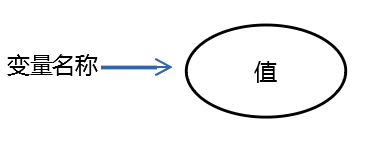
两个变量同一 : 判断 是否 这两个变量指向同一片内存。
两个变量相等 : 判断 是否 这两个变量的类型相同,且值相等。
注:常用的“==”运算符,以及Object类中的equals方法 都是 判断两个变量是否同一。
这是java文档中对object类的说明:
The equals method for class Object implements the most discriminating possible equivalence relation on objects; that is, for any non-null reference values x and y, this method returns true if and only if x and y refer to the same object (x == y has the value true).
Eg:
class PE{ private int number; public PE(int number) { this.number = number; } public int getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(int number) { this.number = number; } } public class equal { public static void main(String[] args) { PE A = new PE(5); PE B = new PE(5); if(A.equals(B)) System.out.println("A == B"); else System.out.println("A != B"); B = A; if(A.equals(B)) System.out.println("A == B"); else System.out.println("A != B"); } }
第一次比较,虽然两个变量的属性成员number都被赋值为5,但二者并未指向同一片内存,故而,二者由“==”运算符判断并不相等
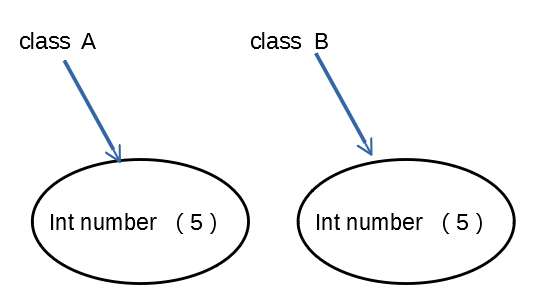
第二次比较,二者指向同一片内存,故而二者由“==”运算符判断相等。
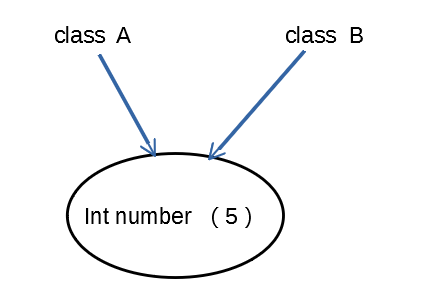
输出结果为:
如何判断相等呢?
所有的对象类型的数据成员最终一定建立在基本数据类型之上的,而以基本数据类型定义的值是不可变的(Immutability)。
也就是说,在内存中只会申请一片空间来表示以基本数据类型定义的值。而被赋以相同的值的变量将会指向同一片内存空间,而不会在内存开辟另一块内存空间。
所以,我们可以判断这些基本数据类型定义的值的同一,来判断变量的相等。
例如:
package blogEqual; class PE{ private int number; public PE(int number) { this.number = number; } public int getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(int number) { this.number = number; } public boolean equals(Object x) { if(this.getClass() != x.getClass()) return false; PE A = (PE)x; return (this.getNumber() == A.getNumber()); } } public class equal { public static void main(String[] args) { PE A = new PE(5); PE B = new PE(5); if(A.equals(B)) System.out.println("A == B"); else System.out.println("A != B"); B = A; if(A.equals(B)) System.out.println("A == B"); else System.out.println("A != B"); } }
具体实现方法为:使用方法的覆盖,对object超类的equals方法进行覆盖,先判断类型相同,继而判断基本数据类型的值相同。
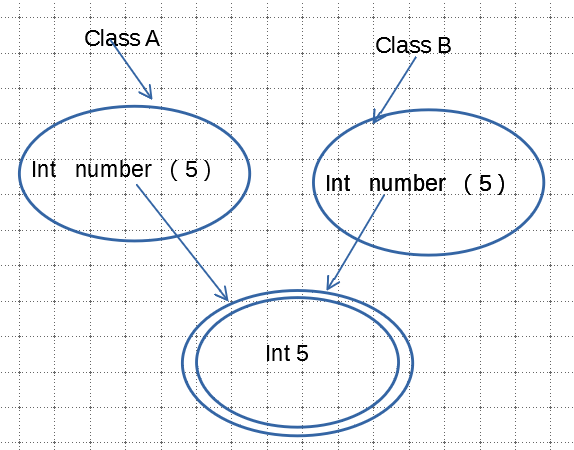
输出结果为: