Java 异常处理
try { //可能发生运行错误的代码; } catch(异常类型 异常对象引用){ //用于处理异常的代码 }
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); //接收所有的异常类型,若它位于try{}后,则不会执行其他catch(){}语句
} finally { //“善后”代码,无论是否发生异常都会执行 }
*Java 7版本后一个catch{} 可捕获多个异常*

【应用举例】
class AboutException {
public static void main(String[] a)
{
int i=1, j=0, k;
public static void main(String[] a)
{
int i=1, j=0, k;
try
{
k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception
//throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!");
}
catch ( ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
if (e instanceof ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("被0除");
else
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
finally
{
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK");
}
}
}
【运行结果】

【多层try{}catch{}嵌套时执行顺序】
public static void main(String args[]) {
int result;
try {
System.out.println("in Level 1");
int result;
try {
System.out.println("in Level 1");
try {
System.out.println("in Level 2");
// result=100/0; //Level 2
try {
System.out.println("in Level 3");
result=100/0; //Level 3
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 3 finally");
}
// result=100/0; //Level 2
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 2 finally");
}
// result = 100 / 0; //level 1
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
. System.out.println("In Level 1 finally");
}
}
运行结果:
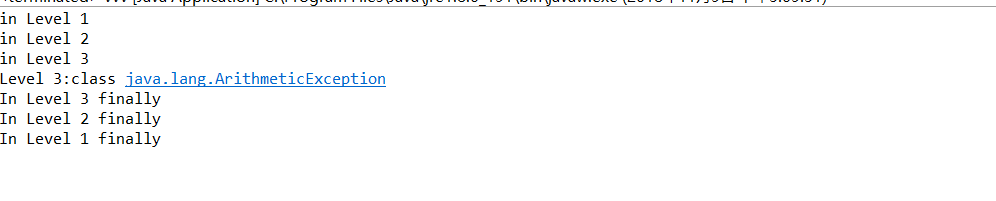
最外层的catch{}先执行,然后执行内层的catch{],内层的fanally{},外层的finally{};
【finally{}不会执行的情况】
public static void main(String args[]) { try{ System.out.println("in main"); throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main"); //System.exit(0); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); System.exit(0);//这条语句表示退出虚拟机,以后的任何代码都将不会被执行 } finally//不会执行 { System.out.println("i am the finally"); } }

public static void main( String args[] ) { try { method1(); } catch ( Exception e ) { System.err.println( e.getMessage() + " " ); e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void method1() throws Exception { method2(); } public static void method2() throws Exception { method3(); } public static void method3() throws Exception { throw new Exception( "Exception thrown in method3" ); }
运行结果
第一行是System.err.println( e.getMessage() + "
" );的运行结果,返回一个字符串,捕获throw new Exception( "Exception thrown in method3" );
后几行是e.printStackTrace();运行的结果,打印方法调用堆栈。
【throws语句的具体用法】
throws语句的异常,系统自己不能处理,需要调用者处理,当一个方法包含throws子句时,需要在调用此方法的代码中使用try/catch/finally进行捕获,或者是重新声明,否则编译错误。
*子类,父类方法同时,子类的抛出异常不能是父类的基类
public class OverrideThrows { public void test()throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt"); } } class Sub extends OverrideThrows { //如果test方法声明抛出了比父类方法更大的异常,比如Exception //则代码将无法编译…… public void test() throws FileNotFoundException { //... } }
【自定义异常处理类MyException】
*通常派生自Exception
*在合适的地方用throws抛出异常 即:throws new MyException();
class MyException extends Exception { public MyException(String Message) { super(Message); } public MyException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public MyException( Throwable cause) { super(cause); } } public class ExceptionLinkInRealWorld { public static void main( String args[] ) { try { throwExceptionMethod(); //有可能抛出异常的方法调用 } catch ( MyException e ) { System.err.println( e.getMessage() ); System.err.println(e.getCause().getMessage()); } catch ( Exception e ) { System.err.println( "Exception handled in main" ); } doesNotThrowException(); //不抛出异常的方法调用 } public static void throwExceptionMethod() throws MyException { try { System.out.println( "Method throwException" ); throw new Exception("系统运行时引发的特定的异常"); // 产生了一个特定的异常 } catch( Exception e ) { System.err.println( "Exception handled in method throwException" ); //转换为一个自定义异常,再抛出 throw new MyException("在方法执行时出现异常",e); } finally { System.err.println( "Finally executed in throwException" ); } // any code here would not be reached } public static void doesNotThrowException() { try { System.out.println( "Method doesNotThrowException" ); } catch( Exception e ) { System.err.println( e.toString() ); } finally { System.err.println( "Finally executed in doesNotThrowException" ); } System.out.println( "End of method doesNotThrowException" ); } }

