题目如下:
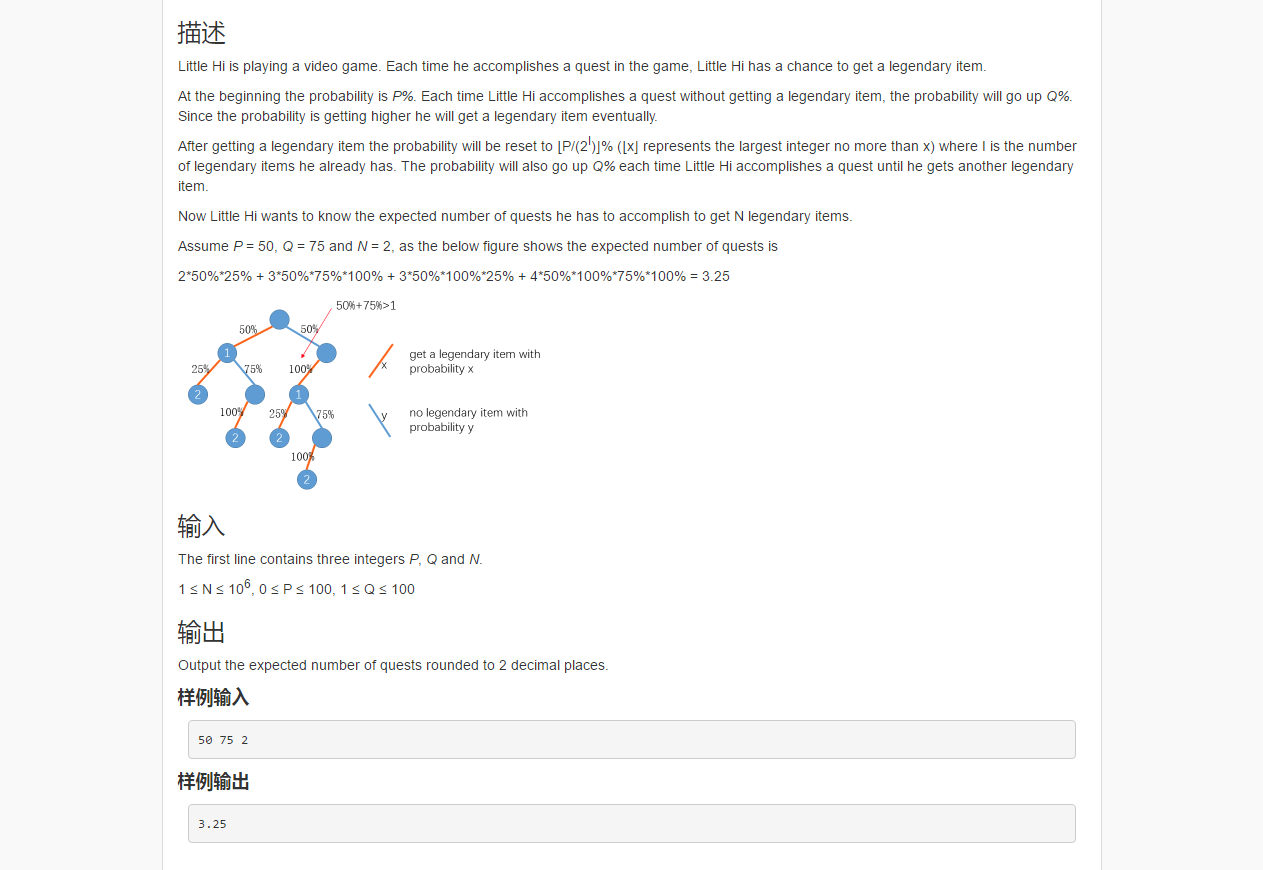
这道题难点不仅在于正确理解题意,判断递归条件,更在于用数学方法推出解决公式。因为N最大为1百万,而内存只有256MB, 所以暴力递归肯定会超时,超空间。
不过,我才疏学浅,又没有大量时间去深究,所以只写出了暴力递归算法。进一步优化的话,可以考虑P在迭代很久后会变为0这一事实,也许可以进一步节省时空消耗。
下面给出算法,由于我注释写的很详细,这里就不进一步解释了。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 4 static int P; 5 static int Q; 6 static int N; 7 8 static double result = 0; 9 10 /** 11 * 12 * @param num 当前获得宝物个数,初始化为0 13 * @param arrayProb 保存每次路径参数 14 * @param prob 当前路径成功概率,初始化为0 15 * @param pathLen 当前路径长度,初始化为0 16 * @param p 初始成功概率,初始化为P 17 */ 18 public static void getPath(int num,int[] arrayProb ,int prob, int pathLen, int p){ 19 if (num < N) 20 { 21 //首先递归左子树,也就是成功路径子树,成功只有三种情况 22 if (prob >= 100){ 23 arrayProb[pathLen] = 100; 24 getPath(num+1, arrayProb, 0, pathLen+1, (int)(p/Math.pow(2,num+1))); 25 }else if(prob > 0){ 26 arrayProb[pathLen] = prob; 27 getPath(num+1,arrayProb,0, pathLen+1, (int)(p/Math.pow(2,num+1))); 28 } else if (p > 0){ 29 arrayProb[pathLen] = p; 30 getPath(num+1, arrayProb, 0, pathLen+1, (int)(p/Math.pow(2,num+1))); 31 } 32 33 //再遍历同层右子树,也就是失败路径概率。prob<100,才有失败可能。 34 if (prob < 100 && p < 100) { 35 int tmp; 36 if(prob == 0){//只有第一次或者成功后prob才会为0 37 tmp = 100 - p; 38 prob = p; 39 }else { 40 tmp = 100 - prob; 41 } 42 arrayProb[pathLen] = tmp; 43 getPath(num, arrayProb, prob + Q, pathLen + 1,p); 44 } 45 } else{ 46 double tmp = 1; 47 for (int i = 0; i < pathLen; i++) { 48 tmp *= 0.01 * arrayProb[i]; 49 System.out.printf(arrayProb[i] + " "); 50 } 51 System.out.println(); 52 tmp *= pathLen; 53 result += tmp; 54 } 55 } 56 57 public static void main(String[] args) { 58 // write your code here 59 int[] array = new int[100000]; 60 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 61 while (scanner.hasNext()){ 62 result = 0; 63 P = scanner.nextInt(); 64 Q = scanner.nextInt(); 65 N = scanner.nextInt(); 66 getPath(0,array,0,0,P); 67 System.out.printf("%.2f", result); 68 } 69 } 70 }