|
本节简单总结torch.nn封装的18种损失函数。【文中思维导图采用MindMaster软件,Latex公式采用在线编码器】 |
目录
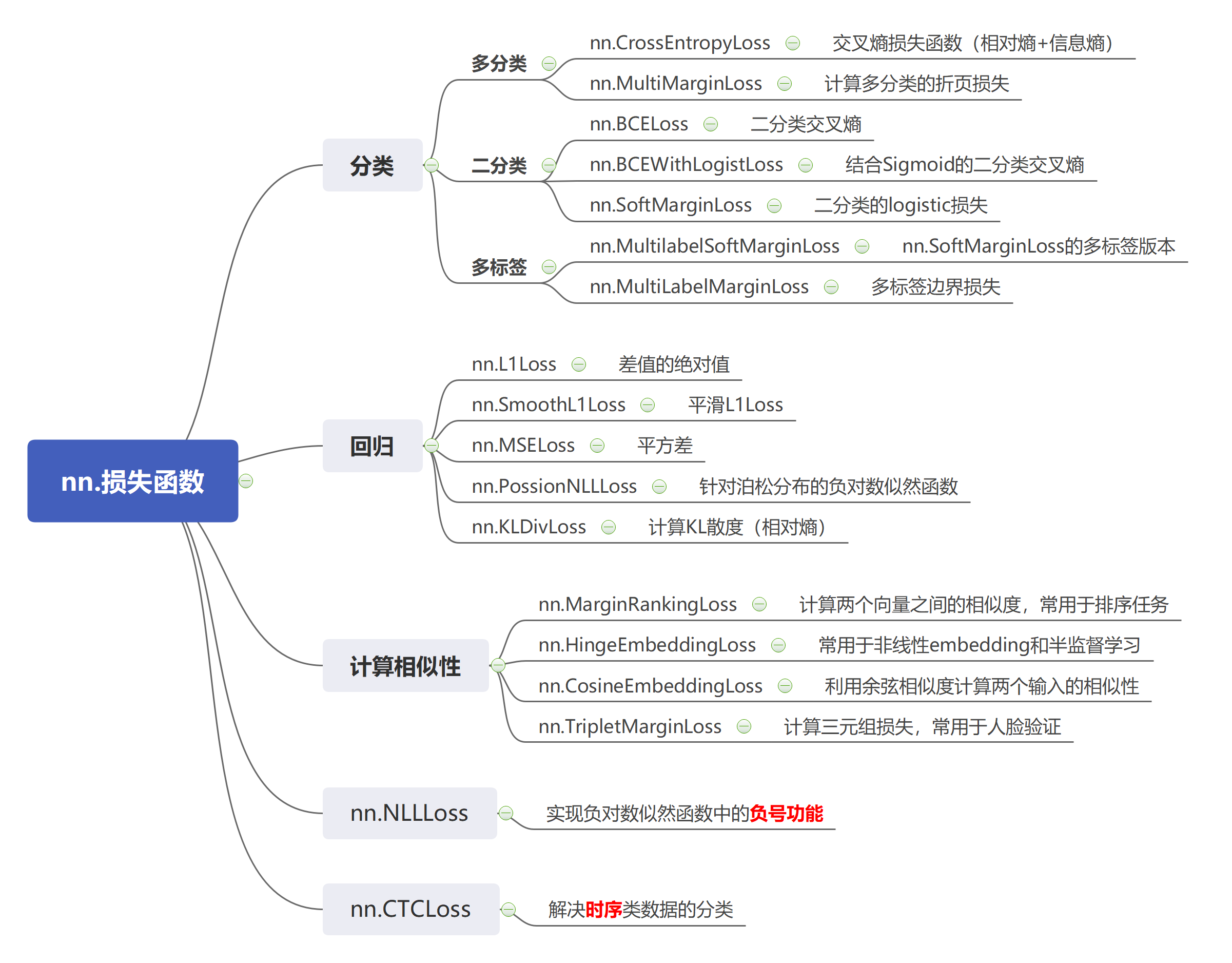
1.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()交叉熵损失函数
这里大家可以进入“一文搞懂交叉熵在机器学习中的使用,透彻理解交叉熵背后的直觉”,这个博主讲的非常好!
loss_f = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')
inputs = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [1, 3], [1, 3]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([0, 1, 1], dtype=torch.long)
loss = loss_f(inputs, target)
# 参数:
# weight:设置各类别的loss的权重,(防止类别数目不平衡)e.g. weights = torch.tensor([1, 2], dtype=torch.float) 两个类别
# ignore_index: 忽略某个类别
# reduction:计算模式 1.'None':逐元素计算,返回张量;2.'sum':所有元素求和,返回标量;3.'mean':加权平均,返回标量
nn.CrossEntropyLoss是nn.LogSoftmax与nn.NLLLoss的结合,公式为:
[lossleft ( x,class
ight )= -log{left ( frac{exp xleft [ class
ight ] }{sum_{j} exp xleft [ j
ight ] }
ight ) }=weightleft [ class
ight ] left ( -xleft [ class
ight ] +log{sum_{j} exp xleft [ j
ight ]}
ight )
]
上述公式的由来:交叉熵 = 信息熵 + 相对熵
- 信息熵:描述整个概率分布上事件的不确定性
[Hleft ( p
ight ) =E_{xsim p} left [ Ileft ( x
ight )
ight ] =sum_{i}^{N} pleft ( x_{i}
ight )left ( -log{pleft ( x_{i}
ight )}
ight )
]
- 相对熵(KL散度):描述两个分布之间的距离
[D_{KL}left ( P,Q
ight ) =E_{xsim p} left [ log{frac{Pleft ( x
ight ) }{Qleft ( x
ight ) } }
ight ]=sum_{i}^{N} Pleft ( x_{i}
ight )left [ log{Pleft ( x_{i}
ight )}- log{Qleft ( x_{i}
ight )}
ight ]
]
- 交叉熵
[Hleft ( P, Q
ight ) =D_{KL}left ( P,Q
ight ) +Hleft ( p
ight ) =-sum_{i}^{N} Pleft ( x_{i}
ight )left [- log{Qleft ( x_{i}
ight )}
ight ]
]
其中 (P) 为真实数据分布,(H(P)) 在优化时为常数,故而 (Hleft ( P,Q ight ) longrightarrow D_{KL}left ( P,Q ight ))。实际代码中, (P) 即为标签,(Q) 为数据经过网络得到的分布,即取(softmax)。
2.nn.BCELoss()二分类交叉熵损失函数
注意:输入值必须在[0,1]之间,表示一个分布。
loss_f = nn.BCELoss(weight=None,reduction='mean')
inputs = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [2, 2], [3, 4], [4, 5]], dtype=torch.float)
target = torch.tensor([[1, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], [0, 1]], dtype=torch.float)
loss = loss_f(inputs, target)
3.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()结合Sigmoid的二分类交叉熵损失函数
loss_f = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=None, reduction='mean', pos_weight=None)
# 参数:
# pos_weight:正样本(标签为1)的权值
4.nn.L1Loss
计算inputs与label之间差值的绝对值
[l_{i}=left | x_{i}-y_{i }
ight |
]
5.nn.MSELoss
计算inputs与label之间的平方差
[l_{i}=left ( x_{i}-y_{i }
ight ) ^{2}
]
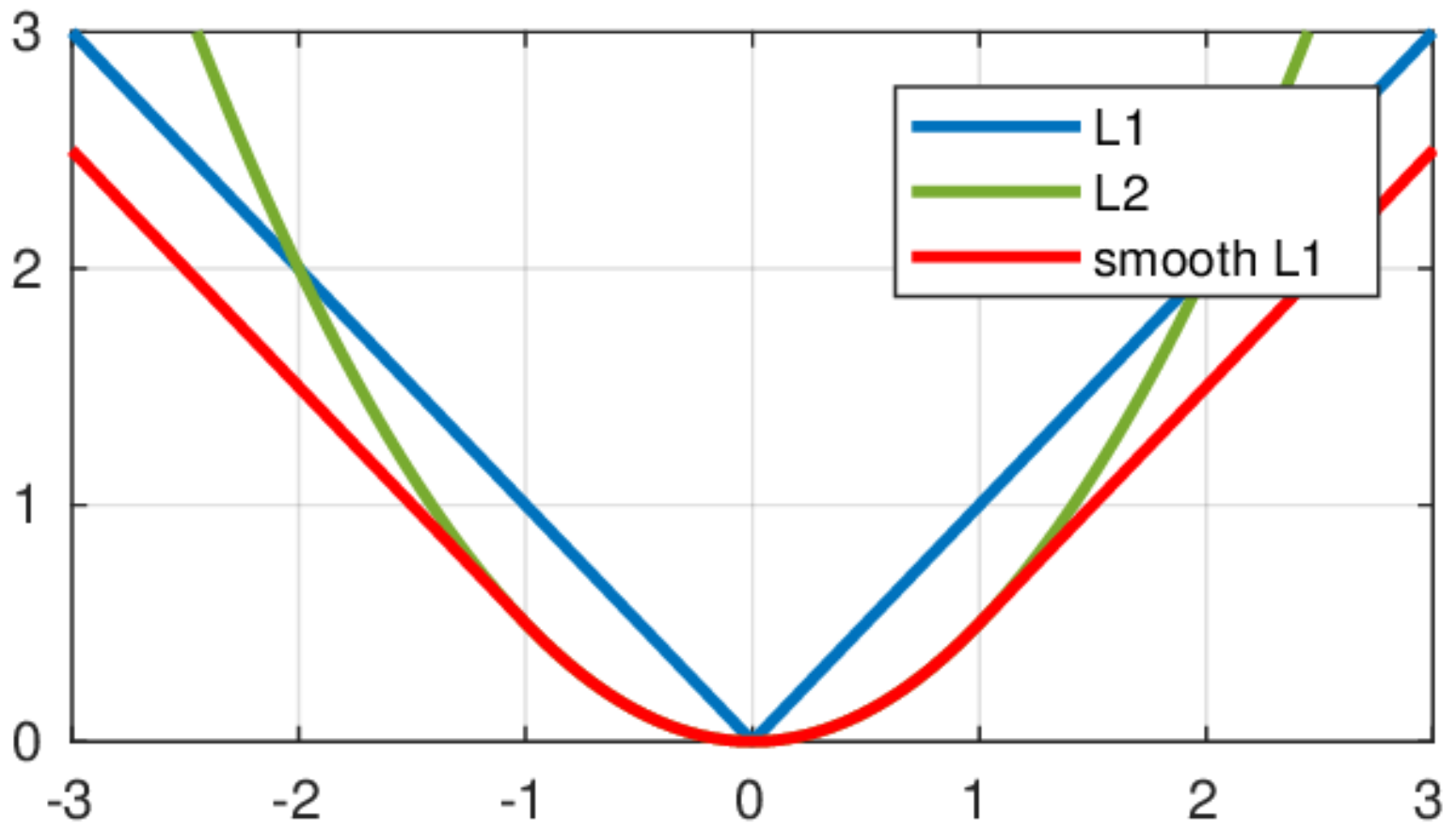
6.nn.SmoothL1Loss
平滑的L1Loss,由图2红色线与蓝色线对比可以看出。通过下面的公式我们也可以知道,SmoothL1损失结合了L1和MSE两者的优点。
[left{egin{matrix}
loss=frac{1}{n}sum_{i}^{n} z_{i}
\z_{i}=egin{cases}
frac{1}{2} left ( x_{i}-y_{i }
ight ) ^{2} & ext{ if } left | x_{i}-y_{i }< 1
ight | \
left | x_{i}-y_{i }
ight |-0.5 & ext{others}
end{cases}
end{matrix}
ight.]