题目描述
在有向图G 中,每条边的长度均为1 ,现给定起点和终点,请你在图中找一条从起点到终点的路径,该路径满足以下条件:
1 .路径上的所有点的出边所指向的点都直接或间接与终点连通。
2 .在满足条件1 的情况下使路径最短。
注意:图G 中可能存在重边和自环,题目保证终点没有出边。
请你输出符合条件的路径的长度。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
输入文件名为road .in。
第一行有两个用一个空格隔开的整数n 和m ,表示图有n 个点和m 条边。
接下来的m 行每行2 个整数x 、y ,之间用一个空格隔开,表示有一条边从点x 指向点y 。
最后一行有两个用一个空格隔开的整数s 、t ,表示起点为s ,终点为t 。
输出格式:
输出文件名为road .out 。
输出只有一行,包含一个整数,表示满足题目᧿述的最短路径的长度。如果这样的路径不存在,输出- 1 。
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
3 2 1 2 2 1 1 3
输出样例#1:
-1
输入样例#2:
6 6 1 2 1 3 2 6 2 5 4 5 3 4 1 5
输出样例#2:
3
说明
解释1:
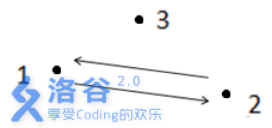
如上图所示,箭头表示有向道路,圆点表示城市。起点1 与终点3 不连通,所以满足题
目᧿述的路径不存在,故输出- 1 。
解释2:
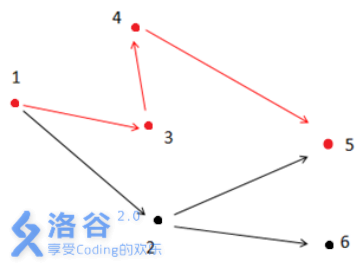
如上图所示,满足条件的路径为1 - >3- >4- >5。注意点2 不能在答案路径中,因为点2连了一条边到点6 ,而点6 不与终点5 连通。
对于30%的数据,0<n≤10,0<m≤20;
对于60%的数据,0<n≤100,0<m≤2000;
对于100%的数据,0<n≤10,000,0<m≤200,000,0<x,y,s,t≤n,x≠t。
- noip2014 day2t2,图论题,不过貌似比较简单。
- 已知只有所有出边都直接或间接指向终点的点才可能被选择,所以就建反边,从终点想起点扫,dfs,bfs均可,在把所有终点不能达到的点打上标记,这些点均不可备选择,并且在反边图中这些点所指向的点也不能被选择(因为在正边图中这些点指向标记点)。因此可以删去图中不符合要求的点,然后跑最短路即可。
- spfa,heap+dijkstra均可,bfs,dfs复杂度为O(n),spfa复杂度为O(ke),heap+dijkstra复杂度为O(nloge),均可通过该题。
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstring> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int tot,total,n,m,ss,tt,l[500050],r[500050],pre[500050],last[10050],other[500050]; 7 int que[10050],d[10050]; 8 bool judge[10050],vis[10050],point[10050]; 9 10 void add(int u,int v) { 11 pre[++tot]=last[u]; 12 last[u]=tot; 13 other[tot]=v; 14 } 15 16 void bfs(int x) { 17 int h=0,t=1; 18 que[1]=x; 19 vis[x]=1; 20 point[x]=1; 21 total++; 22 while (h<t) { 23 int cur=que[++h]; 24 for (int p=last[cur]; p; p=pre[p]) { 25 int q=other[p]; 26 if (!vis[q]) { 27 vis[q]=1; 28 que[++t]=q; 29 total++; 30 point[q]=1; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 36 void spfa(int x) { 37 int h=0,t=1; 38 que[1]=x; 39 memset(d,127,sizeof d); 40 d[x]=0; 41 while (h<t) { 42 int cur=que[++h]; 43 vis[cur]=0; 44 for (int p=last[cur]; p; p=pre[p]) { 45 int q=other[p]; 46 if (!point[q]) continue; 47 if (judge[q]) continue; 48 if (d[q]>d[cur]+1) { 49 d[q]=d[cur]+1; 50 if (!vis[q]) { 51 vis[q]=1; 52 que[++t]=q; 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 59 int main() { 60 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 61 for (int i=1; i<=m; i++) scanf("%d%d",&l[i],&r[i]); 62 scanf("%d%d",&ss,&tt); 63 for (int i=1; i<=m; i++) add(r[i],l[i]); 64 bfs(tt); 65 if (!point[ss]) { 66 printf("%d",-1); 67 return 0; 68 } 69 for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) { 70 if (point[i]) continue; 71 for (int p=last[i]; p; p=pre[p]) { 72 int q=other[p]; 73 judge[q]=1; 74 } 75 } 76 memset(que,0,sizeof que); 77 memset(vis,0,sizeof vis); 78 memset(last,0,sizeof last); 79 tot=0; 80 for (int i=1; i<=m; i++) add(l[i],r[i]); 81 spfa(ss); 82 printf("%d",d[tt]); 83 return 0; 84 }