1. String类的概述
java.lang.Object ==> java.lang.String
只要是java.lang包下面的类,都不用导包,直接就可以使用。
类代码定义
public final class String extends Object implements Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence
String 类代表字符串。
Java 程序中的所有字符串字面值(如 "abc" )都作为此类的实例实现。
package com.heima.string; public class Demo1_String { /** * 字符串字面值“ABC”也可以看成是一个字符串对象。 * 字符串是常量,一旦被赋值,就不能被改变。 * */ public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "abc"; // "abc"可以看成一个字符串对象 str = "def"; // 当把"def"赋值给str,原来的"abc"就变成了垃圾 System.out.println(str); System.out.println(str.toString()); // String类重写了toString方法,返回的是该对象本身。 } }
字符串是常量;
它们的值在创建之后不能更改。
字符串缓冲区支持可变的字符串。因为 String 对象是不可变的,所以可以共享。
2. String类的构造方法
- 常见构造方法:
- public String() 空构造
- public String(byte[] bytes) 把字节数组转换成字符串
- public String(byte[] bytes, int index, int length) 把字节数组的一部分转成字符串
- public String(char[] value) 把字符数组转成字符串
- public String(char[] value, int index, int count) 把字符数组的一部分转成字符串
- public String(String original) 把字符串常量值转换成字符串
- 案例演示:
-
package com.heima.string; public class Demo2_String { /** public String() 空构造 初始化一个新创建的 String 对象,使其表示一个空字符序列。 public String(byte[] bytes) 把字节数组转换成字符串 通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的 byte 数组,构造一个新的 String。 public String(byte[] bytes, int index, int length) 把字节数组的一部分转成字符串 public String(char[] value) 把字符数组转成字符串 public String(char[] value, int index, int count) 把字符数组的一部分转成字符串 public String(String original) 把字符串常量值转换成字符串 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = new String(); System.out.println(s1); byte[] arr1 = {97,98,99}; String s2 = new String(arr1); System.out.println(s2); // 输出abc // 使用项目默认码表中(包含ascii码表)97对应的是a byte[] arr2 = {97,98,99,100,101,102}; String s3 = new String(arr2,2,3); System.out.println(s3); //输出cde char[] arr3 = {'a','b','c','d','e'}; String s4 = new String(arr3); System.out.println(s4); // 输出 abcde String s5 = new String(arr3,2,3); System.out.println(s5); // 输出cde String s6 = new String("heima"); System.out.println(s6); // 输出heima } }
-
3. String类的常见面试题
1.判断定义为String类型的s1和s2是否相等
String s1 = "abc"; String s2 = "abc"; System.out.println(s1 == s2); System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
输出结果:true,true。
结果分析:
- ==号和equals方法的区别
- ==是一个比较运算符号
- 既可以比较基本数据类型 ==> 基本数据类型比较的是值
- 也可以比较引用数据类型 ==> 引用数据类型比较的是地址值
- equals方法是一个方法,只能比较引用数据类型,所有的对象都会继承Object类中的方法,如果没有重写Object类中的equals方法,equals方法和==号比较引用数据类型无区别,重写后的equals方法比较的是对象中的属性
- ==是一个比较运算符号
- String类重写equals方法:
- public boolean equals(Object anObject)
- 将此字符串与指定的对象比较。
- 当且仅当该参数不为 null,并且是与此对象表示相同字符序列的 String 对象时,结果才为 true。
- 覆盖:
- 类 Object 中的 equals
- 参数:
- anObject - 与此 String 进行比较的对象。
- 返回:
- 如果给定对象表示的 String 与此 String 相等,则返回 true;否则返回 false。
- 另请参见:
- compareTo(String), equalsIgnoreCase(String)
- public boolean equals(Object anObject)
- 注意:str类型是引用数据类型,所有继承Object类的对象都是引用数据类型。
- 所以,s1.equals(s2),只要s1和s2的字符序列相同,即相等。
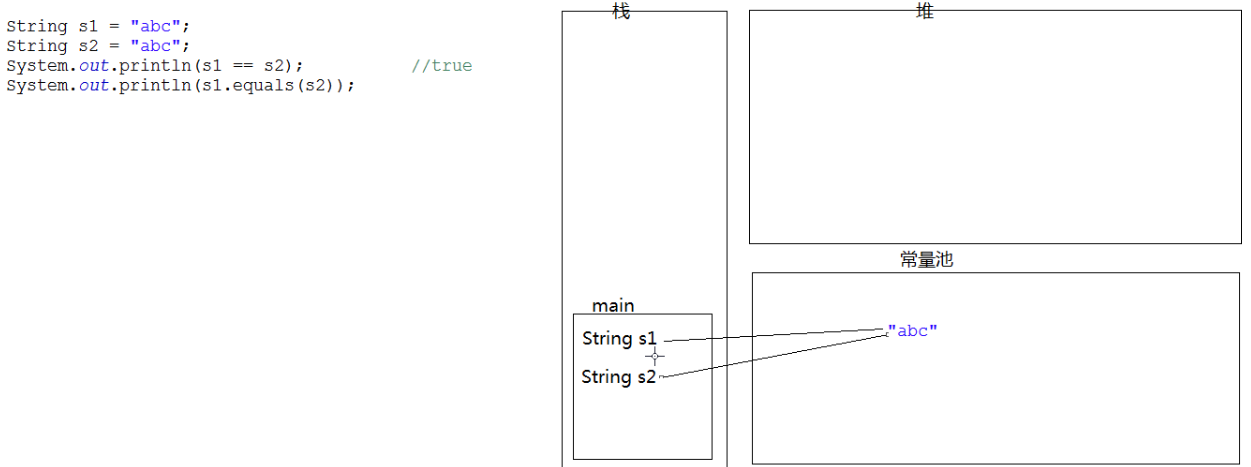
- 而s1 == s2,则需要参考下图中
- 如果常量池中,没有该常量,则创建一个新的常量,并指向s1;
- 如果常量池中,已经有了该常量,则将常量地址指向s2
- 由于s1和s2指向同一个常量,同一个地址,故相等。
2.下面这句话在内存中创建了几个对象?
String s1 = new String("abc");
答案:两个对象,一个对象在堆内存中,一个在方法区的常量池中。

答案解析:
- 在常量池中,如果没有该常量对象,则会创建一个常量对象。
- new String() 表示在堆内存中创建一个对象,将常量池中常量移动到对象中。
- 常量对象和new String() 对象的地址是不同的,故两个是在不同的内存位置的两个对象。
3.判断定义为String类型的s1和s2是否相等
String s1 = new String("abc"); String s2 = "abc"; System.out.println(s1 == s2); System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
解答:false 和 true
答案解析:
-
String s1 = new String("abc"); 记录的是堆内存对象的地址值 -
String s2 = "abc"; 记录的是常量池中的地址值
4.判断定义为String类型的s1和s2是否相等
String s1 = "a" + "b" + "c"; String s2 = "abc"; System.out.println(s1 == s2); System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
解答:true 和 true
答案解析:
- java中有常量优化机制,会将"a" + "b" + "c"编译时直接作为"abc"的常量放在常量池中
- 比如:byte b = 3 + 4; 在编译时就会变成了7,将7赋值给b。
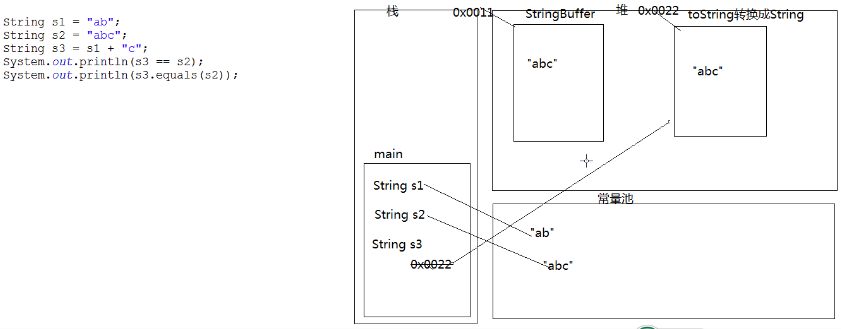
5.判断定义为String类型的s1和s2是否相等
String s1 = "ab"; String s2 = "abc"; String s3 = s1 + "c"; System.out.println(s3 == s2); System.out.println(s3.equals(s2));
解答:false 和 true
答案解析:
-
Java 语言提供对字符串串联符号("+")以及将其他对象转换为字符串的特殊支持。字符串串联是通过
StringBuilder(或StringBuffer)类及其append方法实现的。
4. String类的判断功能
- boolean equals(Object obj): 比较字符串的内容是否相同,区分大小写
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo4_StringMethod { /** boolean equals(Object obj): 比较字符串的内容是否相同,区分大小写 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = "heima"; String s3 = "heiMa"; System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // 输出true System.out.println(s2.equals(s3)); // 输出false } }
-
- boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str): 比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo4_StringMethod { /** boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str): 比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = "heima"; String s3 = "heiMa"; System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); // 输出true System.out.println(s2.equalsIgnoreCase(s3)); // 输出true } }
-
- boolean contains(String str): 判断大字符串中是否包含小字符串
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo4_StringMethod { /** boolean contains(String str): 判断大字符串中是否包含小字符串 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = "ei"; System.out.println(s1.contains("ma")); // 输出true System.out.println(s1.contains(s2)); // 输出true } }
-
- boolean startsWith(String str): 判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串开头
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo4_StringMethod { /** boolean startsWith(String str): 判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串开头 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = "he"; System.out.println(s1.startsWith(s2)); // 输出true System.out.println(s1.startsWith("h")); // 输出true } }
-
- boolean endsWith(String str): 判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串结尾
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo4_StringMethod { /** boolean endsWith(String str): 判断字符串是否以某个指定的字符串结尾 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = "he"; System.out.println(s1.endsWith(s2)); // 输出false System.out.println(s1.endsWith("a")); // 输出true } }
-
- boolean isEmpty(): 判断字符串是否为空
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo4_StringMethod { /** boolean isEmpty(): 判断字符串是否为空 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = ""; String s3 = null; System.out.println(s1.isEmpty()); // 输出false System.out.println(s1.isEmpty()); // 输出false System.out.println(s3.isEmpty()); // java.lang.NullPointerException /* "" 和 null 的区别: ""是字符串常量,同时也是一个String类的对象,既然是对象,当然可以调用String类中的方法 null是空常量,不能调用任何方法,否则会出现空指针异常 */ } }
-
"" 和 null 的区别:
- ""是字符串常量,同时也是一个String类的对象,既然是对象,当然可以调用String类中的方法。
- null是空常量,不能调用任何方法,否则会出现空指针异常。
- null常量可以给任意的引用数据类型赋值。
-
5. 练习:模拟用户登录
- 需求:
- 模拟登录,给三次机会,并提示还有几次
- 用户名和密码都是admin
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.test; import java.util.Scanner; public class Test1 { /** 需求: 模拟登录,给三次机会,并提示还有几次 用户名和密码都是admin */ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for (int i = 0; i <3 ; i++) { System.out.println("请输入用户名:"); String userName = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入密码:"); String password = sc.nextLine(); if ("admin".equals(userName) && "admin".equals(password)) { System.out.println("欢迎" + userName + "登录"); break; } else { if (i == 2) { System.out.println("您已经出错三次,请明天再来吧!"); } else { System.out.println("登录错误,您还有" + (2-i) + "次机会"); } } } } }
6. String类的获取功能
- int length() : 获取字符串的长度
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo5_StringMethod { /** int length() : 获取字符串的长度 */ public static void main(String[] args) { // int[] arr = {11,22,33}; // System.out.println(arr.length); // 数组中的length是属性 String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = "人类命运共同体"; System.out.println(s1.length()); // 输出5 System.out.println(s2.length()); //输出7 } }
-
- char charAt(int index): 获取指定索引位置的字符
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo5_StringMethod { /** char charAt(int index): 获取指定索引位置的字符 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = "人类命运共同体"; System.out.println(s1.charAt(3)); // 输出 m System.out.println(s2.charAt(3)); //输出 运 System.out.println(s1.charAt(10)); // java.lang.StringIndexOutOfBoundsException // 字符串索引越界异常 } }
-
- int indexOf(int ch): 返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo5_StringMethod { /** int indexOf(int ch): 返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = "人类命运共同体"; System.out.println(s1.indexOf(97)); // 输出 4 System.out.println(s1.indexOf("a")); // 输出 4 // 参数接收的是int类型的,传递char类型的会自动提升 System.out.println(s1.indexOf("ma")); // 输出3 System.out.println(s1.indexOf("Ma")); // 输出-1,表示没有出现匹配项 } }
-
- int indexOf(String str): 返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo5_StringMethod { /** int indexOf(int ch): 返回指定字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = "人类命运共同体"; System.out.println(s1.indexOf(97)); // 输出 4 System.out.println(s1.indexOf("a")); // 输出 4 // 参数接收的是int类型的,传递char类型的会自动提升 System.out.println(s1.indexOf("ma")); // 输出3 System.out.println(s1.indexOf("Ma")); // 输出-1,表示没有出现匹配项 } }
-
- int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex): 返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引
- int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex): 返回指定字符串在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引
- lastIndexOf
- 等价 上面两个指定字符串位置前,第一次出现的索引
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo5_StringMethod { /** int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex): 返回指定字符在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引 int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex): 返回指定字符串在此字符串中从指定位置后第一次出现处的索引 lastIndexOf 返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引 int lastIndexOf(int ch) lastIndexOf(int ch,int fromIndex) 返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引处开始进行反向搜索。 int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex) 返回指定子字符串在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始。 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heimaheima"; System.out.println(s1.indexOf(97,5)); // 输出 9 System.out.println(s1.indexOf('a',5)); // 输出 9 System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf('a')); // 输出9,找到字符串中最后一个匹配的索引 System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf(97,9)); // 输出 9 System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf('a',5)); // 输出 4 } }
- String substring(int start): 从指定位置开始截取字符串,默认到末尾
- String substring(int start, int end): 从指定位置开始到指定位置结束截取字符串。
-
 View Code
View Codepackage com.heima.string; public class Demo5_StringMethod { /** String substring(int start): 从指定位置开始截取字符串,默认到末尾 String substring(int start,int end): 从指定位置开始截取字符串,截止到 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "heimaheima"; System.out.println(s1.substring(3)); System.out.println(s1.substring(3,5)); } }
-
7. 字符串的遍历
package com.heima.test; public class Test2 { /** 字符串的遍历 */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "heima"; for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { System.out.println(s.charAt(i)); } } }
8. 统计不同类型字符个数
- 案例演示:
- 统一个字符串中大写字母字符,小写字母字符,数字字符出现的次数,其他字符出现的次数。
- ABCDEabcd123456!@#$%^
-
package com.heima.test; public class Test3 { /** 统一个字符串中大写字母字符,小写字母字符,数字字符出现的次数,其他字符出现的次数。 ABCDEabcd123456!@#$%^ */ public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "ABCDEabcd123456!@#$%^"; int big = 0; int small = 0; int num = 0; int other = 0; for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); if(c >= 'A' && c <='Z'){ big++; } else if(c >= 'a' && c <='z') { small++; } else if(c >= '0' && c <='9') { num++; } else { other++; } } System.out.println(big); System.out.println(small); System.out.println(num); System.out.println(other); } }
9. String类的转换功能
- byte[] getBytes(): 把字符串转换为字节数组
- char[] toCharArray(): 把字符串转换为字符数组
- static String valueOf(char[] data): 把字符数组转成字符串
- static String valueOf(char[] data,int offset, int count): 把从指定索引位置开始截取指定长度的字符数组转成字符串
- static String valueOf(int i): 把int类型的数据转成字符串
- static String valueOf(long l)
- static String valueOf(float f)
- static String valueOf(double d)
- static String valueOf(char c)
- static String valueOf(Object obj)
- 如果实参是对象Object,则调用该对象的toString方法(若该类未重写toString方法,则调用Object顶层类的toString方法)
- 底层是由String类的构造方法实现的
- String toLowerCase(): 小写化
- String toUpperCase(): 大写化
- String concat(String str): 字符串拼接
- 用“+”号拼接字符串更强大,可以用字符串与任意类型相加
- concat方法的参数,只能是字符串
代码示例:

package com.heima.string; public class Demo6_StringMethod { /** byte[] getBytes(): 把字符串转换为字节数组 char[] toCharArray(): 把字符串转换为字符数组 static String valueOf(char[] chs): 把字符数组转成字符串 static String valueOf(int i): 把int类型的数据转成字符串 String toLowerCase(): 小写化 String toUpperCase(): 大写化 String concat(String str): 字符串拼接 */ public static void main(String[] args) { //test1_getBytes(); //test2_toCharArray(); //static String valueOf(char[] chs): 把字符数组转成字符串 //static String valueOf(int i): 把int类型的数据转成字符串 char[] arr1 = {'a','b','c','d'}; System.out.println(String.valueOf(arr1)); System.out.println(String.valueOf(arr1,1,2)); // char[] data,int offset,int count System.out.println(String.valueOf(100)); System.out.println(String.valueOf(true)); // String.valueOf可以将boolean b,char c, char[] data,double d // float f, int i, long l, Object obj等多种类型的数据转换为字符串。 System.out.println(String.valueOf(100) + 100); } public static void test2_toCharArray() { // char[] toCharArray(): 把字符串转换为字符数组 String s2 = "abc中国"; char[] arr = s2.toCharArray(); for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); } } public static void test1_getBytes() { // byte[] getBytes(): 把字符串转换为字节数组 String s1 = "abc中国"; byte[] arr = s1.getBytes(); // 通过gbk码表将字符串转换成字节数组 System.out.println(arr); // 输出[B@831e35, for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); // 输出97,98,99,-42,-48,-71,-6 // 编码:把我们看得懂转换为计算机看的懂的 // gbk码表一个中文代表两个字节 // gbk码表特点,中文的第一个字节肯定负数 } } }
10. 练习:按要求转换字符(链式编程)
需求:
把一个字符串的首字母转成大写,其余为小写。只考虑英文大小写字母字符。
package com.heima.test; public class Test4 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { String test = "we are CHINESE"; System.out.println(test.substring(0,1).toUpperCase().concat(test.substring(1,test.length()).toLowerCase())); } }
链式编程:
只要保证每次调用完方法返回的是对象,就可以继续调用。
11. 练习:把数组转成字符串
需求:
把数组中的数据按照指定格式拼接成一个字符串。
举例:int[] arr = {1,2,3};
输出结果:"[1, 2, 3]"
package com.heima.test; public class Test5 { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1,2,3}; String s = "["; for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { s = s + arr[i] + ", "; } System.out.println(s.substring(0,s.length()-2) + "]"); } }
12. String类的其他功能
- 替换功能
- String replace(char old, char new)
- String replace(String old, String new)
- 去除字符串两侧空格
- String trim()
- 按字典顺序比较两个字符串
- int compareTo(String str)
- 基于字符串各个字符的Unicode值,按字典顺序将此String对象表示的字符序列与参数字符串所表示的字符序列进行比较。
- 如果此String对象位于参数字符串之前,则比较结果为一个负整数
- 如果相等,则结果为0。compareTo只在equals(Object) 返回 true时才返回0
- 如果此String对象位于参数字符串之后,则比较结果为一个正整数。
- int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
- 按字典顺序比较两个字符串,不考虑大小写。
- int compareTo(String str)

package com.heima.string; public class Demo7_StringMethod { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { method1_replace(); method2_trim(); method3_compareTo(); method4_compareToIgnoreCase(); } public static void method4_compareToIgnoreCase() { String s1 = "heima"; String s2 = "HEIMA"; System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); } public static void method3_compareTo() { String s1 = "abc"; String s2 = "pcd"; int num = s1.compareTo(s2); System.out.println(num); // 输出-15 String s3 = "abc"; String s4 = "bcd"; System.out.println(s3.compareTo(s4)); //输出-1 String s5 = "abc"; String s6 = "acd"; System.out.println(s5.compareTo(s6)); //输出-1,首字母相等,则比较第二个字母 String s7 = "a"; String s8 = "aaaaa"; System.out.println(s7.compareTo(s8)); //输出-4,首字母相等,顺位无法比较,则按长度比较,1-5=-4 String s9 = "黑"; String s10 = "马"; System.out.println(s9.compareTo(s10)); //输出1125 /* System.out.println('黑' + 0); // 40657 System.out.println('马' + 0); // 39532 40657 - 39532 = 1125 查找的是unicode码表值 */ } public static void method2_trim() { String s = " we are Chinese! "; System.out.println(s.trim()); } public static void method1_replace() { String s = "heima"; System.out.println(s.replace("i", ",")); //输出he,ma System.out.println(s.replace("ma", "!!")); //输出hei!! } }
13. 练习:字符串反转
需求:把字符串反转
如:把键盘录入“abc”,输出结果“cba”。

package com.heima.test; import java.util.Scanner; public class Test6 { public static void main(String[] args) { method1(); method2(); } public static void method2() { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String s1 = sc.nextLine(); String s2 = ""; char[] arr = s1.toCharArray(); for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { s2 = s2 + arr[i]; } System.out.println(s2); } public static void method1() { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String s1 = sc.nextLine(); String s2 = ""; for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) { s2 = s2 + s1.charAt(s1.length() - i - 1); } System.out.println(s2); } }
14. 练习:在大串中查找小串出现的次数思路图解
需求:统计大串中小串出现的次数
图解:
代码实现:

package com.heima.test; public class Test7 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义大串 String max = "woaiheima,heima butongyu baima,wulun heima haishi baima,zhaodao gongzuo jiushi haoma"; // 定义小串 String min = "heima"; //System.out.println(max.indexOf(min)); int count = 0; int index = 0; while((index = max.indexOf(min)) != -1) { count++; max = max.substring(index + min.length()); } System.out.println(count); } }
