1.点类
要求:定义一个点类,类名为point,将其三维坐标定义为私有成员,通过构造函数为其初始化,并在构造函数中有输出语句,以便于从运行结果看出构造函数的运行。写三个构造函数用于重载,包含一个默认构造函数。定义对象数组,观察构造函数调用的顺序
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Point { 3 private double x; // 横坐标 4 private double y; // 纵坐标 5 private double z; // 竖坐标 6 int n; 7 //构造函数No.1 8 public Point() { 9 x = 0; 10 y = 0; 11 z = 0; 12 n = 1; 13 System.out.println("构造点类No." + n); 14 } 15 //构造函数No.2 16 public Point(double x, double y, int n) { 17 this.x = x; 18 this.y = y; 19 this.z = 0; 20 this.n = n; 21 System.out.println("构造点类No." + n); 22 } 23 //构造函数No.3 24 public Point(double x, double y, double z, int n) { 25 this.x = x; 26 this.y = y; 27 this.z = z; 28 this.n = n; 29 System.out.println("构造点类No." + n); 30 } 31 //点的坐标输入 32 public void input() { 33 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 34 System.out.print("请依次输入坐标和编号:"); 35 x = in.nextDouble(); 36 y = in.nextDouble(); 37 z = in.nextDouble(); 38 n = in.nextInt(); 39 } 40 //点的坐标输出 41 public void output() { 42 System.out.println("该点的坐标为:(" + x + "," + y + "," + z + ")"); 43 } 44 45 public static void main(String[] args) { 46 Point p[] = new Point[3]; 47 p[0] = new Point(); 48 p[1] = new Point(1.2, 0.1, 2); 49 p[2] = new Point(2.5, 0.2, 1, 3); 50 for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) { 51 p[i].output(); 52 } 53 } 54 }

2.复数类
定义复数类,完成复数的加、减、乘、除
1 public class Complex { 2 private double real; // 实部 3 private double image; // 虚部 4 //无参构造函数 5 public Complex() { 6 } 7 //有参构造函数 8 public Complex(double real, double image) { 9 this.real = real; 10 this.image = image; 11 12 public double getReal() { 13 return real; 14 } 15 public void setReal(double real) { 16 this.real = real; 17 } 18 public double getImage() { 19 return image; 20 } 21 public void setImage(double image) { 22 this.image = image; 23 } 24 // 复数的加法 25 public Complex add(Complex r) { 26 double real1 = r.getReal(); 27 double image1 = r.getImage(); 28 double a = real + real1; 29 double b = image + image1; 30 Complex c = new Complex(a, b); 31 return c; 32 } 33 // 复数的减法 34 public Complex sub(Complex r) { 35 double real1 = r.getReal(); 36 double image1 = r.getImage(); 37 double a = real - real1; 38 double b = image - image1; 39 Complex c = new Complex(a, b); 40 return c; 41 } 42 // 复数的乘法 43 public Complex mul(Complex r) { 44 double real1 = r.getReal(); 45 double image1 = r.getImage(); 46 double a = real * real1 - image * image1; 47 double b = real * image1 + image * real1; 48 Complex c = new Complex(a, b); 49 return c; 50 } 51 // 复数的除法 52 public Complex div(Complex r) { 53 double real1 = r.getReal(); 54 double image1 = r.getImage(); 55 double a = (real * real1 + image * image1) / real1 * real1 + image1 * image1; 56 double b = (real1 * image - real * image1) / real1 * real1 + image1 * image1; 57 Complex c = new Complex(a, b); 58 return c; 59 } 60 public void display() { 61 if (image > 0) { 62 System.out.println(real + " + " + image + "i"); 63 } else if (image < 0) { 64 System.out.println(real + " " + image + "i"); 65 } 66 } 67 public static void main(String[] args) { 68 Complex r1 = new Complex(5, 3.1); 69 Complex r2 = new Complex(2, 1); 70 Complex a = new Complex(); 71 Complex b = new Complex(); 72 Complex c = new Complex(); 73 Complex d = new Complex(); 74 a = r1.add(r2); 75 b = r1.sub(r2); 76 c = r1.mul(r2); 77 d = r1.div(r2); 78 System.out.print("复数1:"); 79 r1.display(); 80 System.out.print("复数2:"); 81 r2.display(); 82 System.out.print("相加后:"); 83 a.display(); 84 System.out.print("相减后:"); 85 b.display(); 86 System.out.print("相乘后:"); 87 c.display(); 88 System.out.print("相除后:"); 89 d.display(); 90 } 91 }

3.交通运输类
设计一个交通工具类Vehicle,包含当前载重量和最大载重量两个私有属性,要求具有以下功能和内容:
-
有两个构造函数(其中一个为默认构造函数),
-
可分别获得两个属性的值
-
可分别设置两个属性的值
-
可判断当前载重量是否符合最大载重量以及加入一定重量后是否超载,若超载发出报警信息
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Vehicle { 3 private double nowW; //当前载重量 4 private double maxW; //最大载重量 5 //无参构造函数 6 public Vehicle() { 7 } 8 //有参构造函数 9 public Vehicle(double nowW, double maxW) { 10 this.nowW = nowW; 11 this.maxW = maxW; 12 } 13 public double getNowW() { 14 return nowW; 15 } 16 public void setNowW(double nowW) { 17 this.nowW = nowW; 18 } 19 public double getMaxW() { 20 return maxW; 21 } 22 public void setMaxW(double maxW) { 23 this.maxW = maxW; 24 } 25 //检查目前是否超重 26 public int check() { 27 if(nowW<=maxW) { 28 return 1; 29 }else { 30 return 0; 31 } 32 } 33 //检查增加后是否超重 34 public int add(double a) { 35 nowW+=a; 36 if(nowW<=maxW) { 37 return 1; 38 }else { 39 return 0; 40 } 41 } 42 public void display() { 43 System.out.println("当前载重量:"+nowW); 44 System.out.println("最大载重量:"+maxW); 45 } 46 public static void main(String[] args) { 47 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 48 double now,max,a; 49 int x,y; 50 System.out.print("请输入当前载重量和最大载重量:"); 51 now=in.nextDouble(); 52 max=in.nextDouble(); 53 Vehicle r1=new Vehicle(now,max); 54 r1.display(); 55 x=r1.check(); 56 if(x==0) { 57 System.out.println("超重!"); 58 } 59 else if(x==1) { 60 System.out.println("未超重!"); 61 System.out.print("请输入增加的重量:"); 62 a=in.nextDouble(); 63 y=r1.add(a); 64 if(y==0) { 65 System.out.println("超重!"); 66 }else if(y==1) { 67 System.out.println("未超重!"); 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 }

4.日期类
定义一个日期类Date,私有数据成员有:int型变量year, month, day。公有函数成员有:
-
三个形参均有默认值的构造函数,年月日的默认值依次为1000,1,1;
-
int isleap()判断year是否为闰年,若是返回1,否则返回0;
-
int check()判断日期是否合法,若合法返回1,否则返回0;
-
void setdate()设置year,month,day的值;
-
void display()按 “年-月-日”的格式输出日期,判断是否合法,若不合法输出Error Date,若合法,输出是否是闰年的信息;
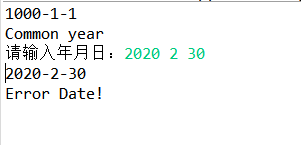
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Date { 3 private int year; // 年 4 private int month; // 月 5 private int day; // 日 6 //有默认值的构造函数 7 public Date() { 8 year = 1000; 9 month = 1; 10 day = 1; 11 } 12 // 判断是否为闰年 13 public int isleap() { 14 if (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)) { 15 return 1; 16 } else { 17 return 0; 18 } 19 } 20 // 判断日期是否合法 21 public int check() { 22 int m, n = 2; 23 m = isleap(); 24 if (month > 12) { 25 n = 0; 26 } 27 if (month < 0 || year < 0 || day < 0) { 28 n = 0; 29 } 30 if (month == 1 || month == 3 || month == 5 || month == 7 || month == 8 || month == 10 || month == 12) { 31 if (day > 31) 32 n = 0; 33 else 34 n = 1; 35 } 36 if (month == 4 || month == 6 || month == 9 || month == 11) { 37 if (day > 30) 38 n = 0; 39 else 40 n = 1; 41 } 42 if (m == 1) { 43 if (month == 2 && day >= 30) 44 n = 0; 45 if (month == 2 && day < 30) 46 n = 1; 47 } 48 if (m == 0) { 49 if (month == 2 && day >= 29) 50 n = 0; 51 if (month == 2 && day < 29) 52 n = 1; 53 } 54 return n; 55 } 56 public void setDate() { 57 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 58 System.out.print("请输入年月日:"); 59 year = in.nextInt(); 60 month = in.nextInt(); 61 day = in.nextInt(); 62 } 63 public void display() { 64 System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day); 65 int a, b; 66 a = isleap(); 67 b = check(); 68 if (b == 0) { 69 System.out.println("Error Date!"); 70 } else if (b == 1) { 71 if (a == 1) 72 System.out.println("Leap year"); 73 if (a == 0) 74 System.out.println("Common year"); 75 } 76 } 77 public static void main(String[] args) { 78 Date d1 = new Date(); 79 Date d2 = new Date(); 80 d1.display(); 81 d2.setDate(); 82 d2.display(); 83 } 84 }