Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
比I麻烦点的就是找到循环开始点TAT
I只是判断是否循环。要求不使用额外空间(不然hash就可以了
按I的思路,我们又慢指针S和快指针F。。。F走两步,S走一步。。。若有环,必定相遇。
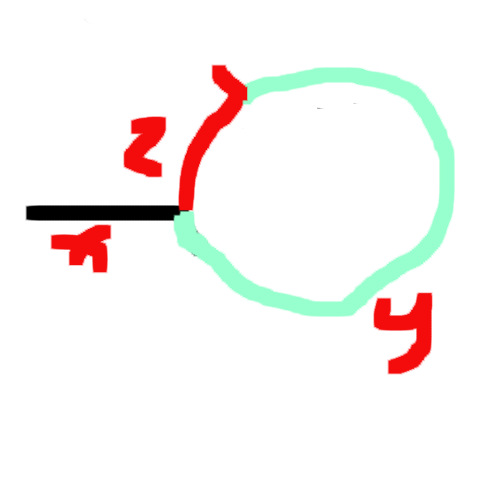
假设在红色凸起的地方相遇了。
F走的路程应该是S的两倍
S = x + y
F = x + y + z + y = x + 2y + z
2*S = F
2x+2y = x + 2y + z
得到x = z
也就是从head到环开始的路程 = 从相遇到环开始的路程
那么。。。只要S和F相遇了,我们拿一个从头开始走,一个从相遇的地方开始走
两个都走一步,那么再次相遇必定是环的开始节点!
C++版本
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode* S = head;
ListNode* F = head;
while(F != NULL) {
if(F) F = F->next;
if(F) F = F->next;
if(S) S = S->next;
if(F != NULL && F == S){
S = head;
while(S != F) {
F = F->next;
S = S->next;
}
return S;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
java版本:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(true){
if(fast == null || fast.next == null){
return null;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(slow == fast)
break;
}
slow = head;
while(slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}